Popular Posts
Regulatory Hurdles in the DeFi Sector: What You Need to Know
Understanding the Regulatory Landscape for DeFi
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) has rapidly transformed the financial industry by offering blockchain-based services such as lending, borrowing, and trading without traditional intermediaries like banks. This innovative approach has attracted a diverse range of users—from individual crypto enthusiasts to large institutional investors—seeking more open and permissionless financial solutions. However, despite its growth and potential, DeFi faces significant regulatory challenges that could impact its future development.
One of the primary issues is the lack of clear regulations tailored specifically for decentralized systems. Existing financial laws are designed around centralized institutions and often do not account for the unique features of DeFi platforms—such as pseudonymous transactions, smart contracts, and autonomous protocols. This regulatory ambiguity creates uncertainty among developers, investors, and users alike because it’s unclear what compliance entails or how existing rules apply.
Furthermore, regulators worldwide are grappling with how to oversee these decentralized ecosystems effectively. Without a centralized authority or identifiable entities behind many platforms, enforcing compliance becomes complex. As a result, many jurisdictions have yet to establish comprehensive frameworks that address DeFi’s nuances while balancing innovation with consumer protection.
The Challenges in Consumer Protection within DeFi
Consumer protection remains one of the most pressing concerns in the DeFi space. Unlike traditional finance where customer funds are safeguarded through insurance schemes or regulatory oversight (like FDIC insurance in banking), most DeFi platforms lack formal mechanisms to protect users from losses due to hacks, bugs in smart contracts, or malicious actors.
This absence exposes participants—especially less experienced users—to significant risks of financial loss. For example, vulnerabilities within code can be exploited by hackers leading to substantial thefts from liquidity pools or user wallets. Additionally, since many platforms operate without KYC (Know Your Customer) procedures or AML (Anti-Money Laundering) checks due to their decentralized nature—and often across multiple jurisdictions—users’ identities remain pseudonymous at best.
The result is a landscape where consumers may find it difficult to seek recourse if something goes wrong—a stark contrast with regulated traditional finance environments that offer dispute resolution mechanisms and legal protections. As adoption grows among mainstream audiences who may not fully understand these risks yet participate actively in DeFi markets; this gap underscores an urgent need for better safeguards.
Addressing AML/KYC Challenges in Decentralized Platforms
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know-Your-Customer (KYC) regulations aim to prevent illicit activities such as money laundering and terrorist financing by verifying user identities before allowing access to financial services. However, implementing effective AML/KYC measures on fully decentralized platforms presents inherent difficulties because these systems prioritize privacy and pseudonymity.
Many DeFi projects struggle with striking a balance between maintaining user privacy—a core principle—and complying with evolving global standards on transparency and accountability. Some industry players attempt self-regulation by adopting optional KYC procedures or integrating third-party verification tools; however, these efforts often fall short of comprehensive enforcement across all protocols.
Without robust AML/KYC controls—or at least some form of transaction monitoring—the risk persists that illicit actors could exploit de-centralized pools for illegal activities like money laundering or tax evasion—which attracts increased scrutiny from regulators worldwide seeking stricter oversight measures.
Market Manipulation Risks: Volatility Meets Decentralization
Market manipulation remains another critical concern within the unregulated environment characteristic of many DeFI markets. The absence of central authorities means price discovery can be easily influenced through practices such as wash trading—or artificially inflating token prices via coordinated actions among traders—leading to heightened volatility.
Such manipulation undermines trust among participants who rely on transparent market signals when making investment decisions; it also poses systemic risks if large-scale manipulations trigger cascading liquidations across interconnected protocols causing broader instability within crypto markets overall.
While some projects implement safeguards like oracle price feeds designed for accuracy; ongoing vigilance is necessary because malicious actors continuously develop new tactics aimed at exploiting protocol vulnerabilities—all emphasizing why regulation must evolve alongside technological advancements rather than lag behind them.
Taxation Uncertainty Hampers Adoption
Tax treatment remains one of the murkiest areas affecting both individual users and service providers operating within DeFI ecosystems globally. Different countries have varying approaches toward taxing cryptocurrencies—including capital gains taxes on trades or income taxes on earnings generated through staking—and applying these rules consistently becomes complicated given cross-border transactions facilitated by blockchain technology.
