Popular Posts
Understanding Valuation Ratios in Financial Analysis
Valuation ratios are fundamental tools used by investors, analysts, and financial professionals to assess the intrinsic value of a company or asset. These ratios help interpret a company's financial health, profitability, and growth potential by comparing market prices to various financial metrics. While traditionally applied within stock markets and corporate finance, understanding valuation ratios is increasingly relevant in the context of cryptocurrencies and digital assets.
Key Valuation Ratios and Their Formulas
Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio
The P/E ratio is one of the most widely recognized valuation metrics in traditional finance. It measures how much investors are willing to pay for each dollar of earnings generated by a company. The formula is straightforward:
P/E = Market Price per Share / Earnings per Share (EPS)
A high P/E ratio often indicates that investors expect higher future earnings growth from the company, whereas a lower P/E might suggest undervaluation or lower growth prospects. For example, if a stock trades at $100 per share with an EPS of $5, its P/E ratio would be 20.
In cryptocurrency markets, however, this metric isn't directly applicable because digital assets typically do not generate earnings like traditional companies do. Instead, alternative indicators such as market capitalization relative to transaction volume or price-to-market-cap ratios serve as proxies for assessing market sentiment and valuation.
Price-to-Book (P/B) Ratio
The P/B ratio compares a company's current market price to its book value—the net asset value recorded on its balance sheet:
P/B = Market Price per Share / Book Value per Share
A low P/B ratio can signal that the stock may be undervalued relative to its assets; conversely, a high P/B might indicate overvaluation or high growth expectations embedded in the stock price.
In crypto markets where companies have no tangible book values like physical assets or equity statements—especially decentralized projects—the concept shifts towards evaluating metrics such as market capitalization relative to circulating supply or network value versus transaction volume.
Dividend Yield
This metric shows how much income an investor receives from dividends relative to the current share price:
Dividend Yield = Annual Dividend Payment per Share / Current Stock Price
It’s particularly useful for income-focused investors seeking steady cash flows from their investments. However, most cryptocurrencies do not pay dividends; instead, some DeFi tokens offer yields through staking protocols or liquidity provision rewards which serve similar purposes but require different analytical approaches.
Debt-to-Equity Ratio
This ratio indicates how leveraged a company is by comparing total debt against shareholders' equity:
Debt-to-Equity Ratio = Total Debt / Total Equity
Higher ratios imply greater leverage and potentially higher risk if debt levels become unsustainable during downturns. In crypto contexts where traditional debt isn’t common—though leveraged trading exists—analysts look at borrowing levels within lending platforms or margin trading activities as analogous indicators of leverage risk.
Return on Equity (ROE)
ROE measures profitability relative to shareholder investment:
ROE = Net Income / Total Equity
It reflects management’s efficiency in generating profits from shareholders’ funds. Since most cryptocurrencies lack equity structures akin to corporations—being decentralized networks rather than entities with shareholders—the direct application is limited; instead, ROI metrics tailored for crypto investments are more prevalent here.
Current Ratio
This liquidity measure compares current assets against current liabilities:
Current Ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities
A higher ratio suggests better short-term financial health and liquidity position—a critical factor for businesses but less directly relevant in crypto markets where liquidity is assessed via trading volumes rather than balance sheet items.
Price-to-Sales (P/S) Ratio
The P/S ratio evaluates how much investors are willing to pay based on sales figures:
P/S Ratio = Market Price per Share / Sales per Share
It's especially useful when companies have negative earnings but positive sales figures. In cryptocurrency terms? Metrics like network activity compared with market cap—or transaction volume versus valuation—serve similar roles in gauging economic activity within blockchain ecosystems.
Recent Trends Impacting Valuation Metrics in Crypto Markets
With rapid technological advancements and evolving regulatory landscapes shaping digital asset valuations today’s analysis incorporates new dimensions beyond traditional formulas. The rise of DeFi has introduced innovative metrics such as yield farming returns—and liquidity pool sizes—that provide insights into project sustainability beyond simple price movements.
Furthermore, increased institutional participation has brought more standardized evaluation techniques into play—including applying familiar financial ratios—but adapting them carefully due to differences between centralized corporate structures versus decentralized networks without conventional balance sheets or income statements.
Regulatory clarity remains crucial: clearer guidelines can lead toward more reliable application of these ratios while reducing speculative excesses that often inflate valuations artificially—a concern especially pertinent given recent volatility spikes across crypto markets driven by hype cycles rather than fundamentals.
Challenges & Risks When Applying Traditional Ratios To Cryptocurrencies
Applying classic valuation formulas directly onto cryptocurrencies presents unique challenges because many foundational assumptions don’t hold true outside traditional business models. For instance:
- Cryptocurrencies generally lack tangible assets reflected on balance sheets.
- Many tokens operate without generating profits.
- Liquidity dynamics differ significantly from those seen with stocks.
Moreover:
- High volatility can distort perceived valuations.
- Lack of standardization across different projects complicates comparative analysis.
Despite these hurdles — understanding these limitations helps prevent misinterpretation while emphasizing context-specific adjustments necessary when analyzing digital assets effectively.
Emerging Developments Shaping Cryptocurrency Valuations
Recent years have seen significant innovations influencing how we evaluate cryptos:
- DeFi Metrics: Yield farming rates — which reflect returns earned through staking tokens — along with liquidity pool sizes provide alternative ways for assessing project viability.
- Institutional Adoption: As large players enter space using familiar tools like discounted cash flow models alongside traditional valuation ratios fosters greater transparency.
- Market Volatility & Sentiment: Rapid swings necessitate combining quantitative analysis with sentiment indicators derived from social media trends and news flow for comprehensive assessment.
Managing Risks Through Financial Analysis
Given inherent risks—including regulatory uncertainty—and potential overvaluation concerns highlighted during bull runs—it’s vital that investors employ robust risk management strategies grounded in sound financial analysis principles:
- Use multiple valuation methods together rather than relying solely on one metric
- Stay updated on regulatory developments impacting token classifications
- Monitor macroeconomic factors influencing both fiat currencies and digital assets
By integrating these practices into your investment approach you enhance decision-making confidence amid volatile conditions.
Understanding key valuation ratios provides essential insights whether you're analyzing stocks or navigating complex cryptocurrency markets today’s landscape demands adaptability combined with rigorous research standards rooted in established principles yet flexible enough for emerging trends—and always aligned with user intent seeking clarity about fundamental evaluation methods across diverse asset classes


Lo
2025-05-19 08:59
What are the formulas and interpretations for key valuation ratios?
Understanding Valuation Ratios in Financial Analysis
Valuation ratios are fundamental tools used by investors, analysts, and financial professionals to assess the intrinsic value of a company or asset. These ratios help interpret a company's financial health, profitability, and growth potential by comparing market prices to various financial metrics. While traditionally applied within stock markets and corporate finance, understanding valuation ratios is increasingly relevant in the context of cryptocurrencies and digital assets.
Key Valuation Ratios and Their Formulas
Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio
The P/E ratio is one of the most widely recognized valuation metrics in traditional finance. It measures how much investors are willing to pay for each dollar of earnings generated by a company. The formula is straightforward:
P/E = Market Price per Share / Earnings per Share (EPS)
A high P/E ratio often indicates that investors expect higher future earnings growth from the company, whereas a lower P/E might suggest undervaluation or lower growth prospects. For example, if a stock trades at $100 per share with an EPS of $5, its P/E ratio would be 20.
In cryptocurrency markets, however, this metric isn't directly applicable because digital assets typically do not generate earnings like traditional companies do. Instead, alternative indicators such as market capitalization relative to transaction volume or price-to-market-cap ratios serve as proxies for assessing market sentiment and valuation.
Price-to-Book (P/B) Ratio
The P/B ratio compares a company's current market price to its book value—the net asset value recorded on its balance sheet:
P/B = Market Price per Share / Book Value per Share
A low P/B ratio can signal that the stock may be undervalued relative to its assets; conversely, a high P/B might indicate overvaluation or high growth expectations embedded in the stock price.
In crypto markets where companies have no tangible book values like physical assets or equity statements—especially decentralized projects—the concept shifts towards evaluating metrics such as market capitalization relative to circulating supply or network value versus transaction volume.
Dividend Yield
This metric shows how much income an investor receives from dividends relative to the current share price:
Dividend Yield = Annual Dividend Payment per Share / Current Stock Price
It’s particularly useful for income-focused investors seeking steady cash flows from their investments. However, most cryptocurrencies do not pay dividends; instead, some DeFi tokens offer yields through staking protocols or liquidity provision rewards which serve similar purposes but require different analytical approaches.
Debt-to-Equity Ratio
This ratio indicates how leveraged a company is by comparing total debt against shareholders' equity:
Debt-to-Equity Ratio = Total Debt / Total Equity
Higher ratios imply greater leverage and potentially higher risk if debt levels become unsustainable during downturns. In crypto contexts where traditional debt isn’t common—though leveraged trading exists—analysts look at borrowing levels within lending platforms or margin trading activities as analogous indicators of leverage risk.
Return on Equity (ROE)
ROE measures profitability relative to shareholder investment:
ROE = Net Income / Total Equity
It reflects management’s efficiency in generating profits from shareholders’ funds. Since most cryptocurrencies lack equity structures akin to corporations—being decentralized networks rather than entities with shareholders—the direct application is limited; instead, ROI metrics tailored for crypto investments are more prevalent here.
Current Ratio
This liquidity measure compares current assets against current liabilities:
Current Ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities
A higher ratio suggests better short-term financial health and liquidity position—a critical factor for businesses but less directly relevant in crypto markets where liquidity is assessed via trading volumes rather than balance sheet items.
Price-to-Sales (P/S) Ratio
The P/S ratio evaluates how much investors are willing to pay based on sales figures:
P/S Ratio = Market Price per Share / Sales per Share
It's especially useful when companies have negative earnings but positive sales figures. In cryptocurrency terms? Metrics like network activity compared with market cap—or transaction volume versus valuation—serve similar roles in gauging economic activity within blockchain ecosystems.
Recent Trends Impacting Valuation Metrics in Crypto Markets
With rapid technological advancements and evolving regulatory landscapes shaping digital asset valuations today’s analysis incorporates new dimensions beyond traditional formulas. The rise of DeFi has introduced innovative metrics such as yield farming returns—and liquidity pool sizes—that provide insights into project sustainability beyond simple price movements.
Furthermore, increased institutional participation has brought more standardized evaluation techniques into play—including applying familiar financial ratios—but adapting them carefully due to differences between centralized corporate structures versus decentralized networks without conventional balance sheets or income statements.
Regulatory clarity remains crucial: clearer guidelines can lead toward more reliable application of these ratios while reducing speculative excesses that often inflate valuations artificially—a concern especially pertinent given recent volatility spikes across crypto markets driven by hype cycles rather than fundamentals.
Challenges & Risks When Applying Traditional Ratios To Cryptocurrencies
Applying classic valuation formulas directly onto cryptocurrencies presents unique challenges because many foundational assumptions don’t hold true outside traditional business models. For instance:
- Cryptocurrencies generally lack tangible assets reflected on balance sheets.
- Many tokens operate without generating profits.
- Liquidity dynamics differ significantly from those seen with stocks.
Moreover:
- High volatility can distort perceived valuations.
- Lack of standardization across different projects complicates comparative analysis.
Despite these hurdles — understanding these limitations helps prevent misinterpretation while emphasizing context-specific adjustments necessary when analyzing digital assets effectively.
Emerging Developments Shaping Cryptocurrency Valuations
Recent years have seen significant innovations influencing how we evaluate cryptos:
- DeFi Metrics: Yield farming rates — which reflect returns earned through staking tokens — along with liquidity pool sizes provide alternative ways for assessing project viability.
- Institutional Adoption: As large players enter space using familiar tools like discounted cash flow models alongside traditional valuation ratios fosters greater transparency.
- Market Volatility & Sentiment: Rapid swings necessitate combining quantitative analysis with sentiment indicators derived from social media trends and news flow for comprehensive assessment.
Managing Risks Through Financial Analysis
Given inherent risks—including regulatory uncertainty—and potential overvaluation concerns highlighted during bull runs—it’s vital that investors employ robust risk management strategies grounded in sound financial analysis principles:
- Use multiple valuation methods together rather than relying solely on one metric
- Stay updated on regulatory developments impacting token classifications
- Monitor macroeconomic factors influencing both fiat currencies and digital assets
By integrating these practices into your investment approach you enhance decision-making confidence amid volatile conditions.
Understanding key valuation ratios provides essential insights whether you're analyzing stocks or navigating complex cryptocurrency markets today’s landscape demands adaptability combined with rigorous research standards rooted in established principles yet flexible enough for emerging trends—and always aligned with user intent seeking clarity about fundamental evaluation methods across diverse asset classes
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What is an Index Hedging Ratio Chart?
Understanding the dynamics of financial markets is crucial for investors aiming to protect their assets while maximizing returns. One of the key tools in this regard is the Index Hedging Ratio Chart, which provides valuable insights into how much of a portfolio is hedged against market risks at any given time. This article explores what an index hedging ratio chart is, its significance in risk management, and how it influences investment strategies.
Defining the Index Hedging Ratio
The index hedging ratio quantifies the proportion of an investment portfolio that has been protected against potential market downturns through various financial instruments such as options or futures contracts. For example, if an investor's total portfolio value is $100,000 and they hedge $50,000 worth of assets, their hedging ratio would be 0.5 or 50%. This metric helps investors gauge their level of exposure to market volatility and adjust their strategies accordingly.
The index hedging ratio serves as a critical indicator for managing risk effectively. A higher ratio indicates more extensive protection but can also limit upside potential if markets perform well. Conversely, a lower ratio exposes investors to greater risks but allows for more significant gains during bullish periods.
How Does an Index Hedging Ratio Chart Work?
An index hedging ratio chart visually represents changes in the hedge level over time relative to market conditions or specific indices like S&P 500 or NASDAQ. These charts typically plot:
- The percentage of portfolio coverage (hedge level)
- Market performance metrics
- Volatility indicators
By analyzing these visualizations, investors can identify patterns—such as increased hedge ratios during volatile periods—and make informed decisions about adjusting their positions.
For instance, during times of heightened uncertainty or economic downturns, many investors increase their hedge ratios to mitigate potential losses. Conversely, when markets are stable or trending upward consistently, they might reduce their hedge levels to capitalize on growth opportunities.
Importance in Risk Management
The primary purpose of utilizing an index hedging ratio chart lies in effective risk management. It enables investors and fund managers to:
- Monitor exposure levels dynamically
- Adjust hedge positions based on changing market conditions
- Prevent over-hedging that could erode profits
- Avoid under-hedging that leaves portfolios vulnerable
In volatile environments—such as during geopolitical tensions or economic crises—the ability to quickly interpret these charts becomes invaluable for safeguarding investments.
Moreover, with advancements in technology—including machine learning algorithms—these charts are now generated with higher accuracy and predictive capabilities than ever before.
Applications Across Asset Classes
While traditionally associated with stock portfolios via index funds like ETFs tracking major indices (e.g., S&P 500), index hedging ratios are increasingly relevant across diverse asset classes:
Stock Market Portfolios
Investors use derivatives such as options and futures contracts tied directly to stock indices for protection against declines without liquidating holdings.
Cryptocurrency Markets
Given cryptocurrencies' notorious volatility—think Bitcoin's rapid price swings—hedge ratios help traders manage downside risks effectively within decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystems.
Commodities Trading
Investors involved in commodities like gold or oil employ similar strategies using futures contracts aligned with commodity indices for price stabilization amid fluctuating global supply-demand dynamics.
Recent Trends Influencing Index Hedging Ratios
Recent developments have significantly impacted how traders approach index hedges:
Cryptocurrency Volatility: The rise of digital assets has led many crypto traders and institutional players alike toward sophisticated indexing tools combined with dynamic hedge adjustments.
Technological Innovations: Machine learning models now enable real-time analysis and prediction adjustments based on historical data trends—making index hedges more precise.
Regulatory Changes: Evolving regulations around derivatives trading influence how easily investors can implement certain types of indexes-based protections; stricter rules may limit some strategies but also improve transparency.
Market Uncertainty: Global events such as geopolitical conflicts or economic policy shifts often prompt rapid increases in hedge ratios across multiple asset classes due to heightened risk perceptions.
These factors underscore why understanding and interpreting index hedging ratio charts have become essential skills for modern-day investors seeking resilience amid unpredictable markets.
Risks Associated With Hedge Ratios
While strategic use of these charts enhances risk mitigation efforts, there are inherent pitfalls:
Over-Hedging Risks
Excessive reliance on protective instruments can lead to diminished returns because part of your capital remains tied up without participating fully in upward movements when markets rally unexpectedly—a phenomenon known as "costly insurance."
Under-Hedging Dangers
Failing to adequately protect your investments exposes you directly to adverse market moves; this oversight could result from misreading signals from the chart or delaying adjustments until too late.
Market Volatility Challenges
Sudden spikes in volatility may outpace your ability—or willingness—to re-balance your position swiftly enough using existing tools.
Understanding these risks emphasizes why continuous monitoring via accurate indexing tools remains vital.
How Investors Can Use Index Hedged Ratios Effectively
To maximize benefits from index hedges while minimizing drawbacks:
- Regularly review trend patterns displayed by the Hedging Ratio Chart.
- Adjust your hedge levels proactively based on macroeconomic indicators.
- Combine quantitative analysis with qualitative insights about current events affecting markets.
- Leverage technological solutions like algorithmic trading platforms designed specifically around dynamic hedge management.
- Maintain flexibility: avoid rigid adherence; adapt according to evolving circumstances.
This disciplined approach ensures you maintain optimal protection aligned with your investment goals without sacrificing growth potential unnecessarily.
By understanding what an Index Hedging Ratio Chart reveals about current risk exposure levels—and integrating this knowledge into broader investment strategies—you position yourself better amidst today's complex financial landscape where volatility remains high yet opportunity persists across asset classes worldwide.
Keywords: Index Hedged Ratio | Portfolio Protection | Risk Management Strategies | Derivatives Trading | Market Volatility | Financial Instruments | Investment Risk Mitigation