This ambiguity discourages participation from mainstream investors wary about potential tax liabilities they might face unexpectedly when engaging with complex derivatives or yield farming strategies prevalent in Defi environments.
Moreover: unclear taxation policies hinder compliance efforts by companies trying to build compliant products while navigating multiple jurisdictions' legal frameworks simultaneously—which can slow down innovation-driven growth initiatives essential for sector expansion.
Recent Regulatory Developments Shaping Future Directions
In recent months there has been increased activity among regulators recognizing both opportunities & risks associated with Defi's rapid evolution:
SEC Roundtable Discussions: In April 2025 , U.S.-based Securities & Exchange Commission held its third crypto-focused roundtable where Chair Paul Atkins emphasized clearer guidelines are needed for market participants involved in digital assets—including those operating within Defi spaces—to foster investor confidence while preventing misuse[1].
Global Regulatory Actions: Agencies like CFTC have issued guidance concerning derivatives trading on blockchain networks aiming at establishing oversight standards applicable across different jurisdictions—even though uniform enforcement remains challenging due largely differences between national laws[2].
Industry-Led Initiatives: Several prominent players have begun adopting self-regulatory measures such as implementing voluntary KYC/AML protocols & transparency disclosures — steps intended not only improve trust but also demonstrate proactive engagement towards aligning industry practices with emerging legal expectations[3].
Balancing Innovation With Regulation: The Path Forward
As regulators increasingly scrutinize Defi’s rapid growth trajectory—with some fearing overreach potentially stifling innovation—the sector faces an ongoing challenge: How do you craft effective regulation without hindering technological progress? Striking this balance requires collaborative efforts involving policymakers,s developers,and community stakeholders working together towards adaptable frameworks rooted in transparency,responsibility,and consumer protection principles .
It’s vital that future regulations recognize decentralization's unique characteristics while providing clear guidance that fosters responsible innovation rather than suppresses it.
By proactively addressing issues related to consumer safety,KYC/AML compliance,and market integrity,the industry can build resilient systems capable of sustainable growth amid evolving legal landscapes.
Staying informed about policy developments will be crucial—for investors,developers,and everyday users alike—as they navigate this dynamic ecosystem poised at a crossroads between freedom & regulation.
References
1. SEC Crypto Roundtable Highlights Need For Clearer Regulations - [Source]
2. CFTC Guidelines On Blockchain Derivatives Trading - [Source]
3. Industry Self-Regulation Initiatives In Crypto Space - [Source]


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-22 23:14
What regulatory hurdles must the DeFi sector overcome?
Regulatory Hurdles in the DeFi Sector: What You Need to Know
Understanding the Regulatory Landscape for DeFi
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) has rapidly transformed the financial industry by offering blockchain-based services such as lending, borrowing, and trading without traditional intermediaries like banks. This innovative approach has attracted a diverse range of users—from individual crypto enthusiasts to large institutional investors—seeking more open and permissionless financial solutions. However, despite its growth and potential, DeFi faces significant regulatory challenges that could impact its future development.
One of the primary issues is the lack of clear regulations tailored specifically for decentralized systems. Existing financial laws are designed around centralized institutions and often do not account for the unique features of DeFi platforms—such as pseudonymous transactions, smart contracts, and autonomous protocols. This regulatory ambiguity creates uncertainty among developers, investors, and users alike because it’s unclear what compliance entails or how existing rules apply.
Furthermore, regulators worldwide are grappling with how to oversee these decentralized ecosystems effectively. Without a centralized authority or identifiable entities behind many platforms, enforcing compliance becomes complex. As a result, many jurisdictions have yet to establish comprehensive frameworks that address DeFi’s nuances while balancing innovation with consumer protection.
The Challenges in Consumer Protection within DeFi
Consumer protection remains one of the most pressing concerns in the DeFi space. Unlike traditional finance where customer funds are safeguarded through insurance schemes or regulatory oversight (like FDIC insurance in banking), most DeFi platforms lack formal mechanisms to protect users from losses due to hacks, bugs in smart contracts, or malicious actors.
This absence exposes participants—especially less experienced users—to significant risks of financial loss. For example, vulnerabilities within code can be exploited by hackers leading to substantial thefts from liquidity pools or user wallets. Additionally, since many platforms operate without KYC (Know Your Customer) procedures or AML (Anti-Money Laundering) checks due to their decentralized nature—and often across multiple jurisdictions—users’ identities remain pseudonymous at best.
The result is a landscape where consumers may find it difficult to seek recourse if something goes wrong—a stark contrast with regulated traditional finance environments that offer dispute resolution mechanisms and legal protections. As adoption grows among mainstream audiences who may not fully understand these risks yet participate actively in DeFi markets; this gap underscores an urgent need for better safeguards.
Addressing AML/KYC Challenges in Decentralized Platforms
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know-Your-Customer (KYC) regulations aim to prevent illicit activities such as money laundering and terrorist financing by verifying user identities before allowing access to financial services. However, implementing effective AML/KYC measures on fully decentralized platforms presents inherent difficulties because these systems prioritize privacy and pseudonymity.
Many DeFi projects struggle with striking a balance between maintaining user privacy—a core principle—and complying with evolving global standards on transparency and accountability. Some industry players attempt self-regulation by adopting optional KYC procedures or integrating third-party verification tools; however, these efforts often fall short of comprehensive enforcement across all protocols.
Without robust AML/KYC controls—or at least some form of transaction monitoring—the risk persists that illicit actors could exploit de-centralized pools for illegal activities like money laundering or tax evasion—which attracts increased scrutiny from regulators worldwide seeking stricter oversight measures.
Market Manipulation Risks: Volatility Meets Decentralization
Market manipulation remains another critical concern within the unregulated environment characteristic of many DeFI markets. The absence of central authorities means price discovery can be easily influenced through practices such as wash trading—or artificially inflating token prices via coordinated actions among traders—leading to heightened volatility.
Such manipulation undermines trust among participants who rely on transparent market signals when making investment decisions; it also poses systemic risks if large-scale manipulations trigger cascading liquidations across interconnected protocols causing broader instability within crypto markets overall.
While some projects implement safeguards like oracle price feeds designed for accuracy; ongoing vigilance is necessary because malicious actors continuously develop new tactics aimed at exploiting protocol vulnerabilities—all emphasizing why regulation must evolve alongside technological advancements rather than lag behind them.
Taxation Uncertainty Hampers Adoption
Tax treatment remains one of the murkiest areas affecting both individual users and service providers operating within DeFI ecosystems globally. Different countries have varying approaches toward taxing cryptocurrencies—including capital gains taxes on trades or income taxes on earnings generated through staking—and applying these rules consistently becomes complicated given cross-border transactions facilitated by blockchain technology.
This ambiguity discourages participation from mainstream investors wary about potential tax liabilities they might face unexpectedly when engaging with complex derivatives or yield farming strategies prevalent in Defi environments.
Moreover: unclear taxation policies hinder compliance efforts by companies trying to build compliant products while navigating multiple jurisdictions' legal frameworks simultaneously—which can slow down innovation-driven growth initiatives essential for sector expansion.
Recent Regulatory Developments Shaping Future Directions
In recent months there has been increased activity among regulators recognizing both opportunities & risks associated with Defi's rapid evolution:
SEC Roundtable Discussions: In April 2025 , U.S.-based Securities & Exchange Commission held its third crypto-focused roundtable where Chair Paul Atkins emphasized clearer guidelines are needed for market participants involved in digital assets—including those operating within Defi spaces—to foster investor confidence while preventing misuse[1].
Global Regulatory Actions: Agencies like CFTC have issued guidance concerning derivatives trading on blockchain networks aiming at establishing oversight standards applicable across different jurisdictions—even though uniform enforcement remains challenging due largely differences between national laws[2].
Industry-Led Initiatives: Several prominent players have begun adopting self-regulatory measures such as implementing voluntary KYC/AML protocols & transparency disclosures — steps intended not only improve trust but also demonstrate proactive engagement towards aligning industry practices with emerging legal expectations[3].
Balancing Innovation With Regulation: The Path Forward
As regulators increasingly scrutinize Defi’s rapid growth trajectory—with some fearing overreach potentially stifling innovation—the sector faces an ongoing challenge: How do you craft effective regulation without hindering technological progress? Striking this balance requires collaborative efforts involving policymakers,s developers,and community stakeholders working together towards adaptable frameworks rooted in transparency,responsibility,and consumer protection principles .