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-19 08:37
What is Index Hedging Ratio Chart?
What is an Index Hedging Ratio Chart?
Understanding the dynamics of financial markets is crucial for investors aiming to protect their assets while maximizing returns. One of the key tools in this regard is the Index Hedging Ratio Chart, which provides valuable insights into how much of a portfolio is hedged against market risks at any given time. This article explores what an index hedging ratio chart is, its significance in risk management, and how it influences investment strategies.
Defining the Index Hedging Ratio
The index hedging ratio quantifies the proportion of an investment portfolio that has been protected against potential market downturns through various financial instruments such as options or futures contracts. For example, if an investor's total portfolio value is $100,000 and they hedge $50,000 worth of assets, their hedging ratio would be 0.5 or 50%. This metric helps investors gauge their level of exposure to market volatility and adjust their strategies accordingly.
The index hedging ratio serves as a critical indicator for managing risk effectively. A higher ratio indicates more extensive protection but can also limit upside potential if markets perform well. Conversely, a lower ratio exposes investors to greater risks but allows for more significant gains during bullish periods.
How Does an Index Hedging Ratio Chart Work?
An index hedging ratio chart visually represents changes in the hedge level over time relative to market conditions or specific indices like S&P 500 or NASDAQ. These charts typically plot:
- The percentage of portfolio coverage (hedge level)
- Market performance metrics
- Volatility indicators
By analyzing these visualizations, investors can identify patterns—such as increased hedge ratios during volatile periods—and make informed decisions about adjusting their positions.
For instance, during times of heightened uncertainty or economic downturns, many investors increase their hedge ratios to mitigate potential losses. Conversely, when markets are stable or trending upward consistently, they might reduce their hedge levels to capitalize on growth opportunities.
Importance in Risk Management
The primary purpose of utilizing an index hedging ratio chart lies in effective risk management. It enables investors and fund managers to:
- Monitor exposure levels dynamically
- Adjust hedge positions based on changing market conditions
- Prevent over-hedging that could erode profits
- Avoid under-hedging that leaves portfolios vulnerable
In volatile environments—such as during geopolitical tensions or economic crises—the ability to quickly interpret these charts becomes invaluable for safeguarding investments.
Moreover, with advancements in technology—including machine learning algorithms—these charts are now generated with higher accuracy and predictive capabilities than ever before.
Applications Across Asset Classes
While traditionally associated with stock portfolios via index funds like ETFs tracking major indices (e.g., S&P 500), index hedging ratios are increasingly relevant across diverse asset classes:
Stock Market Portfolios
Investors use derivatives such as options and futures contracts tied directly to stock indices for protection against declines without liquidating holdings.
Cryptocurrency Markets
Given cryptocurrencies' notorious volatility—think Bitcoin's rapid price swings—hedge ratios help traders manage downside risks effectively within decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystems.
Commodities Trading
Investors involved in commodities like gold or oil employ similar strategies using futures contracts aligned with commodity indices for price stabilization amid fluctuating global supply-demand dynamics.
Recent Trends Influencing Index Hedging Ratios
Recent developments have significantly impacted how traders approach index hedges:
Cryptocurrency Volatility: The rise of digital assets has led many crypto traders and institutional players alike toward sophisticated indexing tools combined with dynamic hedge adjustments.
Technological Innovations: Machine learning models now enable real-time analysis and prediction adjustments based on historical data trends—making index hedges more precise.
Regulatory Changes: Evolving regulations around derivatives trading influence how easily investors can implement certain types of indexes-based protections; stricter rules may limit some strategies but also improve transparency.
Market Uncertainty: Global events such as geopolitical conflicts or economic policy shifts often prompt rapid increases in hedge ratios across multiple asset classes due to heightened risk perceptions.
These factors underscore why understanding and interpreting index hedging ratio charts have become essential skills for modern-day investors seeking resilience amid unpredictable markets.
Risks Associated With Hedge Ratios
While strategic use of these charts enhances risk mitigation efforts, there are inherent pitfalls:
Over-Hedging Risks
Excessive reliance on protective instruments can lead to diminished returns because part of your capital remains tied up without participating fully in upward movements when markets rally unexpectedly—a phenomenon known as "costly insurance."
Under-Hedging Dangers
Failing to adequately protect your investments exposes you directly to adverse market moves; this oversight could result from misreading signals from the chart or delaying adjustments until too late.
Market Volatility Challenges
Sudden spikes in volatility may outpace your ability—or willingness—to re-balance your position swiftly enough using existing tools.
Understanding these risks emphasizes why continuous monitoring via accurate indexing tools remains vital.
How Investors Can Use Index Hedged Ratios Effectively
To maximize benefits from index hedges while minimizing drawbacks:
- Regularly review trend patterns displayed by the Hedging Ratio Chart.
- Adjust your hedge levels proactively based on macroeconomic indicators.
- Combine quantitative analysis with qualitative insights about current events affecting markets.
- Leverage technological solutions like algorithmic trading platforms designed specifically around dynamic hedge management.
- Maintain flexibility: avoid rigid adherence; adapt according to evolving circumstances.
This disciplined approach ensures you maintain optimal protection aligned with your investment goals without sacrificing growth potential unnecessarily.
By understanding what an Index Hedging Ratio Chart reveals about current risk exposure levels—and integrating this knowledge into broader investment strategies—you position yourself better amidst today's complex financial landscape where volatility remains high yet opportunity persists across asset classes worldwide.
Keywords: Index Hedged Ratio | Portfolio Protection | Risk Management Strategies | Derivatives Trading | Market Volatility | Financial Instruments | Investment Risk Mitigation
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Implied Volatility Chart: A Complete Guide to Understanding Market Expectations
What Is Implied Volatility?
Implied volatility (IV) is a key metric used by traders and investors to gauge market sentiment and potential price fluctuations of a security. It reflects the market’s expectations for future volatility based on options prices, rather than historical data. Essentially, IV indicates how much the market anticipates the underlying asset's price will move over a specific period.
Options prices are influenced by various factors, including current stock prices, strike prices, time until expiration, interest rates, and dividends. By analyzing these options through models like Black-Scholes or other advanced algorithms, traders derive implied volatility figures that serve as forward-looking indicators. High implied volatility suggests that investors expect significant price swings—either upward or downward—while low implied volatility points to more stable markets with less anticipated movement.
Understanding this distinction is crucial because IV does not predict direction but rather the magnitude of potential moves. For example, during periods of economic uncertainty or geopolitical tension, implied volatility tends to rise as investors brace for unpredictable outcomes.
Context and Significance in Market Analysis
Implied volatility plays an essential role in options trading strategies and broader financial analysis. It helps traders assess risk levels associated with specific securities and decide on appropriate hedging or speculative positions. When IV spikes unexpectedly—say due to earnings reports or macroeconomic news—it often signals increased uncertainty among market participants.
Market analysts also use implied volatility charts to identify trends over time. For instance, sustained high levels may indicate prolonged periods of instability or investor fear (often called "fear gauges"), while declining IV can suggest growing confidence in an asset’s stability.
Moreover, understanding how implied volatility interacts with other indicators enhances decision-making processes:
- Volatility Skew: Variations in IV across different strike prices reveal investor sentiment about specific price levels.
- Volatility Smile: Patterns where at-the-money options have lower IV compared to out-of-the-money options.
- Historical vs Implied Volatility: Comparing past actual movements against expected future movements provides insights into whether markets are overly optimistic or pessimistic.
Recent Developments Highlighting Implied Volatility Trends
In recent months, notable shifts in implied volatility have been observed across various sectors and assets:
Chord Energy Corporation (WLLBW): The company has exhibited high implied volatilities recently—a sign that traders anticipate substantial upcoming price changes possibly driven by fluctuating oil prices or sector-specific news[1]. Such elevated levels often lead to increased premiums on options contracts but also signal heightened risk exposure for investors.
Iris Energy (IRAA): The renewable energy firm experienced a surge in bullish option activity alongside rising implied volatilities[2]. This pattern indicates growing optimism among investors regarding its growth prospects amid expanding renewable initiatives—a typical scenario where positive sentiment fuels higher option premiums due to expected favorable developments.
Broader Market Trends: In both traditional equity markets and cryptocurrencies alike—such as Bitcoin—the level of implied volatility serves as an important barometer for risk appetite among traders[1][2]. During volatile periods like economic downturns or geopolitical conflicts, these measures tend to spike sharply; conversely, they decline when markets stabilize.
Potential Risks & Strategies: Elevated IV can create lucrative opportunities through strategies such as straddles or strangles but also increases exposure if market moves do not materialize as anticipated[3]. Conversely, low-volatility environments might favor income-generating approaches like covered calls but could signal complacency among investors[4].
Tools for Tracking Implied Volatility
Modern financial platforms provide comprehensive tools enabling real-time monitoring of implied volatility charts:
- Historical Data Analysis: Platforms like Perplexity Finance allow users to examine past trends—identifying patterns before major events.
- Forecasting Models: Advanced algorithms project future changes based on current data points.
- Visual Charts & Graphs: Interactive visualizations help interpret complex data quickly.
These resources empower both professional traders and retail investors with actionable insights rooted in robust analytics.
How Implied Volatility Influences Trading Decisions
Investors leverage information from IV charts when designing their trading strategies:
High IV often correlates with increased premiums; thus buyers might prefer selling options (e.g., covered calls) while sellers look for favorable entry points.
Low IV suggests subdued expectations; this environment may favor buying protective puts if downside risk appears imminent—or engaging in spread strategies that capitalize on minimal premium decay.
Furthermore, understanding whether current conditions reflect genuine uncertainty versus complacency helps refine timing decisions around entries/exits within portfolios.
Key Factors Affecting Implied Volatility Levels
Several elements influence how much the market perceives future risks:
• Economic Indicators – GDP growth rates、inflation figures、employment data• Geopolitical Events – Elections、conflicts、policy changes• Earnings Reports – Company-specific performance announcements• Market Sentiment – Investor confidence indices、news flow
Additionally,macro factors such as monetary policy shifts by central banks significantly impact overall market stability perceptions—and consequently,implyed volatilities across assets。
Interpreting Implied Volatility Charts Effectively
To make meaningful use of these charts,investors should consider several best practices:
1.Compare current levels against historical averages:Identify whether present readings are unusually high/low relative to past cycles。2.Observe trend directions:Rising trends may indicate increasing uncertainty;declining ones suggest stabilization。3.Assess sector-specific patterns:Different industries exhibit unique behaviors based on cyclical nature。4.Combine with other technical indicators:Moving averages、RSI、MACD等工具提供更全面的市场视角。
By integrating these methods,traders can better anticipate potential breakout points或风险点,从而优化投资组合表现。
The Role of Tools Like Perplexity Finance
Platforms such as Perplexity Finance enhance analytical capabilities by offering detailed datasets和 predictive models。用户可以追踪历史波动率数据,分析未来趋势,并利用图表识别潜在的市场转折点。这些工具对于专业交易者和普通投资者都极具价值,因为它们帮助理解复杂的市场动态并做出更明智的决策。
Understanding How Implied Volatility Differs from Other Metrics
While historical realized volatility measures actual past price fluctuations,implied volatility反映的是市场对未来波动性的预期。两者之间的差异可以揭示市场情绪偏差。例如,当隐含波动率远高于历史波动率时,可能意味着投资者对未来的不确定性过度担忧(“恐慌”情绪);反之亦然。
Market Sentiment Indicators & Economic Conditions Impacting Implicit Expectations
Market sentiment指标如VIX指数常被用作衡量整体市场恐惧程度,而其变化与特定资产或行业的IV密切相关。此外,经 济环境如通胀水平和利率变动也会影响投资者对未来价格走势的不确定性预期,从而推动隐含波动率变化。
Why Investors Should Pay Attention To Implicit Trends
持续监控隐含波动率有助于捕捉潜在风险与机会。高企的隐含波动力度可能暗示即将到来的重大事件或转折点,而低迷则可能意味着市场缺乏动力或等待新信息。因此,将IV纳入日常分析框架,有助于实现更科学、更有根据的投资决策,提高整体盈利能力和风险管理水平。


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-19 07:14
What is Implied Volatility Chart?
Implied Volatility Chart: A Complete Guide to Understanding Market Expectations
What Is Implied Volatility?
Implied volatility (IV) is a key metric used by traders and investors to gauge market sentiment and potential price fluctuations of a security. It reflects the market’s expectations for future volatility based on options prices, rather than historical data. Essentially, IV indicates how much the market anticipates the underlying asset's price will move over a specific period.
Options prices are influenced by various factors, including current stock prices, strike prices, time until expiration, interest rates, and dividends. By analyzing these options through models like Black-Scholes or other advanced algorithms, traders derive implied volatility figures that serve as forward-looking indicators. High implied volatility suggests that investors expect significant price swings—either upward or downward—while low implied volatility points to more stable markets with less anticipated movement.
Understanding this distinction is crucial because IV does not predict direction but rather the magnitude of potential moves. For example, during periods of economic uncertainty or geopolitical tension, implied volatility tends to rise as investors brace for unpredictable outcomes.
Context and Significance in Market Analysis
Implied volatility plays an essential role in options trading strategies and broader financial analysis. It helps traders assess risk levels associated with specific securities and decide on appropriate hedging or speculative positions. When IV spikes unexpectedly—say due to earnings reports or macroeconomic news—it often signals increased uncertainty among market participants.
Market analysts also use implied volatility charts to identify trends over time. For instance, sustained high levels may indicate prolonged periods of instability or investor fear (often called "fear gauges"), while declining IV can suggest growing confidence in an asset’s stability.
Moreover, understanding how implied volatility interacts with other indicators enhances decision-making processes:
- Volatility Skew: Variations in IV across different strike prices reveal investor sentiment about specific price levels.
- Volatility Smile: Patterns where at-the-money options have lower IV compared to out-of-the-money options.
- Historical vs Implied Volatility: Comparing past actual movements against expected future movements provides insights into whether markets are overly optimistic or pessimistic.
Recent Developments Highlighting Implied Volatility Trends
In recent months, notable shifts in implied volatility have been observed across various sectors and assets:
Chord Energy Corporation (WLLBW): The company has exhibited high implied volatilities recently—a sign that traders anticipate substantial upcoming price changes possibly driven by fluctuating oil prices or sector-specific news[1]. Such elevated levels often lead to increased premiums on options contracts but also signal heightened risk exposure for investors.
Iris Energy (IRAA): The renewable energy firm experienced a surge in bullish option activity alongside rising implied volatilities[2]. This pattern indicates growing optimism among investors regarding its growth prospects amid expanding renewable initiatives—a typical scenario where positive sentiment fuels higher option premiums due to expected favorable developments.
Broader Market Trends: In both traditional equity markets and cryptocurrencies alike—such as Bitcoin—the level of implied volatility serves as an important barometer for risk appetite among traders[1][2]. During volatile periods like economic downturns or geopolitical conflicts, these measures tend to spike sharply; conversely, they decline when markets stabilize.
Potential Risks & Strategies: Elevated IV can create lucrative opportunities through strategies such as straddles or strangles but also increases exposure if market moves do not materialize as anticipated[3]. Conversely, low-volatility environments might favor income-generating approaches like covered calls but could signal complacency among investors[4].
Tools for Tracking Implied Volatility
Modern financial platforms provide comprehensive tools enabling real-time monitoring of implied volatility charts:
- Historical Data Analysis: Platforms like Perplexity Finance allow users to examine past trends—identifying patterns before major events.
- Forecasting Models: Advanced algorithms project future changes based on current data points.
- Visual Charts & Graphs: Interactive visualizations help interpret complex data quickly.
These resources empower both professional traders and retail investors with actionable insights rooted in robust analytics.
How Implied Volatility Influences Trading Decisions
Investors leverage information from IV charts when designing their trading strategies:
High IV often correlates with increased premiums; thus buyers might prefer selling options (e.g., covered calls) while sellers look for favorable entry points.
Low IV suggests subdued expectations; this environment may favor buying protective puts if downside risk appears imminent—or engaging in spread strategies that capitalize on minimal premium decay.
Furthermore, understanding whether current conditions reflect genuine uncertainty versus complacency helps refine timing decisions around entries/exits within portfolios.
Key Factors Affecting Implied Volatility Levels
Several elements influence how much the market perceives future risks:
• Economic Indicators – GDP growth rates、inflation figures、employment data• Geopolitical Events – Elections、conflicts、policy changes• Earnings Reports – Company-specific performance announcements• Market Sentiment – Investor confidence indices、news flow
Additionally,macro factors such as monetary policy shifts by central banks significantly impact overall market stability perceptions—and consequently,implyed volatilities across assets。
Interpreting Implied Volatility Charts Effectively
To make meaningful use of these charts,investors should consider several best practices:
1.Compare current levels against historical averages:Identify whether present readings are unusually high/low relative to past cycles。2.Observe trend directions:Rising trends may indicate increasing uncertainty;declining ones suggest stabilization。3.Assess sector-specific patterns:Different industries exhibit unique behaviors based on cyclical nature。4.Combine with other technical indicators:Moving averages、RSI、MACD等工具提供更全面的市场视角。
By integrating these methods,traders can better anticipate potential breakout points或风险点,从而优化投资组合表现。
The Role of Tools Like Perplexity Finance
Platforms such as Perplexity Finance enhance analytical capabilities by offering detailed datasets和 predictive models。用户可以追踪历史波动率数据,分析未来趋势,并利用图表识别潜在的市场转折点。这些工具对于专业交易者和普通投资者都极具价值,因为它们帮助理解复杂的市场动态并做出更明智的决策。
Understanding How Implied Volatility Differs from Other Metrics
While historical realized volatility measures actual past price fluctuations,implied volatility反映的是市场对未来波动性的预期。两者之间的差异可以揭示市场情绪偏差。例如,当隐含波动率远高于历史波动率时,可能意味着投资者对未来的不确定性过度担忧(“恐慌”情绪);反之亦然。
Market Sentiment Indicators & Economic Conditions Impacting Implicit Expectations
Market sentiment指标如VIX指数常被用作衡量整体市场恐惧程度,而其变化与特定资产或行业的IV密切相关。此外,经 济环境如通胀水平和利率变动也会影响投资者对未来价格走势的不确定性预期,从而推动隐含波动率变化。
Why Investors Should Pay Attention To Implicit Trends
持续监控隐含波动率有助于捕捉潜在风险与机会。高企的隐含波动力度可能暗示即将到来的重大事件或转折点,而低迷则可能意味着市场缺乏动力或等待新信息。因此,将IV纳入日常分析框架,有助于实现更科学、更有根据的投资决策,提高整体盈利能力和风险管理水平。
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What is Time and Sales (T&S)?
Time and Sales (T&S) is a vital component of financial market data that provides a detailed, real-time record of every trade executed on a stock exchange or trading platform. This data feed captures essential information about each transaction, including the exact timestamp, the price at which the trade occurred, the number of shares traded, and whether it was a buy or sell order. For traders and investors seeking to understand market behavior at a granular level, T&S offers invaluable insights into current trading activity.
Understanding how T&S works is fundamental for grasping its significance in modern trading strategies. When trades happen rapidly during active market hours, T&S displays these transactions almost instantaneously. This allows market participants to see not just price movements but also the volume and direction behind those movements—whether buying pressure dominates or selling interest prevails.
Why Is Time and Sales Data Important?
The importance of T&S data stems from its ability to reveal real-time market dynamics that are often hidden in traditional price charts or aggregated summaries. By analyzing individual trades as they occur, traders can identify emerging trends before they become apparent through standard technical indicators. For example, an unusual surge in buy orders at specific price levels might signal strong institutional interest or impending breakout opportunities.
Investors also rely on T&S for assessing liquidity—the ease with which assets can be bought or sold without impacting their prices—and volatility levels within specific stocks or markets. High liquidity typically indicates smoother trading conditions with less risk of sudden price gaps; conversely, low liquidity may suggest caution due to potential slippage.
Market analysts utilize historical T&S data to detect patterns over time that could forecast future movements. These patterns include clusters of large trades indicating institutional activity or irregular spikes signaling possible news events affecting supply and demand balance.
Key Components of Time and Sales Data
To fully appreciate what T&S provides, it’s helpful to understand its core components:
- Timestamp: The precise moment when each trade occurs—down to milliseconds—allowing for detailed chronological analysis.
- Trade Price: The actual execution price for each transaction; tracking these helps identify support/resistance levels.
- Trade Quantity: The number of shares exchanged during each trade; larger quantities often point toward institutional involvement.
- Trade Direction: Whether the transaction was initiated as a buy (aggressive buying) or sell (selling pressure), offering clues about prevailing market sentiment.
These components collectively enable traders to dissect complex market behaviors into actionable insights.
Applications Across Financial Markets
Time and Sales data serve multiple purposes across different types of traders:
- Real-Time Market Monitoring: Day traders use live T&S feeds during intraday sessions to make quick decisions based on immediate supply-demand shifts.
- Historical Trend Analysis: Longer-term investors analyze past T&S records to identify recurring patterns that could influence future investment choices.
- Risk Management: Both short-term traders and portfolio managers leverage this data for assessing risk exposure by understanding how volatile certain stocks are under current conditions.
- Algorithmic Trading: Automated systems depend heavily on precise timing information from T&S feeds—they execute trades based on predefined criteria derived from live trade activity.
- Technical Analysis Support: Traders incorporate detailed trade-level data into charting tools like volume profile analysis or order flow indicators for more nuanced decision-making.
Recent Developments Enhancing Usefulness
The landscape surrounding Time and Sales has evolved significantly in recent years due to technological advances:
In cryptocurrency markets—which are characterized by high volatility—platforms such as Binance and Coinbase now provide specialized Trade & Sale feeds similar in function but tailored for digital assets like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Artificial Intelligence integration has transformed how traders interpret vast amounts of Trade & Sale data by enabling pattern recognition beyond human capacity—identifying subtle signals indicative of upcoming moves with greater accuracy.
Regulatory considerations have also come into focus recently; authorities aim to ensure transparency while preventing misuse such as market manipulation through overly detailed trade disclosures—a delicate balance requiring ongoing oversight.
Potential Risks Linked With Time & Sales Data
While invaluable, reliance on detailed Trade & Sale information introduces certain risks:
Cybersecurity threats pose significant dangers since breaches could expose sensitive trading activities leading upmarket manipulation attempts.
Excessive transparency might inadvertently facilitate manipulative practices if malicious actors exploit granular details—for instance, spoofing large orders followed by rapid cancellations—to deceive other participants about true supply/demand levels.
Therefore, robust security measures coupled with regulatory safeguards are essential components ensuring that this powerful tool remains beneficial rather than harmful.
The Future Role Of Time And Sales Data In Trading
Looking ahead, several trends indicate an increasing reliance on advanced technologies integrated with Trade & Sale feeds:
Enhanced AI algorithms will continue refining predictive capabilities based on real-time order flow analysis,
Cryptocurrency markets will expand their use cases as digital asset adoption grows,
Regulatory frameworks will evolve alongside technological innovations aiming at maintaining fair markets while safeguarding investor interests,
These developments underscore the critical role that accurate timely Trade & Sale information will play in shaping efficient financial ecosystems.
In summary,
Time And Sales (T& S) stands out as an indispensable resource within modern financial markets — providing granular insight into every executed trade across various asset classes—from equities to cryptocurrencies—and supporting diverse strategies ranging from day-trading tactics through long-term investing approaches.. Its components offer rich detail necessary for understanding immediate supply-demand dynamics while enabling sophisticated analytical techniques.. As technology advances continue pushing boundaries—with AI integration becoming commonplace—the importance placed upon secure handling practices grows ever more vital.. Recognizing both its power benefits along with associated risks ensures stakeholders can harness this tool effectively while maintaining trustworthiness within global financial systems


kai
2025-05-19 03:01
What is Time and Sales (T&S)?
What is Time and Sales (T&S)?
Time and Sales (T&S) is a vital component of financial market data that provides a detailed, real-time record of every trade executed on a stock exchange or trading platform. This data feed captures essential information about each transaction, including the exact timestamp, the price at which the trade occurred, the number of shares traded, and whether it was a buy or sell order. For traders and investors seeking to understand market behavior at a granular level, T&S offers invaluable insights into current trading activity.
Understanding how T&S works is fundamental for grasping its significance in modern trading strategies. When trades happen rapidly during active market hours, T&S displays these transactions almost instantaneously. This allows market participants to see not just price movements but also the volume and direction behind those movements—whether buying pressure dominates or selling interest prevails.
Why Is Time and Sales Data Important?
The importance of T&S data stems from its ability to reveal real-time market dynamics that are often hidden in traditional price charts or aggregated summaries. By analyzing individual trades as they occur, traders can identify emerging trends before they become apparent through standard technical indicators. For example, an unusual surge in buy orders at specific price levels might signal strong institutional interest or impending breakout opportunities.
Investors also rely on T&S for assessing liquidity—the ease with which assets can be bought or sold without impacting their prices—and volatility levels within specific stocks or markets. High liquidity typically indicates smoother trading conditions with less risk of sudden price gaps; conversely, low liquidity may suggest caution due to potential slippage.
Market analysts utilize historical T&S data to detect patterns over time that could forecast future movements. These patterns include clusters of large trades indicating institutional activity or irregular spikes signaling possible news events affecting supply and demand balance.
Key Components of Time and Sales Data
To fully appreciate what T&S provides, it’s helpful to understand its core components:
- Timestamp: The precise moment when each trade occurs—down to milliseconds—allowing for detailed chronological analysis.
- Trade Price: The actual execution price for each transaction; tracking these helps identify support/resistance levels.
- Trade Quantity: The number of shares exchanged during each trade; larger quantities often point toward institutional involvement.
- Trade Direction: Whether the transaction was initiated as a buy (aggressive buying) or sell (selling pressure), offering clues about prevailing market sentiment.
These components collectively enable traders to dissect complex market behaviors into actionable insights.
Applications Across Financial Markets
Time and Sales data serve multiple purposes across different types of traders:
- Real-Time Market Monitoring: Day traders use live T&S feeds during intraday sessions to make quick decisions based on immediate supply-demand shifts.
- Historical Trend Analysis: Longer-term investors analyze past T&S records to identify recurring patterns that could influence future investment choices.
- Risk Management: Both short-term traders and portfolio managers leverage this data for assessing risk exposure by understanding how volatile certain stocks are under current conditions.
- Algorithmic Trading: Automated systems depend heavily on precise timing information from T&S feeds—they execute trades based on predefined criteria derived from live trade activity.
- Technical Analysis Support: Traders incorporate detailed trade-level data into charting tools like volume profile analysis or order flow indicators for more nuanced decision-making.
Recent Developments Enhancing Usefulness
The landscape surrounding Time and Sales has evolved significantly in recent years due to technological advances:
In cryptocurrency markets—which are characterized by high volatility—platforms such as Binance and Coinbase now provide specialized Trade & Sale feeds similar in function but tailored for digital assets like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Artificial Intelligence integration has transformed how traders interpret vast amounts of Trade & Sale data by enabling pattern recognition beyond human capacity—identifying subtle signals indicative of upcoming moves with greater accuracy.
Regulatory considerations have also come into focus recently; authorities aim to ensure transparency while preventing misuse such as market manipulation through overly detailed trade disclosures—a delicate balance requiring ongoing oversight.
Potential Risks Linked With Time & Sales Data
While invaluable, reliance on detailed Trade & Sale information introduces certain risks:
Cybersecurity threats pose significant dangers since breaches could expose sensitive trading activities leading upmarket manipulation attempts.
Excessive transparency might inadvertently facilitate manipulative practices if malicious actors exploit granular details—for instance, spoofing large orders followed by rapid cancellations—to deceive other participants about true supply/demand levels.
Therefore, robust security measures coupled with regulatory safeguards are essential components ensuring that this powerful tool remains beneficial rather than harmful.
The Future Role Of Time And Sales Data In Trading
Looking ahead, several trends indicate an increasing reliance on advanced technologies integrated with Trade & Sale feeds:
Enhanced AI algorithms will continue refining predictive capabilities based on real-time order flow analysis,
Cryptocurrency markets will expand their use cases as digital asset adoption grows,
Regulatory frameworks will evolve alongside technological innovations aiming at maintaining fair markets while safeguarding investor interests,
These developments underscore the critical role that accurate timely Trade & Sale information will play in shaping efficient financial ecosystems.
In summary,
Time And Sales (T& S) stands out as an indispensable resource within modern financial markets — providing granular insight into every executed trade across various asset classes—from equities to cryptocurrencies—and supporting diverse strategies ranging from day-trading tactics through long-term investing approaches.. Its components offer rich detail necessary for understanding immediate supply-demand dynamics while enabling sophisticated analytical techniques.. As technology advances continue pushing boundaries—with AI integration becoming commonplace—the importance placed upon secure handling practices grows ever more vital.. Recognizing both its power benefits along with associated risks ensures stakeholders can harness this tool effectively while maintaining trustworthiness within global financial systems
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Where Can You Buy or Sell Cryptocurrencies Easily?
Understanding where to buy or sell cryptocurrencies efficiently is crucial for both new and experienced investors. The rapid growth of the digital asset market has led to a proliferation of trading platforms, each offering different features, security measures, and fee structures. Selecting the right marketplace can significantly impact your trading experience, security, and profitability.
Top Cryptocurrency Exchanges for Buying and Selling
Several reputable exchanges dominate the market due to their user-friendly interfaces, security standards, liquidity levels, and range of supported assets. Here are some of the most prominent platforms:
Coinbase: Known for its simplicity and ease of use, Coinbase is often recommended for beginners. It supports a wide array of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), Litecoin (LTC), among others. Its regulatory compliance in various jurisdictions adds an extra layer of trustworthiness. Coinbase also offers educational resources that help users understand market dynamics better.
Binance: As one of the largest cryptocurrency exchanges globally by trading volume, Binance provides advanced trading options such as spot trading, futures contracts, options trading, and staking services. Its competitive fee structure makes it attractive for active traders seeking high liquidity across numerous crypto pairs.
Kraken: Recognized for its strong security protocols and extensive selection of cryptocurrencies—over 50 pairs—Kraken appeals to traders who prioritize safety alongside variety. It offers margin trading features as well as futures markets which cater to more sophisticated investors.
Gemini: Founded by the Winklevoss twins in 2014, Gemini emphasizes regulatory compliance and high-security standards. It supports a curated list of cryptocurrencies but excels in providing institutional-grade custody solutions suitable for serious investors looking to safeguard their assets securely.
Recent Market Developments Impacting Crypto Trading Platforms
The landscape surrounding cryptocurrency marketplaces continues evolving with notable developments that influence investor confidence:
Profitability Challenges at Coinbase: Despite reporting a 24% year-over-year revenue increase reaching $2 billion in Q1 2025—a positive indicator—the company’s profits have fallen short compared to analyst expectations. This highlights how even leading platforms face pressures from operational costs or market conditions affecting profitability metrics.
Gemini’s IPO Ambitions: The Winklevoss-founded exchange is exploring an initial public offering scheduled potentially within 2025. An IPO could enhance Gemini’s credibility further while providing increased transparency—a factor valued highly by institutional investors seeking regulated environments.
Broader Fintech Trends with Chime's IPO Filing: Although not directly related to crypto exchanges themselves—Chime's Nasdaq listing signals broader fintech sector growth trends that could indirectly influence cryptocurrency adoption through increased financial innovation funding streams.
Risks That Could Lead To Market Fallout
While investing in cryptocurrencies offers substantial opportunities due to their potential returns and decentralization benefits; several risks threaten stability:
Regulatory Changes: Governments worldwide are continuously updating policies regarding digital assets—from stricter KYC/AML requirements to outright bans on certain activities—which can limit access or increase compliance costs on major exchanges like Binance or Kraken.
Market Volatility: Cryptocurrency prices are notoriously volatile; sudden swings driven by macroeconomic factors or large trades can make buying/selling challenging at desired price points.
Security Concerns & Hacks: Security breaches remain a persistent threat; past incidents involving major exchanges have resulted in significant investor losses—highlighting why choosing platforms with robust cybersecurity measures is essential when buying or selling crypto assets.
How To Choose The Right Platform For Your Needs
When selecting an exchange tailored toward your investment goals:
- Assess Security Features – Look into two-factor authentication (2FA), cold storage options, insurance policies against hacks.
- Consider Supported Cryptocurrencies – Ensure your preferred coins are available on the platform.
- Review Fee Structures – Compare transaction fees per trade along with deposit/withdrawal charges.
- Evaluate User Experience – A straightforward interface helps reduce errors during transactions.
- Check Regulatory Compliance – Platforms adhering strictly to local laws tend to offer safer environments overall.
Final Thoughts on Buying & Selling Cryptocurrencies Safely
Navigating where you can buy or sell cryptocurrencies easily requires understanding each platform's strengths relative to your needs—whether you're aiming for quick trades via user-friendly apps like Coinbase or engaging in more complex strategies through Binance’s advanced tools—and being aware of ongoing developments shaping this dynamic industry landscape will help you make informed decisions confidently while managing risks effectively.
By staying updated on recent trends such as IPO plans from Gemini or profit reports from Coinbase, investors gain insights into potential shifts within marketplaces that could affect liquidity levels and platform reliability over time — key factors when choosing where best suited your crypto transactions should occur.
Remember, always prioritize security practices such as enabling two-factor authentication (2FA) when using any exchange platform — safeguarding your investments against cyber threats remains paramount regardless of market conditions.
This comprehensive overview aims at equipping you with essential knowledge about accessible venues for buying/selling cryptocurrencies safely while understanding current industry trends influencing these choices today—and tomorrow


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-14 23:35
Where can you buy or sell this coin easily?
Where Can You Buy or Sell Cryptocurrencies Easily?
Understanding where to buy or sell cryptocurrencies efficiently is crucial for both new and experienced investors. The rapid growth of the digital asset market has led to a proliferation of trading platforms, each offering different features, security measures, and fee structures. Selecting the right marketplace can significantly impact your trading experience, security, and profitability.
Top Cryptocurrency Exchanges for Buying and Selling
Several reputable exchanges dominate the market due to their user-friendly interfaces, security standards, liquidity levels, and range of supported assets. Here are some of the most prominent platforms:
Coinbase: Known for its simplicity and ease of use, Coinbase is often recommended for beginners. It supports a wide array of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), Litecoin (LTC), among others. Its regulatory compliance in various jurisdictions adds an extra layer of trustworthiness. Coinbase also offers educational resources that help users understand market dynamics better.
Binance: As one of the largest cryptocurrency exchanges globally by trading volume, Binance provides advanced trading options such as spot trading, futures contracts, options trading, and staking services. Its competitive fee structure makes it attractive for active traders seeking high liquidity across numerous crypto pairs.
Kraken: Recognized for its strong security protocols and extensive selection of cryptocurrencies—over 50 pairs—Kraken appeals to traders who prioritize safety alongside variety. It offers margin trading features as well as futures markets which cater to more sophisticated investors.
Gemini: Founded by the Winklevoss twins in 2014, Gemini emphasizes regulatory compliance and high-security standards. It supports a curated list of cryptocurrencies but excels in providing institutional-grade custody solutions suitable for serious investors looking to safeguard their assets securely.
Recent Market Developments Impacting Crypto Trading Platforms
The landscape surrounding cryptocurrency marketplaces continues evolving with notable developments that influence investor confidence:
Profitability Challenges at Coinbase: Despite reporting a 24% year-over-year revenue increase reaching $2 billion in Q1 2025—a positive indicator—the company’s profits have fallen short compared to analyst expectations. This highlights how even leading platforms face pressures from operational costs or market conditions affecting profitability metrics.
Gemini’s IPO Ambitions: The Winklevoss-founded exchange is exploring an initial public offering scheduled potentially within 2025. An IPO could enhance Gemini’s credibility further while providing increased transparency—a factor valued highly by institutional investors seeking regulated environments.
Broader Fintech Trends with Chime's IPO Filing: Although not directly related to crypto exchanges themselves—Chime's Nasdaq listing signals broader fintech sector growth trends that could indirectly influence cryptocurrency adoption through increased financial innovation funding streams.
Risks That Could Lead To Market Fallout
While investing in cryptocurrencies offers substantial opportunities due to their potential returns and decentralization benefits; several risks threaten stability:
Regulatory Changes: Governments worldwide are continuously updating policies regarding digital assets—from stricter KYC/AML requirements to outright bans on certain activities—which can limit access or increase compliance costs on major exchanges like Binance or Kraken.
Market Volatility: Cryptocurrency prices are notoriously volatile; sudden swings driven by macroeconomic factors or large trades can make buying/selling challenging at desired price points.
Security Concerns & Hacks: Security breaches remain a persistent threat; past incidents involving major exchanges have resulted in significant investor losses—highlighting why choosing platforms with robust cybersecurity measures is essential when buying or selling crypto assets.
How To Choose The Right Platform For Your Needs
When selecting an exchange tailored toward your investment goals:
- Assess Security Features – Look into two-factor authentication (2FA), cold storage options, insurance policies against hacks.
- Consider Supported Cryptocurrencies – Ensure your preferred coins are available on the platform.
- Review Fee Structures – Compare transaction fees per trade along with deposit/withdrawal charges.
- Evaluate User Experience – A straightforward interface helps reduce errors during transactions.
- Check Regulatory Compliance – Platforms adhering strictly to local laws tend to offer safer environments overall.
Final Thoughts on Buying & Selling Cryptocurrencies Safely
Navigating where you can buy or sell cryptocurrencies easily requires understanding each platform's strengths relative to your needs—whether you're aiming for quick trades via user-friendly apps like Coinbase or engaging in more complex strategies through Binance’s advanced tools—and being aware of ongoing developments shaping this dynamic industry landscape will help you make informed decisions confidently while managing risks effectively.
By staying updated on recent trends such as IPO plans from Gemini or profit reports from Coinbase, investors gain insights into potential shifts within marketplaces that could affect liquidity levels and platform reliability over time — key factors when choosing where best suited your crypto transactions should occur.
Remember, always prioritize security practices such as enabling two-factor authentication (2FA) when using any exchange platform — safeguarding your investments against cyber threats remains paramount regardless of market conditions.
This comprehensive overview aims at equipping you with essential knowledge about accessible venues for buying/selling cryptocurrencies safely while understanding current industry trends influencing these choices today—and tomorrow
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Do Institutional Prime Brokers Service Crypto Clients?
Institutional prime brokers have long been essential players in traditional financial markets, offering a suite of services to large-scale investors such as hedge funds, asset managers, and pension funds. With the rapid rise of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology, these brokers are now expanding their offerings to cater to digital assets. Understanding how they service crypto clients is crucial for anyone interested in institutional involvement in the crypto space.
What Are Institutional Prime Brokers?
Institutional prime brokers are specialized financial institutions that provide comprehensive services tailored for large-scale investors. Their core functions include custody (safekeeping assets), trade execution (buying and selling securities or digital assets), clearing (finalizing transactions), settlement (transferring ownership), liquidity provision, and risk management. These services enable institutional clients to operate efficiently while managing complex portfolios across multiple asset classes.
Traditionally focused on equities, bonds, and derivatives, prime brokers have increasingly integrated cryptocurrency services into their offerings due to rising demand from institutional investors seeking exposure to digital assets.
Key Services Offered by Prime Brokers for Crypto Assets
As cryptocurrencies become more mainstream among institutional investors, prime brokers are adapting by providing specialized crypto-related services:
Custody Services: Secure storage solutions are critical given the security risks associated with digital wallets. Prime brokers offer custodial solutions that safeguard private keys using advanced security protocols like multi-signature wallets and cold storage.
Execution Services: Facilitating seamless trading across various exchanges is vital due to fragmented liquidity pools in crypto markets. Prime brokers connect clients with multiple trading venues for efficient order execution.
Clearing and Settlement: Managing the transfer of ownership involves ensuring trades settle correctly across different platforms while maintaining compliance with regulatory standards.
Liquidity Provision: Access to deep liquidity pools helps prevent slippage during large trades—an essential factor when dealing with volatile cryptocurrencies.
Risk Management Tools: Given the high volatility inherent in crypto markets, prime brokers provide sophisticated tools such as hedging strategies or margin management systems designed specifically for digital assets.
The Role of Blockchain Technology Integration
Many prime brokerage firms leverage blockchain technology itself to enhance transparency and operational efficiency. Smart contracts automate processes like trade settlement or collateral management without intermediaries—reducing costs and increasing speed. Additionally, decentralized storage solutions help protect sensitive data against hacking attempts or data breaches.
This technological integration not only improves operational workflows but also aligns with regulatory trends emphasizing transparency within financial transactions involving cryptocurrencies.
Navigating Regulatory Challenges
The regulatory landscape surrounding cryptocurrencies remains complex worldwide. Different jurisdictions impose varying rules regarding custody requirements, anti-money laundering (AML) procedures, taxation policies, and licensing standards—all impacting how prime brokers service their crypto clients.
Prime brokerages must stay compliant while innovating new products; this balancing act often involves close collaboration with regulators or participating in industry advocacy groups aiming for clearer guidelines that foster growth without compromising security or investor protection.
Recent Trends Shaping Crypto Services by Prime Brokers
Several recent developments highlight how this sector is evolving:
Growing Institutional Adoption
In 2023 alone, major players like BlackRock and Fidelity launched dedicated cryptocurrency investment products aimed at institutional clients—signaling increased confidence from traditional finance giants toward digital assets.
Regulatory Clarity Boosts Market Confidence
Early 2024 saw several regulators issuing clearer guidelines on cryptocurrency treatment within existing legal frameworks. This clarity reduces uncertainty around compliance obligations—encouraging more institutions to participate actively in crypto markets through licensed prime brokerage channels.
Blockchain & DeFi Integration
By 2025, many prime brokerages began integrating decentralized finance protocols into their service models—for example:
- Using DeFi lending platforms for collateralized borrowing
- Offering tokenized versions of traditional financial instruments like futures ETFs
These innovations expand product offerings beyond conventional trading into innovative areas leveraging blockchain's capabilities directly within brokerage operations.
Risks Facing Crypto Servicing by Prime Brokers
Despite promising growth prospects—and increased interest from institutions—the sector faces notable challenges:
Regulatory Risks: Sudden policy shifts could impact market stability or restrict certain activities altogether.
Security Concerns: Digital asset thefts via hacking remain a persistent threat; robust cybersecurity measures are non-negotiable.
Market Volatility: Cryptocurrency prices can fluctuate wildly over short periods; managing risk exposure requires sophisticated strategies tailored specifically for these volatile environments.
Understanding these risks allows both providers and clients alike to implement appropriate safeguards ensuring resilience amid market uncertainties.
The Future Outlook of Institutional Crypto Services
The ongoing expansion of institutional involvement indicates a sustained trajectory toward broader adoption of cryptocurrencies within mainstream finance infrastructures. As regulations become clearer—and technological innovations continue—the scope of services offered by prime brokers will likely grow further—with enhanced custody options—including insurance-backed safekeeping—and more sophisticated risk mitigation tools tailored explicitly for digital assets.
Furthermore, collaborations between traditional financial firms and emerging fintech companies will accelerate innovation—bringing new products such as ETF-linked tokens or hybrid investment vehicles combining fiat currencies with cryptos into mainstream portfolios.
By prioritizing security measures alongside transparent compliance practices—and fostering industry-wide standards—the sector aims not only at growth but also at building trust among cautious yet increasingly interested institutional participants.
Understanding how institutional prime brokers service crypto clients reveals an evolving landscape where innovation meets regulation—a dynamic environment poised for significant growth over coming years. For investors seeking insight into this transformation—from secure custody solutions through advanced trading infrastructure—it’s clear that professional support structures are becoming integral components enabling larger-scale participation in the burgeoning world of digital assets.