It’s vital that future regulations recognize decentralization's unique characteristics while providing clear guidance that fosters responsible innovation rather than suppresses it.
By proactively addressing issues related to consumer safety,KYC/AML compliance,and market integrity,the industry can build resilient systems capable of sustainable growth amid evolving legal landscapes.
Staying informed about policy developments will be crucial—for investors,developers,and everyday users alike—as they navigate this dynamic ecosystem poised at a crossroads between freedom & regulation.
References
1. SEC Crypto Roundtable Highlights Need For Clearer Regulations - [Source]
2. CFTC Guidelines On Blockchain Derivatives Trading - [Source]
3. Industry Self-Regulation Initiatives In Crypto Space - [Source]
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is the Difference Between a Public Blockchain and a Private Blockchain?
Understanding the fundamental differences between public and private blockchains is essential for anyone interested in blockchain technology, whether for investment, development, or strategic planning. Both types of blockchains serve distinct purposes and are suited to different use cases based on their architecture, security features, and governance models.
Public Blockchains: Openness and Decentralization
Public blockchains are open-source networks that anyone can access and participate in without restrictions. They operate on a decentralized model where no single entity has control over the entire network. This decentralization ensures that transactions are transparent and tamper-proof because they are validated by consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS). Examples like Bitcoin and Ethereum exemplify this approach—allowing users worldwide to send transactions freely while maintaining high levels of security through collective validation.
One key advantage of public blockchains is their transparency; all transaction data is publicly visible on the ledger. This openness fosters trust among participants but also raises privacy concerns depending on the application. Additionally, because they leverage collective computational power across numerous nodes globally, public blockchains tend to be more resilient against attacks but may face scalability challenges due to network congestion.
However, operating openly means these networks often face regulatory scrutiny since their transparency can conflict with privacy regulations in certain jurisdictions. Despite this, public blockchains remain popular for cryptocurrencies due to their decentralization benefits—eliminating reliance on central authorities.
Private Blockchains: Control and Confidentiality
In contrast, private blockchains restrict access exclusively to authorized participants within an organization or consortium. These systems are typically used internally by companies such as Walmart or Maersk for supply chain management or inventory tracking purposes. The controlling entity maintains centralized authority over node participation and transaction validation processes.
This controlled environment allows organizations greater flexibility in customizing consensus mechanisms tailored specifically to their operational needs—such as faster transaction speeds or enhanced privacy controls—and limits exposure of sensitive data outside trusted parties. Consequently, private blockchain networks offer higher confidentiality compared to public counterparts but at some expense of decentralization.
While private chains provide increased control over data integrity within an organization’s ecosystem—a critical factor for enterprise adoption—they may also introduce risks related to central points of failure if not properly managed. Moreover, since access is restricted—and transparency limited—their use cases typically focus on internal operations rather than open financial ecosystems like cryptocurrencies.
Choosing Between Public vs Private Blockchains
The decision between deploying a public versus private blockchain hinges largely on specific project requirements:
- Use Case: For applications demanding full transparency—such as cryptocurrency transactions—a public blockchain makes sense.
- Security & Privacy: When sensitive information must be protected from external visibility—for example in supply chain management—a private blockchain offers better confidentiality.
- Control & Governance: Organizations seeking complete control over who participates prefer private chains; those favoring decentralization lean toward public options.
- Scalability & Performance: Private networks often deliver faster processing times due to fewer nodes involved but might struggle with scaling beyond organizational boundaries.
- Regulatory Environment: Public chains face more regulatory oversight; private chains can be designed with compliance considerations built-in from inception.
Recent Trends & Developments
Over recent years (2023–2025), adoption trends indicate increasing interest across industries in both types of blockchain solutions:
- Many organizations explore hybrid models combining elements from both worlds—using permissioned (private) layers atop open (public) frameworks—to balance transparency with control.
- Governments are providing clearer regulations around digital assets which influence how enterprises implement these technologies.
- The rise of enterprise-grade platforms emphasizes scalability improvements necessary for large-scale deployment while maintaining security standards expected by regulators.
- Concerns about security risks associated with centralized control have prompted investments into robust governance frameworks within private networks.