Lo
2025-05-14 14:11
How do institutional prime brokers service crypto clients?
How Do Institutional Prime Brokers Service Crypto Clients?
Institutional prime brokers have long been essential players in traditional financial markets, offering a suite of services to large-scale investors such as hedge funds, asset managers, and pension funds. With the rapid rise of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology, these brokers are now expanding their offerings to cater to digital assets. Understanding how they service crypto clients is crucial for anyone interested in institutional involvement in the crypto space.
What Are Institutional Prime Brokers?
Institutional prime brokers are specialized financial institutions that provide comprehensive services tailored for large-scale investors. Their core functions include custody (safekeeping assets), trade execution (buying and selling securities or digital assets), clearing (finalizing transactions), settlement (transferring ownership), liquidity provision, and risk management. These services enable institutional clients to operate efficiently while managing complex portfolios across multiple asset classes.
Traditionally focused on equities, bonds, and derivatives, prime brokers have increasingly integrated cryptocurrency services into their offerings due to rising demand from institutional investors seeking exposure to digital assets.
Key Services Offered by Prime Brokers for Crypto Assets
As cryptocurrencies become more mainstream among institutional investors, prime brokers are adapting by providing specialized crypto-related services:
Custody Services: Secure storage solutions are critical given the security risks associated with digital wallets. Prime brokers offer custodial solutions that safeguard private keys using advanced security protocols like multi-signature wallets and cold storage.
Execution Services: Facilitating seamless trading across various exchanges is vital due to fragmented liquidity pools in crypto markets. Prime brokers connect clients with multiple trading venues for efficient order execution.
Clearing and Settlement: Managing the transfer of ownership involves ensuring trades settle correctly across different platforms while maintaining compliance with regulatory standards.
Liquidity Provision: Access to deep liquidity pools helps prevent slippage during large trades—an essential factor when dealing with volatile cryptocurrencies.
Risk Management Tools: Given the high volatility inherent in crypto markets, prime brokers provide sophisticated tools such as hedging strategies or margin management systems designed specifically for digital assets.
The Role of Blockchain Technology Integration
Many prime brokerage firms leverage blockchain technology itself to enhance transparency and operational efficiency. Smart contracts automate processes like trade settlement or collateral management without intermediaries—reducing costs and increasing speed. Additionally, decentralized storage solutions help protect sensitive data against hacking attempts or data breaches.
This technological integration not only improves operational workflows but also aligns with regulatory trends emphasizing transparency within financial transactions involving cryptocurrencies.
Navigating Regulatory Challenges
The regulatory landscape surrounding cryptocurrencies remains complex worldwide. Different jurisdictions impose varying rules regarding custody requirements, anti-money laundering (AML) procedures, taxation policies, and licensing standards—all impacting how prime brokers service their crypto clients.
Prime brokerages must stay compliant while innovating new products; this balancing act often involves close collaboration with regulators or participating in industry advocacy groups aiming for clearer guidelines that foster growth without compromising security or investor protection.
Recent Trends Shaping Crypto Services by Prime Brokers
Several recent developments highlight how this sector is evolving:
Growing Institutional Adoption
In 2023 alone, major players like BlackRock and Fidelity launched dedicated cryptocurrency investment products aimed at institutional clients—signaling increased confidence from traditional finance giants toward digital assets.
Regulatory Clarity Boosts Market Confidence
Early 2024 saw several regulators issuing clearer guidelines on cryptocurrency treatment within existing legal frameworks. This clarity reduces uncertainty around compliance obligations—encouraging more institutions to participate actively in crypto markets through licensed prime brokerage channels.
Blockchain & DeFi Integration
By 2025, many prime brokerages began integrating decentralized finance protocols into their service models—for example:
- Using DeFi lending platforms for collateralized borrowing
- Offering tokenized versions of traditional financial instruments like futures ETFs
These innovations expand product offerings beyond conventional trading into innovative areas leveraging blockchain's capabilities directly within brokerage operations.
Risks Facing Crypto Servicing by Prime Brokers
Despite promising growth prospects—and increased interest from institutions—the sector faces notable challenges:
Regulatory Risks: Sudden policy shifts could impact market stability or restrict certain activities altogether.
Security Concerns: Digital asset thefts via hacking remain a persistent threat; robust cybersecurity measures are non-negotiable.
Market Volatility: Cryptocurrency prices can fluctuate wildly over short periods; managing risk exposure requires sophisticated strategies tailored specifically for these volatile environments.
Understanding these risks allows both providers and clients alike to implement appropriate safeguards ensuring resilience amid market uncertainties.
The Future Outlook of Institutional Crypto Services
The ongoing expansion of institutional involvement indicates a sustained trajectory toward broader adoption of cryptocurrencies within mainstream finance infrastructures. As regulations become clearer—and technological innovations continue—the scope of services offered by prime brokers will likely grow further—with enhanced custody options—including insurance-backed safekeeping—and more sophisticated risk mitigation tools tailored explicitly for digital assets.
Furthermore, collaborations between traditional financial firms and emerging fintech companies will accelerate innovation—bringing new products such as ETF-linked tokens or hybrid investment vehicles combining fiat currencies with cryptos into mainstream portfolios.
By prioritizing security measures alongside transparent compliance practices—and fostering industry-wide standards—the sector aims not only at growth but also at building trust among cautious yet increasingly interested institutional participants.
Understanding how institutional prime brokers service crypto clients reveals an evolving landscape where innovation meets regulation—a dynamic environment poised for significant growth over coming years. For investors seeking insight into this transformation—from secure custody solutions through advanced trading infrastructure—it’s clear that professional support structures are becoming integral components enabling larger-scale participation in the burgeoning world of digital assets.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is a Cryptocurrency Transaction?
Understanding the Basics of Digital Currency Transfers
A cryptocurrency transaction is the process through which digital assets like Bitcoin, Ethereum, or other cryptocurrencies are transferred from one individual or entity to another. Unlike traditional banking transactions that rely on centralized institutions, cryptocurrency transactions operate within a decentralized network called a blockchain. This technology ensures transparency, security, and immutability by recording all transactions in a public ledger accessible to anyone.
Key Components of Cryptocurrency Transactions
To fully grasp how these transactions work, it’s essential to understand their core elements:
Sender and Receiver: Every transaction involves two parties—the sender who initiates the transfer and the receiver who receives the funds. Both parties typically have digital wallets that store their cryptographic keys.
Cryptographic Keys: Security in cryptocurrency relies heavily on cryptography. The sender uses their private key—a secret piece of data—to sign the transaction digitally. This signature verifies ownership and prevents unauthorized transfers. The receiver’s address is derived from their public key and serves as an identifier for receiving funds.
Blockchain Network: Once initiated, the transaction is broadcasted across a peer-to-peer network of computers called nodes. These nodes validate and record transactions onto blocks that form part of the blockchain.
Consensus Mechanism: To ensure all participants agree on which transactions are valid, networks employ consensus algorithms such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS). These mechanisms prevent double-spending and maintain network integrity.
Block Addition: After verification through consensus protocols, validated transactions are grouped into blocks. These blocks are then added sequentially to the existing blockchain ledger—making them permanent and tamper-proof.
Historical Context & Evolution
The concept of digital currency began gaining traction with Bitcoin's creation by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008–2009. The first recorded Bitcoin transaction occurred on January 3rd, 2009 when Nakamoto sent 10 BTC to developer Hal Finney—marking a pivotal moment in financial history. Since then, cryptocurrencies have evolved rapidly with thousands of different tokens now available globally.
Recent Developments Shaping Cryptocurrency Transactions
Advancements in technology continue to influence how cryptocurrency transactions are processed:
Blockchain Scalability Solutions:
- Layer 2 solutions like Lightning Network (for Bitcoin) enable faster off-chain processing while settling final balances on-chain later.
- Sharding techniques divide networks into smaller segments allowing parallel processing—significantly increasing throughput for platforms like Ethereum.
Regulatory Environment:
- Governments worldwide are establishing frameworks for crypto operations; examples include FinCEN regulations in the U.S., MiCA proposals within Europe.
- Taxation policies now often require reporting gains/losses from crypto trading—adding compliance layers for users.
Security Challenges:
- Phishing attacks targeting private keys remain prevalent; users must adopt robust security practices such as hardware wallets.
- Smart contract vulnerabilities have led to notable exploits—including incidents like The DAO hack (2016) or DeFi protocol breaches (2020)—highlighting ongoing risks.
Environmental Impact Concerns:
- Energy-intensive mining processes raise sustainability issues; Bitcoin mining alone consumes substantial electricity contributing to environmental degradation.
Adoption Trends & Integration
- Major corporations including PayPal and Visa now support cryptocurrencies for payments—accelerating mainstream acceptance.
- Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs), such as China's digital yuan or potential USD-backed tokens by Federal Reserve plans aim at integrating digital currencies into official monetary systems.
Potential Risks & Challenges Facing Cryptocurrency Transactions
While innovations continue apace, several hurdles threaten widespread adoption:
Regulatory Uncertainty: Lack of clear legal frameworks can cause confusion among users and businesses alike—potentially stifling growth if not addressed effectively.
Security Risks: Persistent threats like hacking attempts undermine trust; high-profile breaches can lead investors away from cryptocurrencies altogether.
Environmental Concerns: Growing awareness about energy consumption associated with proof-of-work mining may result in restrictions or bans affecting certain coins’ viability.
Market Volatility: Cryptocurrencies exhibit significant price swings driven by speculation rather than fundamentals—which can deter risk-sensitive investors seeking stability.
Understanding How Cryptocurrency Transactions Impact Financial Ecosystems
Cryptocurrency transactions underpin decentralized finance (DeFi), enabling peer-to-peer lending, staking rewards, token swaps—and even cross-border remittances without intermediaries like banks or payment processors. Their transparent nature fosters trust among participants but also raises questions about privacy rights versus regulatory oversight.
As adoption expands—from individual users managing personal portfolios to institutional investors entering markets—the importance of secure infrastructure grows correspondingly alongside concerns over fraud prevention and compliance adherence.
Emerging Trends Influencing Future Transactions
Looking ahead, several trends could redefine how cryptocurrency transfers occur:
- Increased integration with traditional financial systems via stablecoins tied to fiat currencies
- Enhanced privacy features through zero-knowledge proofs
- Greater emphasis on sustainable practices amid environmental debates
- Development of more user-friendly interfaces making crypto management accessible even for novices
By staying informed about these developments—and understanding both technical aspects and regulatory landscapes—stakeholders can better navigate this rapidly evolving space while mitigating risks associated with security breaches or market instability.
Everyday Implications & User Considerations
For individuals engaging with cryptocurrencies today—from casual traders to institutional players—it’s vital to prioritize security measures such as using reputable wallets and verifying recipient addresses before sending funds. Awareness about potential scams—including phishing schemes—is crucial since private keys grant full control over assets once compromised cannot be recovered easily.
Moreover, understanding transaction fees—which vary depending on network congestion—and confirmation times helps optimize user experience during transfers across different blockchains.
The Role Of Regulation And Its Effect On Transaction Processes
Regulatory frameworks significantly influence how cryptocurrency transactions function globally—they determine what is permissible regarding anti-money laundering measures (“AML”), know-your-customer (“KYC”) requirements—and impact taxation policies that govern gains made through trading activities.
In some jurisdictions where regulation remains ambiguous—or outright restrictive—the volume of legitimate activity may decline due to uncertainty or fear among users; conversely—with clearer rules—adoption could accelerate thanks to increased legitimacy.
Final Thoughts
Cryptocurrency transactions form an integral part of modern decentralized finance ecosystems—they leverage cryptography combined with distributed ledger technology ensuring secure transfer mechanisms without central authorities' oversight.. As technological innovations emerge alongside evolving regulatory landscapes—with ongoing debates around environmental sustainability—the future trajectory promises both opportunities for broader adoption yet challenges related primarilyto security risksand policy uncertainties.
Staying informed about these dynamics enables stakeholders—from everyday users up through large-scale institutions—to participate confidently while navigating complexities inherent within this transformative financial frontier


kai
2025-05-11 10:32
What is a cryptocurrency transaction?
What Is a Cryptocurrency Transaction?
Understanding the Basics of Digital Currency Transfers
A cryptocurrency transaction is the process through which digital assets like Bitcoin, Ethereum, or other cryptocurrencies are transferred from one individual or entity to another. Unlike traditional banking transactions that rely on centralized institutions, cryptocurrency transactions operate within a decentralized network called a blockchain. This technology ensures transparency, security, and immutability by recording all transactions in a public ledger accessible to anyone.
Key Components of Cryptocurrency Transactions
To fully grasp how these transactions work, it’s essential to understand their core elements:
Sender and Receiver: Every transaction involves two parties—the sender who initiates the transfer and the receiver who receives the funds. Both parties typically have digital wallets that store their cryptographic keys.
Cryptographic Keys: Security in cryptocurrency relies heavily on cryptography. The sender uses their private key—a secret piece of data—to sign the transaction digitally. This signature verifies ownership and prevents unauthorized transfers. The receiver’s address is derived from their public key and serves as an identifier for receiving funds.
Blockchain Network: Once initiated, the transaction is broadcasted across a peer-to-peer network of computers called nodes. These nodes validate and record transactions onto blocks that form part of the blockchain.
Consensus Mechanism: To ensure all participants agree on which transactions are valid, networks employ consensus algorithms such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS). These mechanisms prevent double-spending and maintain network integrity.
Block Addition: After verification through consensus protocols, validated transactions are grouped into blocks. These blocks are then added sequentially to the existing blockchain ledger—making them permanent and tamper-proof.
Historical Context & Evolution
The concept of digital currency began gaining traction with Bitcoin's creation by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008–2009. The first recorded Bitcoin transaction occurred on January 3rd, 2009 when Nakamoto sent 10 BTC to developer Hal Finney—marking a pivotal moment in financial history. Since then, cryptocurrencies have evolved rapidly with thousands of different tokens now available globally.
Recent Developments Shaping Cryptocurrency Transactions
Advancements in technology continue to influence how cryptocurrency transactions are processed:
Blockchain Scalability Solutions:
- Layer 2 solutions like Lightning Network (for Bitcoin) enable faster off-chain processing while settling final balances on-chain later.
- Sharding techniques divide networks into smaller segments allowing parallel processing—significantly increasing throughput for platforms like Ethereum.
Regulatory Environment:
- Governments worldwide are establishing frameworks for crypto operations; examples include FinCEN regulations in the U.S., MiCA proposals within Europe.
- Taxation policies now often require reporting gains/losses from crypto trading—adding compliance layers for users.
Security Challenges:
- Phishing attacks targeting private keys remain prevalent; users must adopt robust security practices such as hardware wallets.
- Smart contract vulnerabilities have led to notable exploits—including incidents like The DAO hack (2016) or DeFi protocol breaches (2020)—highlighting ongoing risks.
Environmental Impact Concerns:
- Energy-intensive mining processes raise sustainability issues; Bitcoin mining alone consumes substantial electricity contributing to environmental degradation.
Adoption Trends & Integration
- Major corporations including PayPal and Visa now support cryptocurrencies for payments—accelerating mainstream acceptance.
- Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs), such as China's digital yuan or potential USD-backed tokens by Federal Reserve plans aim at integrating digital currencies into official monetary systems.
Potential Risks & Challenges Facing Cryptocurrency Transactions
While innovations continue apace, several hurdles threaten widespread adoption:
Regulatory Uncertainty: Lack of clear legal frameworks can cause confusion among users and businesses alike—potentially stifling growth if not addressed effectively.
Security Risks: Persistent threats like hacking attempts undermine trust; high-profile breaches can lead investors away from cryptocurrencies altogether.
Environmental Concerns: Growing awareness about energy consumption associated with proof-of-work mining may result in restrictions or bans affecting certain coins’ viability.
Market Volatility: Cryptocurrencies exhibit significant price swings driven by speculation rather than fundamentals—which can deter risk-sensitive investors seeking stability.
Understanding How Cryptocurrency Transactions Impact Financial Ecosystems
Cryptocurrency transactions underpin decentralized finance (DeFi), enabling peer-to-peer lending, staking rewards, token swaps—and even cross-border remittances without intermediaries like banks or payment processors. Their transparent nature fosters trust among participants but also raises questions about privacy rights versus regulatory oversight.
As adoption expands—from individual users managing personal portfolios to institutional investors entering markets—the importance of secure infrastructure grows correspondingly alongside concerns over fraud prevention and compliance adherence.
Emerging Trends Influencing Future Transactions
Looking ahead, several trends could redefine how cryptocurrency transfers occur:
- Increased integration with traditional financial systems via stablecoins tied to fiat currencies
- Enhanced privacy features through zero-knowledge proofs
- Greater emphasis on sustainable practices amid environmental debates
- Development of more user-friendly interfaces making crypto management accessible even for novices
By staying informed about these developments—and understanding both technical aspects and regulatory landscapes—stakeholders can better navigate this rapidly evolving space while mitigating risks associated with security breaches or market instability.
Everyday Implications & User Considerations
For individuals engaging with cryptocurrencies today—from casual traders to institutional players—it’s vital to prioritize security measures such as using reputable wallets and verifying recipient addresses before sending funds. Awareness about potential scams—including phishing schemes—is crucial since private keys grant full control over assets once compromised cannot be recovered easily.
Moreover, understanding transaction fees—which vary depending on network congestion—and confirmation times helps optimize user experience during transfers across different blockchains.
The Role Of Regulation And Its Effect On Transaction Processes
Regulatory frameworks significantly influence how cryptocurrency transactions function globally—they determine what is permissible regarding anti-money laundering measures (“AML”), know-your-customer (“KYC”) requirements—and impact taxation policies that govern gains made through trading activities.
In some jurisdictions where regulation remains ambiguous—or outright restrictive—the volume of legitimate activity may decline due to uncertainty or fear among users; conversely—with clearer rules—adoption could accelerate thanks to increased legitimacy.
Final Thoughts
Cryptocurrency transactions form an integral part of modern decentralized finance ecosystems—they leverage cryptography combined with distributed ledger technology ensuring secure transfer mechanisms without central authorities' oversight.. As technological innovations emerge alongside evolving regulatory landscapes—with ongoing debates around environmental sustainability—the future trajectory promises both opportunities for broader adoption yet challenges related primarilyto security risksand policy uncertainties.
Staying informed about these dynamics enables stakeholders—from everyday users up through large-scale institutions—to participate confidently while navigating complexities inherent within this transformative financial frontier
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is the Market Facilitation Index (BW MFI)?
The Market Facilitation Index (BW MFI) is a technical indicator used primarily in cryptocurrency trading to assess the strength of buying and selling pressures within the market. Developed by Bitwise Asset Management, this tool aims to provide traders with insights into market dynamics that are not immediately visible through price movements alone. Unlike traditional indicators that focus solely on price or volume, BW MFI combines both elements to offer a more nuanced view of market activity.
At its core, the BW MFI helps identify whether current price movements are supported by significant trading activity or if they are likely to be false signals caused by low liquidity. This makes it especially valuable in volatile markets like cryptocurrencies, where sudden price swings can often mislead traders relying solely on basic technical analysis.
How Does the BW MFI Calculate Market Strength?
The calculation of BW MFI involves analyzing both price data and trading volume over a specific period. It typically ranges from 0 to 100, with higher values indicating strong buying pressure and lower values signaling dominant selling pressure. The index is derived from a combination of factors:
- Price Range: The difference between high and low prices within a given timeframe.
- Volume Data: The total amount traded during that period.
- Market Activity: How these two elements interact—whether high volume accompanies large price moves or if movement occurs with minimal trade activity.
This dual approach allows traders to distinguish between genuine momentum shifts and false signals caused by low liquidity or manipulation.
Signals generated by BW MFI depend heavily on its levels relative to historical averages. When the index crosses above certain thresholds—commonly around 50—it suggests increasing buying interest, potentially signaling an upward trend continuation or start. Conversely, falling below this threshold indicates weakening momentum and possible downward movement.
Interpreting Signals: When Does BW MFI Indicate Price Moves?
Understanding how BW MFI signals potential market moves is crucial for effective trading strategies:
Buy Signal: When the index rises above 50, it generally indicates that buyers are gaining control with substantial trading activity supporting rising prices. Traders might interpret this as an opportunity for entering long positions.
Sell Signal: Conversely, when the index drops below 50, it suggests sellers have stronger influence; prices may decline unless reversed quickly.
However, it's important not to rely solely on these signals without considering other factors such as trend lines or moving averages. Combining BW MFI readings with additional indicators enhances accuracy and reduces false positives—a common concern given cryptocurrency's inherent volatility.
Recent Developments in Using BW MFI
Since its introduction in 2020 by Bitwise Asset Management, there has been continuous refinement of the BW MFI algorithm. In recent years—particularly around 2022–2023—the company integrated advanced machine learning techniques into its calculations aimed at improving predictive accuracy amid rapidly changing market conditions.
Furthermore, many crypto exchanges and trading platforms have incorporated the indicator into their tools dashboards due to growing demand among retail investors seeking actionable insights amidst high volatility environments typical of digital assets like Bitcoin and altcoins.
Integration With Other Technical Tools
Traders increasingly use combined strategies involving moving averages (e.g., EMA), trend lines, RSI (Relative Strength Index), along with BW MFI for comprehensive analysis before executing trades. This multi-faceted approach helps mitigate risks associated with relying exclusively on one indicator in unpredictable markets.
Community Feedback & Adoption Trends
The broader crypto community has responded positively toward using BWMF as part of their technical toolkit because it provides real-time insights into underlying market forces rather than just surface-level price action alone. Many successful trades have been attributed partly to timely interpretation of BWMF signals aligned with other indicators' cues.
Limitations & Risks Associated With Using BWMF
Despite its advantages—such as providing deeper insight into liquidity-driven movements—the Market Facilitation Index is not foolproof:
Overreliance Risks: Relying exclusively on BWMF can lead traders astray if they ignore broader market context or fundamental factors influencing cryptocurrencies.
Market Volatility Impact: Cryptocurrency markets are highly volatile; sudden news events can cause sharp moves that render technical signals temporarily unreliable.
False Signals During Consolidation Phases: During sideways markets or periods of low volatility, BWMF may generate misleading indications about potential breakouts or breakdowns.
To mitigate these risks:
- Use BWMF alongside other indicators
- Confirm signals through multiple timeframes
- Stay updated on macroeconomic developments affecting crypto assets
Future Outlook for Market Facilitation Index Usage
As cryptocurrency markets continue evolving—with increased institutional participation and technological advancements—the role of tools like BWMF is expected to grow stronger yet more sophisticated too. Ongoing research efforts aim at integrating machine learning models further capable of adapting dynamically across different asset classes within digital finance ecosystems.
Bitwise Asset Management’s commitment toward refining this indicator suggests future iterations could incorporate alternative data sources such as social sentiment analysis or blockchain-specific metrics for even richer insights.
Final Thoughts: Is BWMF Suitable for Your Trading Strategy?
For traders seeking an edge in understanding underlying market forces beyond mere price charts—and who appreciate combining multiple analytical layers—the Market Facilitation Index offers valuable perspective especially when used correctly alongside complementary tools.
However:
- Always consider risk management practices
- Avoid overdependence solely upon any single indicator
- Keep abreast of ongoing developments within crypto analytics
By doing so—and maintaining disciplined execution—you enhance your ability not only to interpret current trends but also anticipate future movements effectively within dynamic cryptocurrency landscapes.
Keywords: Market Facilitation Index ,BW MFI ,cryptocurrency trading ,technical analysis ,market dynamics ,price movement signals ,crypto volatility ,trading strategies


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-09 20:49
What is the Market Facilitation Index (BW MFI) and how does it signal price moves?
What Is the Market Facilitation Index (BW MFI)?
The Market Facilitation Index (BW MFI) is a technical indicator used primarily in cryptocurrency trading to assess the strength of buying and selling pressures within the market. Developed by Bitwise Asset Management, this tool aims to provide traders with insights into market dynamics that are not immediately visible through price movements alone. Unlike traditional indicators that focus solely on price or volume, BW MFI combines both elements to offer a more nuanced view of market activity.
At its core, the BW MFI helps identify whether current price movements are supported by significant trading activity or if they are likely to be false signals caused by low liquidity. This makes it especially valuable in volatile markets like cryptocurrencies, where sudden price swings can often mislead traders relying solely on basic technical analysis.
How Does the BW MFI Calculate Market Strength?
The calculation of BW MFI involves analyzing both price data and trading volume over a specific period. It typically ranges from 0 to 100, with higher values indicating strong buying pressure and lower values signaling dominant selling pressure. The index is derived from a combination of factors:
- Price Range: The difference between high and low prices within a given timeframe.
- Volume Data: The total amount traded during that period.
- Market Activity: How these two elements interact—whether high volume accompanies large price moves or if movement occurs with minimal trade activity.
This dual approach allows traders to distinguish between genuine momentum shifts and false signals caused by low liquidity or manipulation.
Signals generated by BW MFI depend heavily on its levels relative to historical averages. When the index crosses above certain thresholds—commonly around 50—it suggests increasing buying interest, potentially signaling an upward trend continuation or start. Conversely, falling below this threshold indicates weakening momentum and possible downward movement.
Interpreting Signals: When Does BW MFI Indicate Price Moves?
Understanding how BW MFI signals potential market moves is crucial for effective trading strategies:
Buy Signal: When the index rises above 50, it generally indicates that buyers are gaining control with substantial trading activity supporting rising prices. Traders might interpret this as an opportunity for entering long positions.
Sell Signal: Conversely, when the index drops below 50, it suggests sellers have stronger influence; prices may decline unless reversed quickly.
However, it's important not to rely solely on these signals without considering other factors such as trend lines or moving averages. Combining BW MFI readings with additional indicators enhances accuracy and reduces false positives—a common concern given cryptocurrency's inherent volatility.
Recent Developments in Using BW MFI
Since its introduction in 2020 by Bitwise Asset Management, there has been continuous refinement of the BW MFI algorithm. In recent years—particularly around 2022–2023—the company integrated advanced machine learning techniques into its calculations aimed at improving predictive accuracy amid rapidly changing market conditions.
Furthermore, many crypto exchanges and trading platforms have incorporated the indicator into their tools dashboards due to growing demand among retail investors seeking actionable insights amidst high volatility environments typical of digital assets like Bitcoin and altcoins.
Integration With Other Technical Tools
Traders increasingly use combined strategies involving moving averages (e.g., EMA), trend lines, RSI (Relative Strength Index), along with BW MFI for comprehensive analysis before executing trades. This multi-faceted approach helps mitigate risks associated with relying exclusively on one indicator in unpredictable markets.
Community Feedback & Adoption Trends
The broader crypto community has responded positively toward using BWMF as part of their technical toolkit because it provides real-time insights into underlying market forces rather than just surface-level price action alone. Many successful trades have been attributed partly to timely interpretation of BWMF signals aligned with other indicators' cues.
Limitations & Risks Associated With Using BWMF
Despite its advantages—such as providing deeper insight into liquidity-driven movements—the Market Facilitation Index is not foolproof:
Overreliance Risks: Relying exclusively on BWMF can lead traders astray if they ignore broader market context or fundamental factors influencing cryptocurrencies.
Market Volatility Impact: Cryptocurrency markets are highly volatile; sudden news events can cause sharp moves that render technical signals temporarily unreliable.
False Signals During Consolidation Phases: During sideways markets or periods of low volatility, BWMF may generate misleading indications about potential breakouts or breakdowns.
To mitigate these risks:
- Use BWMF alongside other indicators
- Confirm signals through multiple timeframes
- Stay updated on macroeconomic developments affecting crypto assets
Future Outlook for Market Facilitation Index Usage
As cryptocurrency markets continue evolving—with increased institutional participation and technological advancements—the role of tools like BWMF is expected to grow stronger yet more sophisticated too. Ongoing research efforts aim at integrating machine learning models further capable of adapting dynamically across different asset classes within digital finance ecosystems.
Bitwise Asset Management’s commitment toward refining this indicator suggests future iterations could incorporate alternative data sources such as social sentiment analysis or blockchain-specific metrics for even richer insights.
Final Thoughts: Is BWMF Suitable for Your Trading Strategy?
For traders seeking an edge in understanding underlying market forces beyond mere price charts—and who appreciate combining multiple analytical layers—the Market Facilitation Index offers valuable perspective especially when used correctly alongside complementary tools.
However:
- Always consider risk management practices
- Avoid overdependence solely upon any single indicator
- Keep abreast of ongoing developments within crypto analytics
By doing so—and maintaining disciplined execution—you enhance your ability not only to interpret current trends but also anticipate future movements effectively within dynamic cryptocurrency landscapes.
Keywords: Market Facilitation Index ,BW MFI ,cryptocurrency trading ,technical analysis ,market dynamics ,price movement signals ,crypto volatility ,trading strategies
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Gas Tokens Like GST2 Are Used to Reduce Blockchain Transaction Fees
Blockchain networks, especially Ethereum, have revolutionized digital finance and decentralized applications. However, one persistent challenge has been the high transaction fees—commonly known as gas fees—that can make using these networks costly and sometimes prohibitive for users. Gas tokens such as GST2 have emerged as innovative solutions to mitigate these expenses. This article explores how gas tokens function within blockchain ecosystems to reduce transaction costs, offering insights into their mechanisms, benefits, and potential challenges.
Understanding Gas Tokens in Blockchain Ecosystems
Gas tokens are specialized cryptocurrencies designed specifically to optimize transaction costs on blockchain platforms like Ethereum. Unlike traditional cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ether (ETH), gas tokens serve a unique purpose: they act as prepaid units of computational work that can be redeemed when network congestion is high.
GST2 is one of the most prominent examples of a gas token tailored for Ethereum. It was developed during the network’s transition phase from proof-of-work (PoW) to proof-of-stake (PoS). The core idea behind GST2 is to allow users to "store" gas when prices are low and "release" it during periods of high demand when fees spike.
How Do Gas Tokens Help Reduce Transaction Fees?
The primary way gas tokens like GST2 reduce costs involves strategic timing and efficient resource management:
Pre-Purchasing During Low Fee Periods: Users buy or mint gas tokens when network congestion is low—meaning transaction fees are minimal. This process involves executing specific smart contract operations that generate new gas tokens by exploiting certain features of the blockchain's architecture.
Redeeming During Peak Congestion: When network activity surges and transaction fees increase significantly, users can use their stored gas tokens instead of paying directly in ETH for each transaction. Redeeming a token effectively refunds part of the fee paid in ETH by utilizing previously stored computational work.
Reducing Overall Cost: By leveraging this mechanism, users pay less in native cryptocurrency (like ETH) for executing transactions during busy periods because they offset some fee costs with their accumulated gas tokens.
This approach essentially acts like a financial hedge against fluctuating network congestion levels—buy low, use high—to minimize expenses over time.
The Technical Mechanism Behind Gas Token Usage
Gas tokens operate based on specific smart contract functionalities that exploit how blockchain networks handle storage and computation:
Minting Gas Tokens: When network conditions are favorable (i.e., lower demand), users execute transactions that create new instances of the token through clever contract interactions—often involving storing data temporarily or performing particular computations that consume minimal actual cost but generate value.
Storing Value: These minted tokens represent "stored" computational work or unused capacity that can later be redeemed.
Redeeming During High Demand: When user activity increases—and so do associated fees—they execute another set of transactions where they burn or redeem their stored GASTokens instead of paying full price in ETH directly for each operation.
Refund Mechanism: Redeeming GASTokens effectively refunds part of the original fee paid by leveraging earlier pre-paid computational resources—a process often called “gas refund” or “gas rebate.”
This cycle allows traders and developers to optimize their operational costs dynamically based on real-time network conditions without sacrificing performance or security.
Practical Benefits for Users and Developers
Using GASTokens offers several tangible advantages:
Cost Efficiency: Significantly lowers transactional expenses during peak times without waiting for off-peak hours.
Enhanced User Experience: Enables smoother interactions with decentralized apps (dApps), DeFi protocols, NFTs marketplaces—all while managing budget constraints more effectively.
Incentivizes Network Participation: Encourages active participation from miners/stakers who benefit from optimized fee structures created through these mechanisms.
Supports Network Scalability: By reducing individual user costs temporarily via token redemption strategies, GASTokens contribute indirectly toward easing overall congestion pressures on blockchain networks.
Recent Trends & Adoption Drivers
The adoption rate for gases like GST2 has increased alongside broader trends such as DeFi growth and NFT proliferation since 2020–2021. As more applications rely heavily on frequent smart contract interactions—and consequently incur higher fees—the need for cost-saving tools becomes critical.
Furthermore, Ethereum’s move toward PoS with upgrades like Shanghai/Capella has opened new avenues where efficient fee management becomes even more relevant due to changes in block validation processes affecting overall throughput and cost structure.
Regulatory clarity around cryptocurrencies also influences adoption; clearer frameworks encourage both retail investors and institutional players to explore advanced tools like GASTokens confidently within compliant environments.
Challenges Facing Gas Token Utilization
Despite promising benefits, several hurdles could impact widespread usage:
Market Volatility: Fluctuations in cryptocurrency prices affect the value proposition behind holding or minting GASTokens.
Scalability Concerns: As demand grows exponentially with increasing dApp usage—including DeFi protocols—the effectiveness of current GASToken models may diminish if not scaled appropriately.
Security Risks: Vulnerabilities within smart contracts governing thesetokens could lead to exploits risking user funds or system integrity.
Key Dates & Developments Shaping Future Use Cases
Some notable milestones include:
The announcement in 2020 about Ethereum’s transition plans toward PoS—a move expected fully completed by mid–2023—which enhances efficiency opportunities related to fee reduction strategies involving gases.
Launches like GST2 early 2023 aimed at integrating seamlessly into this evolving ecosystem while supporting ongoing scalability efforts.
Growing regulatory discussions across jurisdictions such as the US SEC's activities influencing broader acceptance pathways.
Final Thoughts on Using Gas Tokens Effectively
Gas tokens such as GST2 exemplify innovative approaches within blockchain technology aimed at making decentralized systems more accessible by reducing operational costs during periods of high demand. Their strategic use enables both individual users and developers alike to navigate fluctuating market conditions efficiently while contributing positively toward scalable ecosystem development.
As blockchain ecosystems continue evolving—with upgrades focusing on scalability, security enhancements—and regulatory landscapes clarifying further adoption pathways—the role played by tools like GASTokens will likely expand accordingly — fostering a more sustainable future where decentralization remains practical even amid rising global interest.
By understanding how gases like GST2 operate—from minting at low-cost periods through redeeming during peak demands—users gain powerful leverage over transaction expenses. This knowledge empowers smarter engagement with decentralized platforms while supporting ongoing innovations shaping tomorrow’s digital economy