Potential Challenges Facing Both Types
Despite promising developments, several issues persist:
- Security vulnerabilities remain a concern especially if controlling entities fail adequately securing their infrastructure.
- Scalability limitations could hinder growth if network demands increase significantly without technological upgrades.
- Regulatory uncertainty continues around how different jurisdictions will treat various forms of blockchain activity—particularly regarding privacy laws like GDPR—which could impact future deployments.
Understanding these dynamics helps stakeholders make informed decisions aligned with organizational goals while navigating evolving legal landscapes effectively.
How Different Industries Use Public vs Private Blockchains
Various sectors leverage each type based on specific needs:
Financial Services: Often utilize public blockchains like Ethereum for decentralized finance applications due to transparency requirements but may adopt permissioned ledgers internally for compliance reasons.
Supply Chain Management: Companies such as Maersk deploy private blockchains that enable secure sharing among trusted partners without exposing sensitive commercial data publicly.
Healthcare: Uses hybrid approaches where patient records might be stored privately yet linked via secure protocols accessible only by authorized personnel under strict regulatory oversight.
Key Factors Influencing Blockchain Choice
When selecting between a public or private solution consider factors such as:
- Data Sensitivity
- Speed Requirements
- Regulatory Compliance4.. Degree Of Decentralization Needed5.. Cost Implications6.. Long-term Scalability Goals
Emerging Trends Shaping Future Adoption
Looking ahead into 2024–2025:
Hybrid models will become increasingly prevalent as organizations seek balanced solutions combining openness with controlled access.
Enhanced interoperability protocols will facilitate smoother integration between different types of ledgers across industries
Regulatory clarity will continue improving which encourages broader adoption beyond niche markets
By understanding these core distinctions alongside current trends—and aligning them with your strategic objectives—you can better navigate the complex landscape surrounding blockchain technology today.
Keywords:public vs private blockchain comparison,differences between decentralized vs permissioned ledger,blockchain technology applications,enterprise blockchain solutions,blockchain regulation updates


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-22 15:22
What is the difference between a public blockchain and a private blockchain?
What Is the Difference Between a Public Blockchain and a Private Blockchain?
Understanding the fundamental differences between public and private blockchains is essential for anyone interested in blockchain technology, whether for investment, development, or strategic planning. Both types of blockchains serve distinct purposes and are suited to different use cases based on their architecture, security features, and governance models.
Public Blockchains: Openness and Decentralization
Public blockchains are open-source networks that anyone can access and participate in without restrictions. They operate on a decentralized model where no single entity has control over the entire network. This decentralization ensures that transactions are transparent and tamper-proof because they are validated by consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS). Examples like Bitcoin and Ethereum exemplify this approach—allowing users worldwide to send transactions freely while maintaining high levels of security through collective validation.
One key advantage of public blockchains is their transparency; all transaction data is publicly visible on the ledger. This openness fosters trust among participants but also raises privacy concerns depending on the application. Additionally, because they leverage collective computational power across numerous nodes globally, public blockchains tend to be more resilient against attacks but may face scalability challenges due to network congestion.
However, operating openly means these networks often face regulatory scrutiny since their transparency can conflict with privacy regulations in certain jurisdictions. Despite this, public blockchains remain popular for cryptocurrencies due to their decentralization benefits—eliminating reliance on central authorities.
Private Blockchains: Control and Confidentiality
In contrast, private blockchains restrict access exclusively to authorized participants within an organization or consortium. These systems are typically used internally by companies such as Walmart or Maersk for supply chain management or inventory tracking purposes. The controlling entity maintains centralized authority over node participation and transaction validation processes.
This controlled environment allows organizations greater flexibility in customizing consensus mechanisms tailored specifically to their operational needs—such as faster transaction speeds or enhanced privacy controls—and limits exposure of sensitive data outside trusted parties. Consequently, private blockchain networks offer higher confidentiality compared to public counterparts but at some expense of decentralization.
While private chains provide increased control over data integrity within an organization’s ecosystem—a critical factor for enterprise adoption—they may also introduce risks related to central points of failure if not properly managed. Moreover, since access is restricted—and transparency limited—their use cases typically focus on internal operations rather than open financial ecosystems like cryptocurrencies.
Choosing Between Public vs Private Blockchains
The decision between deploying a public versus private blockchain hinges largely on specific project requirements:
- Use Case: For applications demanding full transparency—such as cryptocurrency transactions—a public blockchain makes sense.