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-09 18:15
How are gas tokens (e.g., GST2) used to reduce fees?
How Gas Tokens Like GST2 Are Used to Reduce Blockchain Transaction Fees
Blockchain networks, especially Ethereum, have revolutionized digital finance and decentralized applications. However, one persistent challenge has been the high transaction fees—commonly known as gas fees—that can make using these networks costly and sometimes prohibitive for users. Gas tokens such as GST2 have emerged as innovative solutions to mitigate these expenses. This article explores how gas tokens function within blockchain ecosystems to reduce transaction costs, offering insights into their mechanisms, benefits, and potential challenges.
Understanding Gas Tokens in Blockchain Ecosystems
Gas tokens are specialized cryptocurrencies designed specifically to optimize transaction costs on blockchain platforms like Ethereum. Unlike traditional cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ether (ETH), gas tokens serve a unique purpose: they act as prepaid units of computational work that can be redeemed when network congestion is high.
GST2 is one of the most prominent examples of a gas token tailored for Ethereum. It was developed during the network’s transition phase from proof-of-work (PoW) to proof-of-stake (PoS). The core idea behind GST2 is to allow users to "store" gas when prices are low and "release" it during periods of high demand when fees spike.
How Do Gas Tokens Help Reduce Transaction Fees?
The primary way gas tokens like GST2 reduce costs involves strategic timing and efficient resource management:
Pre-Purchasing During Low Fee Periods: Users buy or mint gas tokens when network congestion is low—meaning transaction fees are minimal. This process involves executing specific smart contract operations that generate new gas tokens by exploiting certain features of the blockchain's architecture.
Redeeming During Peak Congestion: When network activity surges and transaction fees increase significantly, users can use their stored gas tokens instead of paying directly in ETH for each transaction. Redeeming a token effectively refunds part of the fee paid in ETH by utilizing previously stored computational work.
Reducing Overall Cost: By leveraging this mechanism, users pay less in native cryptocurrency (like ETH) for executing transactions during busy periods because they offset some fee costs with their accumulated gas tokens.
This approach essentially acts like a financial hedge against fluctuating network congestion levels—buy low, use high—to minimize expenses over time.
The Technical Mechanism Behind Gas Token Usage
Gas tokens operate based on specific smart contract functionalities that exploit how blockchain networks handle storage and computation:
Minting Gas Tokens: When network conditions are favorable (i.e., lower demand), users execute transactions that create new instances of the token through clever contract interactions—often involving storing data temporarily or performing particular computations that consume minimal actual cost but generate value.
Storing Value: These minted tokens represent "stored" computational work or unused capacity that can later be redeemed.
Redeeming During High Demand: When user activity increases—and so do associated fees—they execute another set of transactions where they burn or redeem their stored GASTokens instead of paying full price in ETH directly for each operation.
Refund Mechanism: Redeeming GASTokens effectively refunds part of the original fee paid by leveraging earlier pre-paid computational resources—a process often called “gas refund” or “gas rebate.”
This cycle allows traders and developers to optimize their operational costs dynamically based on real-time network conditions without sacrificing performance or security.
Practical Benefits for Users and Developers
Using GASTokens offers several tangible advantages:
Cost Efficiency: Significantly lowers transactional expenses during peak times without waiting for off-peak hours.
Enhanced User Experience: Enables smoother interactions with decentralized apps (dApps), DeFi protocols, NFTs marketplaces—all while managing budget constraints more effectively.
Incentivizes Network Participation: Encourages active participation from miners/stakers who benefit from optimized fee structures created through these mechanisms.
Supports Network Scalability: By reducing individual user costs temporarily via token redemption strategies, GASTokens contribute indirectly toward easing overall congestion pressures on blockchain networks.
Recent Trends & Adoption Drivers
The adoption rate for gases like GST2 has increased alongside broader trends such as DeFi growth and NFT proliferation since 2020–2021. As more applications rely heavily on frequent smart contract interactions—and consequently incur higher fees—the need for cost-saving tools becomes critical.
Furthermore, Ethereum’s move toward PoS with upgrades like Shanghai/Capella has opened new avenues where efficient fee management becomes even more relevant due to changes in block validation processes affecting overall throughput and cost structure.
Regulatory clarity around cryptocurrencies also influences adoption; clearer frameworks encourage both retail investors and institutional players to explore advanced tools like GASTokens confidently within compliant environments.
Challenges Facing Gas Token Utilization
Despite promising benefits, several hurdles could impact widespread usage:
Market Volatility: Fluctuations in cryptocurrency prices affect the value proposition behind holding or minting GASTokens.
Scalability Concerns: As demand grows exponentially with increasing dApp usage—including DeFi protocols—the effectiveness of current GASToken models may diminish if not scaled appropriately.
Security Risks: Vulnerabilities within smart contracts governing thesetokens could lead to exploits risking user funds or system integrity.
Key Dates & Developments Shaping Future Use Cases
Some notable milestones include:
The announcement in 2020 about Ethereum’s transition plans toward PoS—a move expected fully completed by mid–2023—which enhances efficiency opportunities related to fee reduction strategies involving gases.
Launches like GST2 early 2023 aimed at integrating seamlessly into this evolving ecosystem while supporting ongoing scalability efforts.
Growing regulatory discussions across jurisdictions such as the US SEC's activities influencing broader acceptance pathways.
Final Thoughts on Using Gas Tokens Effectively
Gas tokens such as GST2 exemplify innovative approaches within blockchain technology aimed at making decentralized systems more accessible by reducing operational costs during periods of high demand. Their strategic use enables both individual users and developers alike to navigate fluctuating market conditions efficiently while contributing positively toward scalable ecosystem development.
As blockchain ecosystems continue evolving—with upgrades focusing on scalability, security enhancements—and regulatory landscapes clarifying further adoption pathways—the role played by tools like GASTokens will likely expand accordingly — fostering a more sustainable future where decentralization remains practical even amid rising global interest.
By understanding how gases like GST2 operate—from minting at low-cost periods through redeeming during peak demands—users gain powerful leverage over transaction expenses. This knowledge empowers smarter engagement with decentralized platforms while supporting ongoing innovations shaping tomorrow’s digital economy
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Does SPV (Simplified Payment Verification) Work in Bitcoin?
Understanding the Basics of SPV in Bitcoin
Simplified Payment Verification (SPV) is a method that allows Bitcoin users to verify transactions without downloading and storing the entire blockchain. This approach is especially beneficial for lightweight clients like mobile wallets, which have limited storage capacity and computational resources. Unlike full nodes that maintain a complete copy of all transaction data, SPV enables users to confirm that their transactions are included in the blockchain efficiently and securely.
At its core, SPV relies on a minimal set of data—specifically, block headers—to verify transaction validity. This design significantly reduces resource requirements while maintaining a reasonable level of security for everyday use. As Bitcoin continues to grow, SPV remains an essential tool for increasing accessibility and scalability within the network.
The Mechanics Behind SPV: How It Verifies Transactions
The process begins with downloading only the block headers rather than entire blocks filled with transaction data. Each block header contains critical information such as:
- The hash of the previous block
- A timestamp
- The Merkle root (a cryptographic summary of all transactions within that block)
- Other metadata like difficulty target and nonce
This compact data structure allows clients to track the blockchain's overall state without handling every individual transaction.
To verify whether a specific transaction has been confirmed on the network, an SPV client requests a proof of inclusion from a full node—an entity that maintains complete blockchain data. This proof includes:
- The transaction ID
- A sequence of hashes forming a path through the Merkle tree from the specific transaction up to its Merkle root
Using this proof, users can perform two key checks:
- Merkle Proof Validation: Confirming that their transaction is part of the Merkle tree by reconstructing hashes along the provided path.
- Block Header Validation: Ensuring that this particular Merkle root matches one present in an accepted block header.
If both checks pass successfully, it indicates with high confidence that their transaction was included in an accepted block on the Bitcoin network.
Why Was SPV Introduced? Its Historical Context
SPV was first introduced by Greg Maxwell in 2011 as part of efforts to make Bitcoin more accessible beyond technical enthusiasts running full nodes. Prior to this innovation, verifying transactions required downloading and validating every piece of blockchain data—a process impractical for devices with limited resources like smartphones or web-based wallets.
The goal was clear: enable lightweight clients to participate securely without demanding extensive hardware capabilities or bandwidth consumption. Since then, SPV has become integral for many wallet implementations worldwide due to its simplicity and efficiency.
Security Considerations When Using SPV
While SPV offers significant advantages regarding resource efficiency and user convenience, it does come with inherent security risks worth understanding:
Susceptibility to Fake Chains: Because lightweight clients rely on external full nodes for proofs but do not independently validate all chain history fully, they could be misled if connected to malicious nodes controlling false information.
51% Attacks: If an attacker gains majority control over mining power (a 51% attack), they could potentially manipulate which blocks are considered valid or produce fraudulent proofs affecting verification accuracy.
Centralization Risks: Heavy reliance on trusted full nodes might inadvertently lead toward centralization tendencies if most users depend on few providers for validation services.
Despite these concerns, various protocol enhancements—such as better proof-of-inclusion methods—and best practices like connecting only trusted nodes help mitigate potential vulnerabilities associated with using SPV-based wallets.
Recent Advances Improving Security & Efficiency
Over recent years, developers have focused on refining how proofs are generated and verified within SPI protocols:
Enhanced Merkle Tree Structures:
- Newer algorithms optimize how hashes are combined into trees.
- These improvements reduce verification time while increasing resistance against manipulation attempts.
Better Proof Generation Methods:
- Techniques such as Compact Block Filters allow faster validation processes.
- They also minimize bandwidth usage during synchronization between peers.
Integration With Layer 2 Solutions
- Technologies like Lightning Network leverage simplified verification methods alongside traditional protocols.
- These integrations aim at scaling Bitcoin further while maintaining security standards suitable for lightweight clients.
Furthermore, ongoing research aims at developing more robust mechanisms against potential attacks targeting light client verification processes—ensuring safer participation even under adversarial conditions.
Key Milestones & Facts About SPV Development
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 2011 | Introduction of Simplified Payment Verification by Greg Maxwell |
| 2012 | Inclusion into early versions of Bitcoin Core software |
| 2013 | Identification of vulnerabilities related to fake chain attacks |
| Present | Continuous protocol improvements focusing on security enhancements |
These milestones highlight both foundational development efforts and ongoing innovations aimed at strengthening trustworthiness across different types of wallet implementations utilizing SPI techniques.
How Light Clients Benefit From Using SPI Protocols
Lightweight wallets employing SPI protocols benefit primarily through reduced storage needs—they only store minimal blockchain summaries rather than entire histories—and faster synchronization times compared with full node setups. This makes them ideal choices for mobile devices where hardware limitations restrict traditional node operation capabilities.
Limitations & Future Directions in Blockchain Verification
Despite advancements made over recent years—including improved proof structures—the reliance on external full nodes still introduces some trust assumptions not present when operating fully validating nodes independently; thus emphasizing importance around selecting reputable sources during verification processes.
Looking ahead , ongoing research focuses heavily upon enhancing decentralization aspects by enabling more secure peer-to-peer validation schemes alongside integrating new cryptographic techniques such as zero-knowledge proofs — promising even greater privacy-preserving features combined with scalable verification solutions suited specifically for future decentralized ecosystems.
Final Thoughts
Understanding how Simplified Payment Verification works provides valuable insight into making cryptocurrency networks more accessible without compromising too much security or decentralization principles . As technology evolves—with continuous protocol improvements addressing current vulnerabilities—SPV remains vital within broader efforts toward scalable adoption across diverse user bases worldwide.


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-09 16:37
How does SPV (Simplified Payment Verification) work in Bitcoin?
How Does SPV (Simplified Payment Verification) Work in Bitcoin?
Understanding the Basics of SPV in Bitcoin
Simplified Payment Verification (SPV) is a method that allows Bitcoin users to verify transactions without downloading and storing the entire blockchain. This approach is especially beneficial for lightweight clients like mobile wallets, which have limited storage capacity and computational resources. Unlike full nodes that maintain a complete copy of all transaction data, SPV enables users to confirm that their transactions are included in the blockchain efficiently and securely.
At its core, SPV relies on a minimal set of data—specifically, block headers—to verify transaction validity. This design significantly reduces resource requirements while maintaining a reasonable level of security for everyday use. As Bitcoin continues to grow, SPV remains an essential tool for increasing accessibility and scalability within the network.
The Mechanics Behind SPV: How It Verifies Transactions
The process begins with downloading only the block headers rather than entire blocks filled with transaction data. Each block header contains critical information such as:
- The hash of the previous block
- A timestamp
- The Merkle root (a cryptographic summary of all transactions within that block)
- Other metadata like difficulty target and nonce
This compact data structure allows clients to track the blockchain's overall state without handling every individual transaction.
To verify whether a specific transaction has been confirmed on the network, an SPV client requests a proof of inclusion from a full node—an entity that maintains complete blockchain data. This proof includes:
- The transaction ID
- A sequence of hashes forming a path through the Merkle tree from the specific transaction up to its Merkle root
Using this proof, users can perform two key checks:
- Merkle Proof Validation: Confirming that their transaction is part of the Merkle tree by reconstructing hashes along the provided path.
- Block Header Validation: Ensuring that this particular Merkle root matches one present in an accepted block header.
If both checks pass successfully, it indicates with high confidence that their transaction was included in an accepted block on the Bitcoin network.
Why Was SPV Introduced? Its Historical Context
SPV was first introduced by Greg Maxwell in 2011 as part of efforts to make Bitcoin more accessible beyond technical enthusiasts running full nodes. Prior to this innovation, verifying transactions required downloading and validating every piece of blockchain data—a process impractical for devices with limited resources like smartphones or web-based wallets.
The goal was clear: enable lightweight clients to participate securely without demanding extensive hardware capabilities or bandwidth consumption. Since then, SPV has become integral for many wallet implementations worldwide due to its simplicity and efficiency.
Security Considerations When Using SPV
While SPV offers significant advantages regarding resource efficiency and user convenience, it does come with inherent security risks worth understanding:
Susceptibility to Fake Chains: Because lightweight clients rely on external full nodes for proofs but do not independently validate all chain history fully, they could be misled if connected to malicious nodes controlling false information.
51% Attacks: If an attacker gains majority control over mining power (a 51% attack), they could potentially manipulate which blocks are considered valid or produce fraudulent proofs affecting verification accuracy.
Centralization Risks: Heavy reliance on trusted full nodes might inadvertently lead toward centralization tendencies if most users depend on few providers for validation services.
Despite these concerns, various protocol enhancements—such as better proof-of-inclusion methods—and best practices like connecting only trusted nodes help mitigate potential vulnerabilities associated with using SPV-based wallets.
Recent Advances Improving Security & Efficiency
Over recent years, developers have focused on refining how proofs are generated and verified within SPI protocols:
Enhanced Merkle Tree Structures:
- Newer algorithms optimize how hashes are combined into trees.
- These improvements reduce verification time while increasing resistance against manipulation attempts.
Better Proof Generation Methods:
- Techniques such as Compact Block Filters allow faster validation processes.
- They also minimize bandwidth usage during synchronization between peers.
Integration With Layer 2 Solutions
- Technologies like Lightning Network leverage simplified verification methods alongside traditional protocols.
- These integrations aim at scaling Bitcoin further while maintaining security standards suitable for lightweight clients.
Furthermore, ongoing research aims at developing more robust mechanisms against potential attacks targeting light client verification processes—ensuring safer participation even under adversarial conditions.
Key Milestones & Facts About SPV Development
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 2011 | Introduction of Simplified Payment Verification by Greg Maxwell |
| 2012 | Inclusion into early versions of Bitcoin Core software |
| 2013 | Identification of vulnerabilities related to fake chain attacks |
| Present | Continuous protocol improvements focusing on security enhancements |
These milestones highlight both foundational development efforts and ongoing innovations aimed at strengthening trustworthiness across different types of wallet implementations utilizing SPI techniques.
How Light Clients Benefit From Using SPI Protocols
Lightweight wallets employing SPI protocols benefit primarily through reduced storage needs—they only store minimal blockchain summaries rather than entire histories—and faster synchronization times compared with full node setups. This makes them ideal choices for mobile devices where hardware limitations restrict traditional node operation capabilities.
Limitations & Future Directions in Blockchain Verification
Despite advancements made over recent years—including improved proof structures—the reliance on external full nodes still introduces some trust assumptions not present when operating fully validating nodes independently; thus emphasizing importance around selecting reputable sources during verification processes.
Looking ahead , ongoing research focuses heavily upon enhancing decentralization aspects by enabling more secure peer-to-peer validation schemes alongside integrating new cryptographic techniques such as zero-knowledge proofs — promising even greater privacy-preserving features combined with scalable verification solutions suited specifically for future decentralized ecosystems.
Final Thoughts
Understanding how Simplified Payment Verification works provides valuable insight into making cryptocurrency networks more accessible without compromising too much security or decentralization principles . As technology evolves—with continuous protocol improvements addressing current vulnerabilities—SPV remains vital within broader efforts toward scalable adoption across diverse user bases worldwide.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Public vs. Private Blockchain: What’s the Difference?
Understanding the distinctions between public and private blockchains is essential for anyone interested in blockchain technology, whether you're an investor, developer, or business leader. Both types of blockchains leverage distributed ledger technology (DLT), but they serve different purposes and operate under different principles. This article provides a clear overview of what sets them apart, their key features, use cases, and recent trends shaping their development.
What Is a Public Blockchain?
A public blockchain is an open-source network where anyone can participate without restrictions. These networks are fully decentralized—meaning no single entity controls the entire system—and rely on consensus mechanisms like proof-of-work (PoW) or proof-of-stake (PoS) to validate transactions. Because they are accessible to everyone globally, public blockchains promote transparency and security through widespread participation.
For example, Bitcoin was the first successful public blockchain that introduced peer-to-peer digital currency without intermediaries such as banks. Ethereum expanded on this concept by enabling smart contracts—self-executing agreements written into code—that facilitate complex decentralized applications (dApps). These platforms have fueled innovations like decentralized finance (DeFi), which allows users to lend, borrow, or trade assets directly on blockchain networks.
Public blockchains are particularly suited for applications requiring transparency and censorship resistance. Their open nature makes them ideal for financial transactions involving cryptocurrencies but also extends to supply chain tracking and voting systems where trustlessness is vital.
Characteristics of Public Blockchains
- Decentralization: Anyone can join as a node; no central authority controls the network.
- Open Access: No permission needed; anyone can read data or participate in validation.
- Transparency: All transaction data is publicly visible.
- Immutability: Once recorded, data cannot be altered retroactively.
- Security Through Consensus: Network security relies on collective agreement mechanisms like PoW or PoS.
These features foster trust among participants because they eliminate single points of failure while ensuring data integrity across all nodes.
What Is a Private Blockchain?
In contrast to public blockchains, private blockchains restrict access to authorized participants only. They are often used within organizations or consortia that require controlled environments for sharing sensitive information securely. Managed by a central authority—or sometimes by multiple trusted entities—private networks prioritize privacy and efficiency over complete decentralization.
Private blockchains enable organizations such as banks or supply chain companies to automate internal processes while maintaining strict control over who can view or modify data. For instance, Hyperledger Fabric—a popular private blockchain framework—is widely adopted in enterprise settings due to its modular architecture allowing customization according to specific compliance needs.
Because access is limited and permissions are managed centrally—or through consortium governance—private chains tend not to be fully transparent externally but offer higher throughput speeds suitable for enterprise-scale operations requiring confidentiality.
Key Features of Private Blockchains
- Controlled Access: Only selected users with permissions can join the network.
- Closed Source/Permissioned: The codebase may not be publicly available; modifications are controlled.
- Data Privacy: Transaction details are visible only among authorized parties.
- Higher Performance & Scalability: Reduced consensus overhead leads to faster transaction processing.
- Governance & Compliance Focused: Designed with regulatory requirements in mind—for example GDPR compliance in Europe.
This structure makes private blockchains attractive for industries needing secure yet confidential recordkeeping without exposing sensitive information externally.
Comparing Public vs Private Blockchains
| Feature | Public Blockchain | Private Blockchain |
|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Open worldwide | Restricted membership |
| Decentralization | Fully decentralized | Partially centralized |
| Transparency | Complete visibility | Limited visibility |
| Speed & Scalability | Lower due to consensus complexity | Higher performance |
| Use Cases | Cryptocurrencies; DeFi; voting systems | Internal processes; supply chains; compliance |
While both types aim at enhancing security through cryptography and distributed ledgers, their design choices reflect differing priorities: openness versus control depending on application needs.
Recent Trends & Developments
The landscape of blockchain continues evolving rapidly:
Enterprise Adoption: Many corporations prefer private chains like Hyperledger Fabric because they align with regulatory standards while offering scalability benefits necessary for large-scale operations such as banking transactions or healthcare records management.
Hybrid Models: Some projects combine elements from both worlds—public permissioned chains—to balance transparency with privacy concerns effectively—a trend gaining traction especially within regulated sectors like finance and government services.
Regulatory Environment: As governments scrutinize cryptocurrencies more closely—with notable figures such as SEC Chair Paul Atkins emphasizing oversight—the distinction between public tokens versus permissioned networks becomes increasingly significant from legal perspectives.
Security Considerations: While both models provide high levels of cryptographic security when properly implemented, private networks face risks related mainly to insider threats if governance isn’t robust enough.
Technological Innovations: Advances include interoperability solutions allowing seamless communication between different types of ledgers—a step toward integrated multi-chain ecosystems supporting diverse organizational needs.
Understanding these developments helps stakeholders make informed decisions about deploying appropriate blockchain solutions aligned with strategic goals and compliance requirements.
Which Type Fits Your Needs?
Choosing between a public versus private blockchain depends heavily on your specific objectives:
If your priority is transparency —such as tracking product provenance across global supply chains—or creating open financial ecosystems—public chains might be best suited—you should consider factors like scalability limitations due to consensus protocols though these remain areas under active research improving performance metrics over time.
Conversely if your organization handles sensitive customer data requiring strict confidentiality—and you need faster transaction speeds—a private chain offers better control over access rights while still leveraging core DLT benefits.
Ultimately understanding these differences enables better alignment with industry standards—including E-A-T principles—to ensure trustworthy implementation that meets user expectations regarding security expertise and authoritative practices.
Final Thoughts
The debate between public versus private blockchains centers around balancing openness against control based on application demands—from democratized cryptocurrency markets favoring decentralization towards highly regulated industries prioritizing privacy/security measures respectively.. As technological innovations continue pushing boundaries—including interoperability protocols—the lines may blur further creating hybrid models tailored precisely per organizational needs.
Staying informed about recent trends ensures stakeholders harness blockchain's full potential responsibly while adhering best practices rooted in transparency—and building trust among users across various sectors seeking reliable digital transformation tools today


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-09 12:19
What is the difference between a public and a private blockchain?
Public vs. Private Blockchain: What’s the Difference?
Understanding the distinctions between public and private blockchains is essential for anyone interested in blockchain technology, whether you're an investor, developer, or business leader. Both types of blockchains leverage distributed ledger technology (DLT), but they serve different purposes and operate under different principles. This article provides a clear overview of what sets them apart, their key features, use cases, and recent trends shaping their development.
What Is a Public Blockchain?
A public blockchain is an open-source network where anyone can participate without restrictions. These networks are fully decentralized—meaning no single entity controls the entire system—and rely on consensus mechanisms like proof-of-work (PoW) or proof-of-stake (PoS) to validate transactions. Because they are accessible to everyone globally, public blockchains promote transparency and security through widespread participation.
For example, Bitcoin was the first successful public blockchain that introduced peer-to-peer digital currency without intermediaries such as banks. Ethereum expanded on this concept by enabling smart contracts—self-executing agreements written into code—that facilitate complex decentralized applications (dApps). These platforms have fueled innovations like decentralized finance (DeFi), which allows users to lend, borrow, or trade assets directly on blockchain networks.
Public blockchains are particularly suited for applications requiring transparency and censorship resistance. Their open nature makes them ideal for financial transactions involving cryptocurrencies but also extends to supply chain tracking and voting systems where trustlessness is vital.
Characteristics of Public Blockchains
- Decentralization: Anyone can join as a node; no central authority controls the network.
- Open Access: No permission needed; anyone can read data or participate in validation.
- Transparency: All transaction data is publicly visible.
- Immutability: Once recorded, data cannot be altered retroactively.
- Security Through Consensus: Network security relies on collective agreement mechanisms like PoW or PoS.
These features foster trust among participants because they eliminate single points of failure while ensuring data integrity across all nodes.
What Is a Private Blockchain?
In contrast to public blockchains, private blockchains restrict access to authorized participants only. They are often used within organizations or consortia that require controlled environments for sharing sensitive information securely. Managed by a central authority—or sometimes by multiple trusted entities—private networks prioritize privacy and efficiency over complete decentralization.
Private blockchains enable organizations such as banks or supply chain companies to automate internal processes while maintaining strict control over who can view or modify data. For instance, Hyperledger Fabric—a popular private blockchain framework—is widely adopted in enterprise settings due to its modular architecture allowing customization according to specific compliance needs.
Because access is limited and permissions are managed centrally—or through consortium governance—private chains tend not to be fully transparent externally but offer higher throughput speeds suitable for enterprise-scale operations requiring confidentiality.
Key Features of Private Blockchains
- Controlled Access: Only selected users with permissions can join the network.
- Closed Source/Permissioned: The codebase may not be publicly available; modifications are controlled.
- Data Privacy: Transaction details are visible only among authorized parties.
- Higher Performance & Scalability: Reduced consensus overhead leads to faster transaction processing.
- Governance & Compliance Focused: Designed with regulatory requirements in mind—for example GDPR compliance in Europe.
This structure makes private blockchains attractive for industries needing secure yet confidential recordkeeping without exposing sensitive information externally.
Comparing Public vs Private Blockchains
| Feature | Public Blockchain | Private Blockchain |
|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Open worldwide | Restricted membership |
| Decentralization | Fully decentralized | Partially centralized |
| Transparency | Complete visibility | Limited visibility |
| Speed & Scalability | Lower due to consensus complexity | Higher performance |
| Use Cases | Cryptocurrencies; DeFi; voting systems | Internal processes; supply chains; compliance |
While both types aim at enhancing security through cryptography and distributed ledgers, their design choices reflect differing priorities: openness versus control depending on application needs.
Recent Trends & Developments
The landscape of blockchain continues evolving rapidly:
Enterprise Adoption: Many corporations prefer private chains like Hyperledger Fabric because they align with regulatory standards while offering scalability benefits necessary for large-scale operations such as banking transactions or healthcare records management.
Hybrid Models: Some projects combine elements from both worlds—public permissioned chains—to balance transparency with privacy concerns effectively—a trend gaining traction especially within regulated sectors like finance and government services.
Regulatory Environment: As governments scrutinize cryptocurrencies more closely—with notable figures such as SEC Chair Paul Atkins emphasizing oversight—the distinction between public tokens versus permissioned networks becomes increasingly significant from legal perspectives.
Security Considerations: While both models provide high levels of cryptographic security when properly implemented, private networks face risks related mainly to insider threats if governance isn’t robust enough.
Technological Innovations: Advances include interoperability solutions allowing seamless communication between different types of ledgers—a step toward integrated multi-chain ecosystems supporting diverse organizational needs.
Understanding these developments helps stakeholders make informed decisions about deploying appropriate blockchain solutions aligned with strategic goals and compliance requirements.
Which Type Fits Your Needs?
Choosing between a public versus private blockchain depends heavily on your specific objectives:
If your priority is transparency —such as tracking product provenance across global supply chains—or creating open financial ecosystems—public chains might be best suited—you should consider factors like scalability limitations due to consensus protocols though these remain areas under active research improving performance metrics over time.
Conversely if your organization handles sensitive customer data requiring strict confidentiality—and you need faster transaction speeds—a private chain offers better control over access rights while still leveraging core DLT benefits.
Ultimately understanding these differences enables better alignment with industry standards—including E-A-T principles—to ensure trustworthy implementation that meets user expectations regarding security expertise and authoritative practices.
Final Thoughts
The debate between public versus private blockchains centers around balancing openness against control based on application demands—from democratized cryptocurrency markets favoring decentralization towards highly regulated industries prioritizing privacy/security measures respectively.. As technological innovations continue pushing boundaries—including interoperability protocols—the lines may blur further creating hybrid models tailored precisely per organizational needs.
Staying informed about recent trends ensures stakeholders harness blockchain's full potential responsibly while adhering best practices rooted in transparency—and building trust among users across various sectors seeking reliable digital transformation tools today
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Why is Volume Confirmation Critical for Pattern Validity in Crypto Trading?
In the fast-paced world of cryptocurrency trading, understanding market signals is essential for making informed decisions. Among these signals, chart patterns such as head and shoulders, triangles, or double bottoms are widely used by traders to predict future price movements. However, not all patterns are equally reliable on their own. This is where volume confirmation plays a vital role—adding a layer of validation that can significantly improve the accuracy of pattern-based predictions.
What Is Volume Confirmation in Cryptocurrency Trading?
Volume confirmation involves analyzing trading volume alongside price movements to verify the legitimacy of technical patterns. When a pattern forms on a chart—say, an ascending triangle—the accompanying trading volume provides insight into whether this pattern reflects genuine market interest or if it’s potentially misleading. High trading volume during the formation or breakout of a pattern suggests strong participation and conviction among traders, increasing confidence that the trend will continue in the predicted direction.
Conversely, low volume may indicate lack of interest or even manipulation—such as wash trading or fakeouts—that can produce false signals. Therefore, integrating volume data helps traders distinguish between authentic trends and deceptive moves driven by short-term speculation or market manipulation.
The Role of Volume Confirmation in Technical Analysis
Technical analysis relies heavily on identifying consistent patterns within historical price data to forecast future movements. However, without considering trade activity levels (volume), these patterns can sometimes be unreliable indicators due to false breakouts or reversals.
Volume acts as an additional filter: when combined with chart formations like flags or pennants, it confirms whether buyers and sellers genuinely support the move. For example:
- Bullish Signals: A breakout from resistance accompanied by high volume indicates strong buying interest.
- Bearish Signals: A breakdown below support with increased selling activity suggests genuine downward momentum.
This synergy between price action and trade activity enhances decision-making accuracy and reduces exposure to false positives—a common pitfall in crypto markets characterized by rapid swings and speculative behavior.
Key Benefits of Using Volume Confirmation
1. Validating Market Sentiment
High volumes during upward moves reflect robust buying pressure; similarly, elevated selling volumes during declines signal strong bearish sentiment. Recognizing these cues helps traders gauge overall market mood more precisely than relying solely on price charts.
2. Improving Pattern Reliability
Patterns confirmed with significant trade volumes tend to be more trustworthy than those formed on thin liquidity conditions. For instance:
- An ascending triangle with rising volume before breakout indicates genuine accumulation.
- Conversely, if breakout occurs on low volume amid sideways movement, caution is warranted as it might be a false signal.
3. Enhancing Risk Management Strategies
By observing how volumes behave around key levels (support/resistance), traders can better assess entry points and set stop-loss orders accordingly—reducing potential losses from sudden reversals caused by manipulated trades or fakeouts prevalent in unregulated crypto markets.
4. Detecting Market Manipulation
Large players (whales) often attempt to manipulate prices through coordinated trades that generate artificial spikes in volume without real underlying demand—a tactic known as "pump-and-dump." Recognizing discrepancies between price action and abnormal surges in traded volumes allows experienced traders to avoid falling victim to such schemes.
Recent Trends Impacting Volume Confirmation Practices
The last few years have seen notable developments affecting how traders utilize volume confirmation:
Market Volatility: The rise of DeFi projects and NFTs has increased overall trading activity but also introduced higher volatility levels—making careful analysis crucial.
Regulatory Changes: Authorities like the U.S SEC have issued guidelines impacting transparency standards across exchanges; this influences how accurately traded volumes reflect true market interest.
Technological Advancements: Modern platforms now offer real-time analytics powered by AI algorithms capable of detecting suspicious activities related to abnormal trade volumes.
Community Insights: Social media buzz often correlates with spikes in trading activity; monitoring community sentiment alongside technical signals adds depth for validating patterns through social listening tools integrated into many platforms today.
Risks Associated With Relying Solely on Volume Data
While incorporating volume confirmation improves prediction reliability significantly, over-reliance carries risks:
False Signals Due To Manipulation: Large-volume trades orchestrated by whales can create misleading impressions about true supply/demand dynamics.
Market Noise During High Volatility Periods: Rapid swings may distort typical relationships between price movement and traded volumes.
Limited Contextual Information: Sole focus on one indicator ignores other critical factors like macroeconomic news events influencing trader behavior globally.
To mitigate these risks effectively:
- Use multiple indicators (e.g., RSI , Bollinger Bands) alongside volume data
- Confirm signals across different timeframes
- Stay updated about regulatory changes affecting exchange transparency
Educational resources—including webinars & courses—are increasingly available for traders seeking mastery over combining various analytical tools responsibly.
How Traders Can Effectively Use Volume Confirmation Today
For optimal results:
Look for confluence — situations where multiple indicators align—for example:
- Price breaking resistance with increasing high-volume candles
- Divergence where declining prices occur despite rising volumes indicating potential exhaustion
Pay attention during volatile periods: heightened caution ensures you don’t misinterpret fakeouts caused by manipulative tactics
3.. Incorporate community insights: social media trends often precede large moves; combining this qualitative data with quantitative analysis enhances decision-making
4.. Regularly review recent market trends: understanding broader shifts helps contextualize individual pattern validity
In summary, integrating volume confirmation into your crypto trading strategy isn’t just advisable—it’s essential for validating chart patterns' authenticity amidst unpredictable markets filled with noise & manipulation risks . By paying close attention not only to what prices are doing but also how actively they’re being traded at each step along the way , you position yourself better against false signals while gaining deeper insights into genuine shifts within dynamic digital asset markets .