- Security & Privacy: When sensitive information must be protected from external visibility—for example in supply chain management—a private blockchain offers better confidentiality.
- Control & Governance: Organizations seeking complete control over who participates prefer private chains; those favoring decentralization lean toward public options.
- Scalability & Performance: Private networks often deliver faster processing times due to fewer nodes involved but might struggle with scaling beyond organizational boundaries.
- Regulatory Environment: Public chains face more regulatory oversight; private chains can be designed with compliance considerations built-in from inception.
Recent Trends & Developments
Over recent years (2023–2025), adoption trends indicate increasing interest across industries in both types of blockchain solutions:
- Many organizations explore hybrid models combining elements from both worlds—using permissioned (private) layers atop open (public) frameworks—to balance transparency with control.
- Governments are providing clearer regulations around digital assets which influence how enterprises implement these technologies.
- The rise of enterprise-grade platforms emphasizes scalability improvements necessary for large-scale deployment while maintaining security standards expected by regulators.
- Concerns about security risks associated with centralized control have prompted investments into robust governance frameworks within private networks.
Potential Challenges Facing Both Types
Despite promising developments, several issues persist:
- Security vulnerabilities remain a concern especially if controlling entities fail adequately securing their infrastructure.
- Scalability limitations could hinder growth if network demands increase significantly without technological upgrades.
- Regulatory uncertainty continues around how different jurisdictions will treat various forms of blockchain activity—particularly regarding privacy laws like GDPR—which could impact future deployments.
Understanding these dynamics helps stakeholders make informed decisions aligned with organizational goals while navigating evolving legal landscapes effectively.
How Different Industries Use Public vs Private Blockchains
Various sectors leverage each type based on specific needs:
Financial Services: Often utilize public blockchains like Ethereum for decentralized finance applications due to transparency requirements but may adopt permissioned ledgers internally for compliance reasons.
Supply Chain Management: Companies such as Maersk deploy private blockchains that enable secure sharing among trusted partners without exposing sensitive commercial data publicly.
Healthcare: Uses hybrid approaches where patient records might be stored privately yet linked via secure protocols accessible only by authorized personnel under strict regulatory oversight.
Key Factors Influencing Blockchain Choice
When selecting between a public or private solution consider factors such as:
- Data Sensitivity
- Speed Requirements
- Regulatory Compliance4.. Degree Of Decentralization Needed5.. Cost Implications6.. Long-term Scalability Goals
Emerging Trends Shaping Future Adoption
Looking ahead into 2024–2025:
Hybrid models will become increasingly prevalent as organizations seek balanced solutions combining openness with controlled access.
Enhanced interoperability protocols will facilitate smoother integration between different types of ledgers across industries
Regulatory clarity will continue improving which encourages broader adoption beyond niche markets
By understanding these core distinctions alongside current trends—and aligning them with your strategic objectives—you can better navigate the complex landscape surrounding blockchain technology today.
Keywords:public vs private blockchain comparison,differences between decentralized vs permissioned ledger,blockchain technology applications,enterprise blockchain solutions,blockchain regulation updates
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Who Created Bitcoin (BTC)?
Understanding the origins of Bitcoin is essential for grasping its significance in the digital currency landscape. Bitcoin was created by an individual or a group operating under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. Despite extensive speculation and numerous claims, Nakamoto’s true identity remains unknown, adding an element of mystery that has fueled both intrigue and debate within the cryptocurrency community. This anonymity has contributed to Bitcoin’s decentralized ethos, emphasizing that no single entity controls it.
The creation of Bitcoin marked a revolutionary shift in how we perceive money and financial transactions. Unlike traditional currencies issued by governments or central banks, Bitcoin operates on a peer-to-peer network without intermediaries such as banks or payment processors. This decentralization aims to provide users with greater control over their assets while reducing reliance on centralized authorities.
The story begins with Nakamoto publishing the whitepaper titled "Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System" on October 31, 2008. This document laid out the technical blueprint for a new kind of digital currency that could facilitate secure, transparent transactions without third-party oversight. The whitepaper detailed innovative concepts like blockchain technology—a distributed ledger system—and proof-of-work consensus mechanisms that underpin Bitcoin's security.