Lo
2025-05-09 06:20
Why is volume confirmation critical for pattern validity?
Why is Volume Confirmation Critical for Pattern Validity in Crypto Trading?
In the fast-paced world of cryptocurrency trading, understanding market signals is essential for making informed decisions. Among these signals, chart patterns such as head and shoulders, triangles, or double bottoms are widely used by traders to predict future price movements. However, not all patterns are equally reliable on their own. This is where volume confirmation plays a vital role—adding a layer of validation that can significantly improve the accuracy of pattern-based predictions.
What Is Volume Confirmation in Cryptocurrency Trading?
Volume confirmation involves analyzing trading volume alongside price movements to verify the legitimacy of technical patterns. When a pattern forms on a chart—say, an ascending triangle—the accompanying trading volume provides insight into whether this pattern reflects genuine market interest or if it’s potentially misleading. High trading volume during the formation or breakout of a pattern suggests strong participation and conviction among traders, increasing confidence that the trend will continue in the predicted direction.
Conversely, low volume may indicate lack of interest or even manipulation—such as wash trading or fakeouts—that can produce false signals. Therefore, integrating volume data helps traders distinguish between authentic trends and deceptive moves driven by short-term speculation or market manipulation.
The Role of Volume Confirmation in Technical Analysis
Technical analysis relies heavily on identifying consistent patterns within historical price data to forecast future movements. However, without considering trade activity levels (volume), these patterns can sometimes be unreliable indicators due to false breakouts or reversals.
Volume acts as an additional filter: when combined with chart formations like flags or pennants, it confirms whether buyers and sellers genuinely support the move. For example:
- Bullish Signals: A breakout from resistance accompanied by high volume indicates strong buying interest.
- Bearish Signals: A breakdown below support with increased selling activity suggests genuine downward momentum.
This synergy between price action and trade activity enhances decision-making accuracy and reduces exposure to false positives—a common pitfall in crypto markets characterized by rapid swings and speculative behavior.
Key Benefits of Using Volume Confirmation
1. Validating Market Sentiment
High volumes during upward moves reflect robust buying pressure; similarly, elevated selling volumes during declines signal strong bearish sentiment. Recognizing these cues helps traders gauge overall market mood more precisely than relying solely on price charts.
2. Improving Pattern Reliability
Patterns confirmed with significant trade volumes tend to be more trustworthy than those formed on thin liquidity conditions. For instance:
- An ascending triangle with rising volume before breakout indicates genuine accumulation.
- Conversely, if breakout occurs on low volume amid sideways movement, caution is warranted as it might be a false signal.
3. Enhancing Risk Management Strategies
By observing how volumes behave around key levels (support/resistance), traders can better assess entry points and set stop-loss orders accordingly—reducing potential losses from sudden reversals caused by manipulated trades or fakeouts prevalent in unregulated crypto markets.
4. Detecting Market Manipulation
Large players (whales) often attempt to manipulate prices through coordinated trades that generate artificial spikes in volume without real underlying demand—a tactic known as "pump-and-dump." Recognizing discrepancies between price action and abnormal surges in traded volumes allows experienced traders to avoid falling victim to such schemes.
Recent Trends Impacting Volume Confirmation Practices
The last few years have seen notable developments affecting how traders utilize volume confirmation:
Market Volatility: The rise of DeFi projects and NFTs has increased overall trading activity but also introduced higher volatility levels—making careful analysis crucial.
Regulatory Changes: Authorities like the U.S SEC have issued guidelines impacting transparency standards across exchanges; this influences how accurately traded volumes reflect true market interest.
Technological Advancements: Modern platforms now offer real-time analytics powered by AI algorithms capable of detecting suspicious activities related to abnormal trade volumes.
Community Insights: Social media buzz often correlates with spikes in trading activity; monitoring community sentiment alongside technical signals adds depth for validating patterns through social listening tools integrated into many platforms today.
Risks Associated With Relying Solely on Volume Data
While incorporating volume confirmation improves prediction reliability significantly, over-reliance carries risks:
False Signals Due To Manipulation: Large-volume trades orchestrated by whales can create misleading impressions about true supply/demand dynamics.
Market Noise During High Volatility Periods: Rapid swings may distort typical relationships between price movement and traded volumes.
Limited Contextual Information: Sole focus on one indicator ignores other critical factors like macroeconomic news events influencing trader behavior globally.
To mitigate these risks effectively:
- Use multiple indicators (e.g., RSI , Bollinger Bands) alongside volume data
- Confirm signals across different timeframes
- Stay updated about regulatory changes affecting exchange transparency
Educational resources—including webinars & courses—are increasingly available for traders seeking mastery over combining various analytical tools responsibly.
How Traders Can Effectively Use Volume Confirmation Today
For optimal results:
Look for confluence — situations where multiple indicators align—for example:
- Price breaking resistance with increasing high-volume candles
- Divergence where declining prices occur despite rising volumes indicating potential exhaustion
Pay attention during volatile periods: heightened caution ensures you don’t misinterpret fakeouts caused by manipulative tactics
3.. Incorporate community insights: social media trends often precede large moves; combining this qualitative data with quantitative analysis enhances decision-making
4.. Regularly review recent market trends: understanding broader shifts helps contextualize individual pattern validity
In summary, integrating volume confirmation into your crypto trading strategy isn’t just advisable—it’s essential for validating chart patterns' authenticity amidst unpredictable markets filled with noise & manipulation risks . By paying close attention not only to what prices are doing but also how actively they’re being traded at each step along the way , you position yourself better against false signals while gaining deeper insights into genuine shifts within dynamic digital asset markets .
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
When Is a Rounding Bottom Reliable as a Reversal Signal?
Understanding the Rounding Bottom Pattern in Technical Analysis
A rounding bottom is a distinctive chart pattern that signals potential trend reversals from bearish to bullish. It appears as a smooth, rounded shape on price charts, reflecting gradual shifts in market sentiment. Traders and investors often look for this pattern because it suggests that selling pressure is waning and buying interest is beginning to take over. Recognizing when this pattern becomes reliable can significantly improve decision-making, especially during uncertain or volatile market conditions.
The Formation of the Rounding Bottom: Key Characteristics
The formation of a rounding bottom involves several stages:
- Initial Decline: The price moves downward with lower lows and lower highs, indicating persistent selling pressure.
- Gradual Transition: As the decline slows down, higher lows start forming while the highs remain relatively stable or slightly decrease.
- Rounded Shape Emerges: Over time, these movements create a smooth curve resembling an arc or bowl.
- Breakout Point: The pattern confirms when prices break above the neckline—the resistance level drawn across the highest point of the rounded shape—signaling potential reversal.
This gradual transition from downtrend to uptrend makes it distinct from abrupt reversal patterns like head-and-shoulders or double bottoms.
Factors That Influence Reliability of Rounding Bottoms
While technically appealing, not all rounding bottoms are equally reliable signals. Their effectiveness depends on multiple factors:
Volume Confirmation
A key indicator supporting reliability is increased trading volume during breakout confirmation. Strong volume indicates robust buying interest and reduces chances of false signals.Market Context
Broader market conditions heavily influence pattern validity. For instance:- In bullish overall markets, rounding bottoms tend to be more dependable.
- During sustained bear markets or economic downturns, even confirmed patterns may fail.
Additional Technical Indicators
Combining other tools enhances confidence:- Moving averages (e.g., 50-day or 200-day) crossing upward
- Relative Strength Index (RSI) showing oversold conditions turning bullish
- MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) signaling momentum shifts
Pattern Duration
Longer formation periods—often several weeks to months—tend to produce more reliable signals than quick formations which might be false alarms.Market Sentiment & News Flow
Positive news catalysts such as earnings beats, macroeconomic improvements, or policy changes can reinforce breakout reliability following a rounding bottom.
When Is a Rounding Bottom Most Reliable?
The reliability increases under specific circumstances:
- When accompanied by high trading volume at breakout points; volume spikes validate strong buyer participation.
- If confirmed by multiple technical indicators aligning in bullish territory; for example, RSI rising above 30–40 after being oversold supports trend reversal.
- During periods where fundamental analysis aligns with technical signals—for instance, improving company fundamentals in stock markets or positive macroeconomic data in cryptocurrencies—adding weight to the pattern's credibility.
- When formed over an extended period (generally several months), allowing traders ample time for confirmation rather than rushing into trades based on short-term fluctuations.
Conversely, if these conditions are absent—such as low-volume breakouts or conflicting indicators—the likelihood of false positives rises significantly.
Recognizing False Signals and Limitations
Despite its usefulness, traders should remain cautious about relying solely on the rounding bottom pattern due to potential pitfalls:
- False Breakouts: Prices may temporarily breach resistance levels but quickly reverse back downward if underlying fundamentals haven't improved.
- Market Sentiment Shifts: Negative news events can invalidate technical setups even after initial confirmation.
- Overfitting Patterns: Not every rounded shape signifies genuine trend change; some may be mere consolidations mistaken for reversals.
Therefore, integrating risk management strategies like stop-loss orders and position sizing becomes essential when trading based on this pattern.
Historical Examples Demonstrating Reliability
Historical instances underscore when rounding bottoms proved effective:
2008 Financial Crisis Recovery
Many stocks exhibited rounded bottoms before rebounding amid economic recovery signs post-crisis—for example,companies like General Electric showed clear arc-shaped recoveries supported by increasing volumes and improving fundamentals.2020 COVID Market Rebound
During pandemic-induced downturns followed by recovery phases,stocks such as Microsoft and Amazon formed recognizable rounded bottoms before significant upward moves fueled by stimulus measures and technological demand surges.Cryptocurrency Market Trends
Bitcoin’s 2018 downturn was followed by prolonged consolidation forming a rounded bottom—a precursor to its rally in late 2019 driven by institutional interest and macroeconomic factors influencing crypto adoption rates.
How Traders Can Maximize Reliability When Using Rounding Bottoms
To enhance accuracy when applying this pattern within their trading strategies:
- Combine multiple technical tools rather than relying solely on visual recognition of shapes.
- Confirm breakouts with high-volume candles indicating strong participation from buyers.
- Monitor broader market trends alongside specific asset behavior for contextual validation.4.. Be patient; wait for clear confirmations over extended periods rather than impulsively entering trades at early signs.
Final Thoughts: Assessing Pattern Validity Before Acting
While recognizing that no single indicator guarantees success remains crucial — especially given market complexities — understanding when a rounding bottom offers reliable reversal signals empowers traders with better judgment calls.. By considering factors such as volume dynamics , multi-indicator alignment , duration ,and overall sentiment , investors can improve their chances of capitalizing on genuine trend reversals while minimizing risks associated with false positives.


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-09 06:15
When is a rounding bottom reliable as a reversal signal?
When Is a Rounding Bottom Reliable as a Reversal Signal?
Understanding the Rounding Bottom Pattern in Technical Analysis
A rounding bottom is a distinctive chart pattern that signals potential trend reversals from bearish to bullish. It appears as a smooth, rounded shape on price charts, reflecting gradual shifts in market sentiment. Traders and investors often look for this pattern because it suggests that selling pressure is waning and buying interest is beginning to take over. Recognizing when this pattern becomes reliable can significantly improve decision-making, especially during uncertain or volatile market conditions.
The Formation of the Rounding Bottom: Key Characteristics
The formation of a rounding bottom involves several stages:
- Initial Decline: The price moves downward with lower lows and lower highs, indicating persistent selling pressure.
- Gradual Transition: As the decline slows down, higher lows start forming while the highs remain relatively stable or slightly decrease.
- Rounded Shape Emerges: Over time, these movements create a smooth curve resembling an arc or bowl.
- Breakout Point: The pattern confirms when prices break above the neckline—the resistance level drawn across the highest point of the rounded shape—signaling potential reversal.
This gradual transition from downtrend to uptrend makes it distinct from abrupt reversal patterns like head-and-shoulders or double bottoms.
Factors That Influence Reliability of Rounding Bottoms
While technically appealing, not all rounding bottoms are equally reliable signals. Their effectiveness depends on multiple factors:
Volume Confirmation
A key indicator supporting reliability is increased trading volume during breakout confirmation. Strong volume indicates robust buying interest and reduces chances of false signals.Market Context
Broader market conditions heavily influence pattern validity. For instance:- In bullish overall markets, rounding bottoms tend to be more dependable.
- During sustained bear markets or economic downturns, even confirmed patterns may fail.
Additional Technical Indicators
Combining other tools enhances confidence:- Moving averages (e.g., 50-day or 200-day) crossing upward
- Relative Strength Index (RSI) showing oversold conditions turning bullish
- MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) signaling momentum shifts
Pattern Duration
Longer formation periods—often several weeks to months—tend to produce more reliable signals than quick formations which might be false alarms.Market Sentiment & News Flow
Positive news catalysts such as earnings beats, macroeconomic improvements, or policy changes can reinforce breakout reliability following a rounding bottom.
When Is a Rounding Bottom Most Reliable?
The reliability increases under specific circumstances:
- When accompanied by high trading volume at breakout points; volume spikes validate strong buyer participation.
- If confirmed by multiple technical indicators aligning in bullish territory; for example, RSI rising above 30–40 after being oversold supports trend reversal.
- During periods where fundamental analysis aligns with technical signals—for instance, improving company fundamentals in stock markets or positive macroeconomic data in cryptocurrencies—adding weight to the pattern's credibility.
- When formed over an extended period (generally several months), allowing traders ample time for confirmation rather than rushing into trades based on short-term fluctuations.
Conversely, if these conditions are absent—such as low-volume breakouts or conflicting indicators—the likelihood of false positives rises significantly.
Recognizing False Signals and Limitations
Despite its usefulness, traders should remain cautious about relying solely on the rounding bottom pattern due to potential pitfalls:
- False Breakouts: Prices may temporarily breach resistance levels but quickly reverse back downward if underlying fundamentals haven't improved.
- Market Sentiment Shifts: Negative news events can invalidate technical setups even after initial confirmation.
- Overfitting Patterns: Not every rounded shape signifies genuine trend change; some may be mere consolidations mistaken for reversals.
Therefore, integrating risk management strategies like stop-loss orders and position sizing becomes essential when trading based on this pattern.
Historical Examples Demonstrating Reliability
Historical instances underscore when rounding bottoms proved effective:
2008 Financial Crisis Recovery
Many stocks exhibited rounded bottoms before rebounding amid economic recovery signs post-crisis—for example,companies like General Electric showed clear arc-shaped recoveries supported by increasing volumes and improving fundamentals.2020 COVID Market Rebound
During pandemic-induced downturns followed by recovery phases,stocks such as Microsoft and Amazon formed recognizable rounded bottoms before significant upward moves fueled by stimulus measures and technological demand surges.Cryptocurrency Market Trends
Bitcoin’s 2018 downturn was followed by prolonged consolidation forming a rounded bottom—a precursor to its rally in late 2019 driven by institutional interest and macroeconomic factors influencing crypto adoption rates.
How Traders Can Maximize Reliability When Using Rounding Bottoms
To enhance accuracy when applying this pattern within their trading strategies:
- Combine multiple technical tools rather than relying solely on visual recognition of shapes.
- Confirm breakouts with high-volume candles indicating strong participation from buyers.
- Monitor broader market trends alongside specific asset behavior for contextual validation.4.. Be patient; wait for clear confirmations over extended periods rather than impulsively entering trades at early signs.
Final Thoughts: Assessing Pattern Validity Before Acting
While recognizing that no single indicator guarantees success remains crucial — especially given market complexities — understanding when a rounding bottom offers reliable reversal signals empowers traders with better judgment calls.. By considering factors such as volume dynamics , multi-indicator alignment , duration ,and overall sentiment , investors can improve their chances of capitalizing on genuine trend reversals while minimizing risks associated with false positives.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
🔹Trading Time: August 6, 2025, 07:00 (UTC)
🪧More: https://bit.ly/45k4icb



JuCoin Community
2025-08-06 05:14
JuCoin to List PROVE/USDT Trading Pair on August 6, 2025
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
📅 August 4 2025
🎉 Stay updated with the latest crypto market trends!
👉 Trade on:https://bit.ly/3DFYq30
👉 X:https://twitter.com/Jucoinex
👉 APP download: https://www.jucoin.com/en/community-downloads
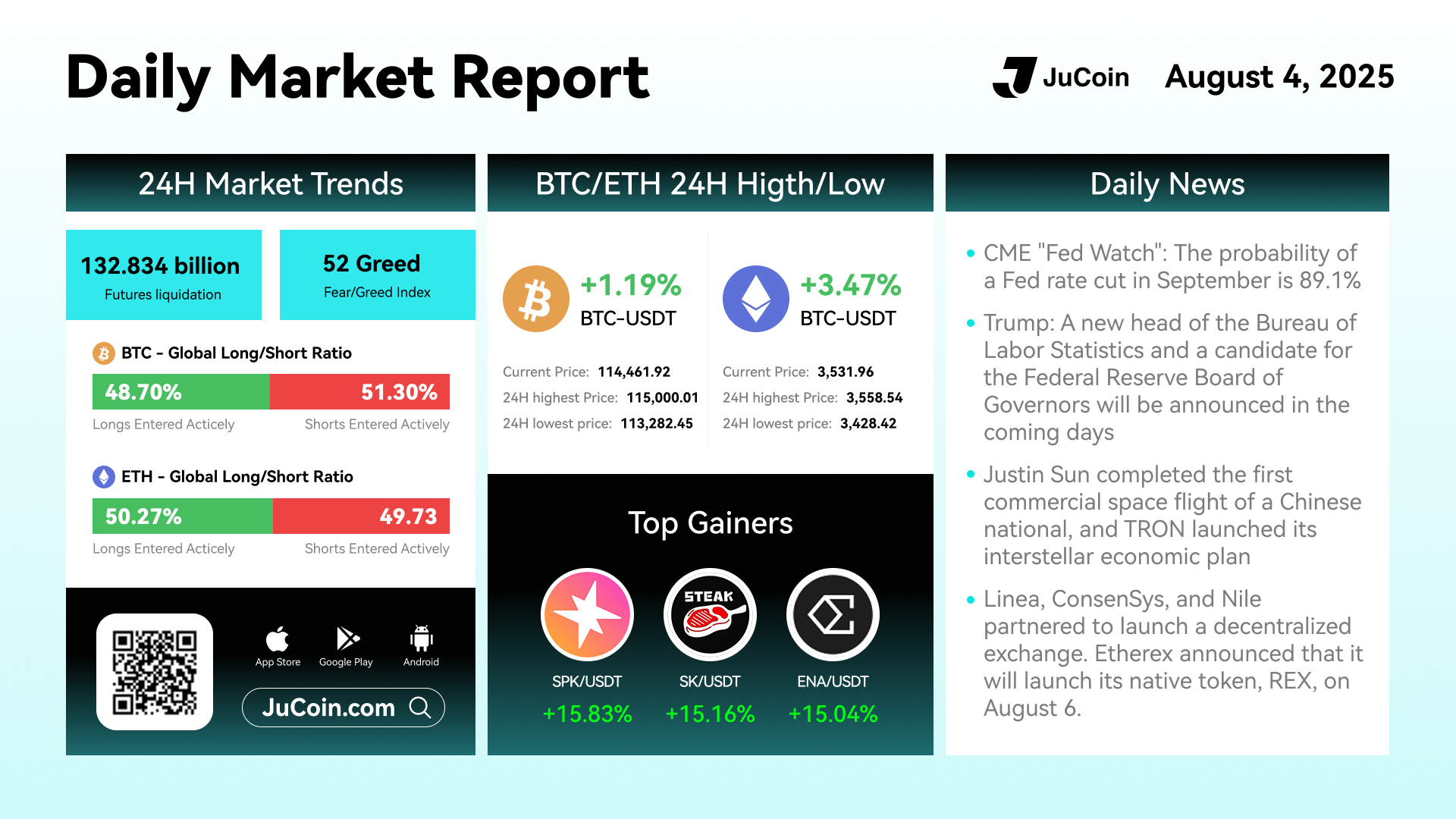


JuCoin Community
2025-08-04 04:34
🚀 #JuCoin Daily Market Report
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
👌JuCoin will list the RA/USDT trading pair on Aug. 4, 2025
🔷Deposit & Withdrawal: 10:00 (UTC) on Aug. 3, 2025
🔷Trading: 15:00 (UTC) on Aug. 4, 2025
👉More:https://bit.ly/4oerW2p



JuCoin Community
2025-08-04 03:43
📢New Listing
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
TA used to be charts, indicators, and KD lines 🎯 Now it’s just tweets, vibes, and memes 🫥 Accurate enough, right?
Check out our YouTube Channel 👉
#TechnicalAnalysis #MemeTrading #CryptoTA


JuCoin Media
2025-08-01 11:33
Technical Analysis Cryptocurrency 📊 | The Only Chart That Matters
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Me in 2050 telling my grandkids: “Bitcoin was only 100k back then!” 😌 They’ll never believe how good we had it 🪙 The golden age of crypto
Check out our YouTube Channel 👉
#BitcoinMemories #FutureInvestorTales #CryptoLegend


JuCoin Media
2025-08-01 11:29
My Bitcoin Investment Story They Won’t Believe in 2050 🕰️
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Bitcoin Profit — every bull run cycle hits the same 😅 "This is my last year broke..." Meanwhile the house is collapsing behind you 🫠 Hopium never dies, even when profits do 🙃
Check out our YouTube Channel 👉
#BullRunCycle #BitcoinProfit #HopiumLives


JuCoin Media
2025-08-01 11:13
Hoping for That Bitcoin Profit Every Bull Run Cycle 📈
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
USELESS leverages the motto "useless is fun" to create a unique meme-driven ecosystem combining entertainment with real decentralized governance. Since launching in 2021, it has attracted tens of thousands of active users and secured liquidity across multiple DEX platforms.
💰 Core Features:
-
1 billion total supply with ~850 million currently circulating
Innovative burn-and-mint dual adjustment mechanism
U-DAO on-chain governance system for holder proposals and voting
Live on PancakeSwap & Uniswap with $5M+ daily trading volumes
🔥 Dynamic Tokenomics:
-
Quarterly Burns: Community votes to buy back and burn 1-5% of circulating supply
Monthly Mints: 0.5-2% strategic minting for community rewards and development
Liquidity Support: 10% reserved for DEX liquidity mining rewards
Governance Staking: Stake tokens in U-DAO for voting rights and rewards
🎯 Participation Strategy: 1️⃣ Stake 10,000+ USELESS in U-DAO to gain proposal and voting rights 2️⃣ Provide liquidity on PancakeSwap/Uniswap for LP rewards and fee sharing 3️⃣ Join monthly "Burn Parties" and meme contests for airdrops 4️⃣ Engage with NFT and DeFi partnership opportunities
🏆 Community Highlights:
-
"Useless Fund" proposal approved by 65% of holders
Regular meme contests and community-driven content creation
Strategic partnerships with NFT projects and DeFi protocols
Strong community engagement and governance participation
💡 Investment Thesis: USELESS stands out in the meme token space by combining genuine entertainment value with robust governance mechanisms. The dynamic supply adjustment model and active community governance create sustainable value beyond typical meme token speculation.
Read the complete in-depth analysis: 👇
https://blog.jucoin.com/useless-coin-project-analysis/?utm_source=blog
#USELESS #MemeToken #DecentralizedGovernance #DeFi #CommunityDriven #PancakeSwap #Uniswap #BurnMechanism #U-DAO #JuCoin #Blockchain #Tokenomics #LiquidityMining #NFT #Web3 #Governance



JU Blog
2025-08-01 08:57
🎭 USELESS: The "Most Useless" Meme Token with Serious Governance Power!
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