When Was Bitcoin Launched?
Bitcoin officially came into existence on January 3, 2009, with the mining of its first block known as the Genesis Block. Embedded within this initial block was a message referencing contemporary economic concerns: "The Times 03/Jan/2009 Chancellor on brink of second bailout for banks." This message not only timestamped its creation but also subtly critiqued traditional banking systems and monetary policies—highlighting one of Bitcoin’s core motivations: providing an alternative to fiat currencies susceptible to inflation and government control.
What Is Blockchain Technology?
At its core, Bitcoin relies heavily on blockchain technology—a decentralized ledger maintained collectively by thousands of computers worldwide called nodes. Each transaction is verified through cryptographic processes and added as a block linked sequentially to previous blocks—forming an immutable chain accessible publicly for transparency purposes.
This open-source nature ensures no single authority can alter transaction history unilaterally, fostering trust among participants despite lacking central oversight. Blockchain's resilience against tampering makes it highly secure but also requires significant computational power—especially during mining—to validate new transactions efficiently.
How Does Mining Work?
Mining is fundamental to how new Bitcoins are created and how transaction integrity is maintained within the network. Miners use powerful hardware to solve complex mathematical puzzles—a process known as proof-of-work—which validates transactions before they are recorded onto the blockchain.
Successful miners are rewarded with newly minted Bitcoins; this process introduces new coins into circulation while incentivizing miners’ participation in maintaining network security. Initially set at 50 BTC per block when launched in 2009, this reward halves approximately every four years during scheduled “halving” events—reducing supply inflation over time.
Recent Developments in Bitcoin
Halving Events
Bitcoin's protocol includes programmed halving events designed to control supply growth systematically:
- The third halving occurred on May 11, 2020 — reducing rewards from 12.5 BTC to 6.25 BTC per block.
- The upcoming fourth halving is expected around mid-2024 — further decreasing rewards to approximately 3.125 BTC per block.
These halvings tend to influence market dynamics significantly by constraining supply growth amid increasing demand.
Regulatory Environment
Globally, regulatory attitudes toward cryptocurrencies vary widely:
- El Salvador made headlines as it became the first country officially adopting Bitcoin as legal tender in September 2021.
- In contrast, countries like China have imposed strict bans on crypto trading and mining activities.
In jurisdictions like the United States, agencies such as SEC actively regulate aspects related to cryptocurrencies—including enforcement actions against entities involved in securities violations related to tokens like XRP issued by Ripple Labs.
Market Volatility & Institutional Adoption
Bitcoin remains highly volatile; prices can swing dramatically due primarily to regulatory news or macroeconomic factors affecting investor sentiment globally—for example:
- Price surges driven by institutional interest from firms like Fidelity or PayPal offering integrated services.
- Sharp declines during market corrections or adverse regulatory developments (e.g., dropping below $30K during late-2022).
Technological Innovations
Advancements continue at pace:
- Layer two solutions such as Lightning Network aim at scaling capabilities—enabling faster transactions with lower fees suitable for everyday use.
- Efforts toward integrating smart contract functionalities into existing protocols are ongoing through proposals like RSK (Rootstock), which seeks compatibility with Ethereum-based smart contracts while leveraging Bitcoin’s security model.
Potential Risks Facing Cryptocurrency
While innovation propels adoption forward, several risks threaten long-term stability:
Regulatory Risks: Uncertain legal frameworks could lead governments worldwide either embracing or restricting usage altogether—impacting investor confidence significantly.
Security Concerns: Despite robust cryptography securing most operations today—including high-profile hacks such as Mt Gox—the threat persists from potential attacks like “51% attacks,” where malicious actors gain majority control over mining power enabling double-spending frauds if unchecked.
Environmental Impact: The energy-intensive nature of proof-of-work mining has sparked debates about sustainability; some advocate transitioning toward greener alternatives without compromising decentralization principles fully yet remain cautious about environmental costs associated with current practices.
Market Volatility & Future Outlook
Price fluctuations remain characteristic features influencing both retail investors and institutional players alike—from rapid bull runs followed by sharp corrections—as seen during recent years including dips below $30K amid broader economic uncertainties in late 2022.
Despite these challenges—and ongoing discussions about regulation—the overall trajectory indicates growing acceptance across sectors worldwide coupled with technological innovations aimed at scalability and sustainability.
Understanding these elements provides crucial insights into what shapes bitcoin’s past evolution—and what might influence its future path amidst evolving global financial landscapes.
By examining who created bitcoin along with key milestones since inception—including technological advances and regulatory shifts—we gain comprehensive perspective essential for anyone interested in cryptocurrency markets today.


Lo
2025-05-22 14:31
Who created Bitcoin (BTC)?
Who Created Bitcoin (BTC)?
Understanding the origins of Bitcoin is essential for grasping its significance in the digital currency landscape. Bitcoin was created by an individual or a group operating under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. Despite extensive speculation and numerous claims, Nakamoto’s true identity remains unknown, adding an element of mystery that has fueled both intrigue and debate within the cryptocurrency community. This anonymity has contributed to Bitcoin’s decentralized ethos, emphasizing that no single entity controls it.
The creation of Bitcoin marked a revolutionary shift in how we perceive money and financial transactions. Unlike traditional currencies issued by governments or central banks, Bitcoin operates on a peer-to-peer network without intermediaries such as banks or payment processors. This decentralization aims to provide users with greater control over their assets while reducing reliance on centralized authorities.
The story begins with Nakamoto publishing the whitepaper titled "Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System" on October 31, 2008. This document laid out the technical blueprint for a new kind of digital currency that could facilitate secure, transparent transactions without third-party oversight. The whitepaper detailed innovative concepts like blockchain technology—a distributed ledger system—and proof-of-work consensus mechanisms that underpin Bitcoin's security.
When Was Bitcoin Launched?
Bitcoin officially came into existence on January 3, 2009, with the mining of its first block known as the Genesis Block. Embedded within this initial block was a message referencing contemporary economic concerns: "The Times 03/Jan/2009 Chancellor on brink of second bailout for banks." This message not only timestamped its creation but also subtly critiqued traditional banking systems and monetary policies—highlighting one of Bitcoin’s core motivations: providing an alternative to fiat currencies susceptible to inflation and government control.
What Is Blockchain Technology?
At its core, Bitcoin relies heavily on blockchain technology—a decentralized ledger maintained collectively by thousands of computers worldwide called nodes. Each transaction is verified through cryptographic processes and added as a block linked sequentially to previous blocks—forming an immutable chain accessible publicly for transparency purposes.
This open-source nature ensures no single authority can alter transaction history unilaterally, fostering trust among participants despite lacking central oversight. Blockchain's resilience against tampering makes it highly secure but also requires significant computational power—especially during mining—to validate new transactions efficiently.
How Does Mining Work?
Mining is fundamental to how new Bitcoins are created and how transaction integrity is maintained within the network. Miners use powerful hardware to solve complex mathematical puzzles—a process known as proof-of-work—which validates transactions before they are recorded onto the blockchain.
Successful miners are rewarded with newly minted Bitcoins; this process introduces new coins into circulation while incentivizing miners’ participation in maintaining network security. Initially set at 50 BTC per block when launched in 2009, this reward halves approximately every four years during scheduled “halving” events—reducing supply inflation over time.
Recent Developments in Bitcoin
Halving Events
Bitcoin's protocol includes programmed halving events designed to control supply growth systematically:
- The third halving occurred on May 11, 2020 — reducing rewards from 12.5 BTC to 6.25 BTC per block.
- The upcoming fourth halving is expected around mid-2024 — further decreasing rewards to approximately 3.125 BTC per block.
These halvings tend to influence market dynamics significantly by constraining supply growth amid increasing demand.
Regulatory Environment
Globally, regulatory attitudes toward cryptocurrencies vary widely:
- El Salvador made headlines as it became the first country officially adopting Bitcoin as legal tender in September 2021.
- In contrast, countries like China have imposed strict bans on crypto trading and mining activities.
In jurisdictions like the United States, agencies such as SEC actively regulate aspects related to cryptocurrencies—including enforcement actions against entities involved in securities violations related to tokens like XRP issued by Ripple Labs.
Market Volatility & Institutional Adoption
Bitcoin remains highly volatile; prices can swing dramatically due primarily to regulatory news or macroeconomic factors affecting investor sentiment globally—for example:
- Price surges driven by institutional interest from firms like Fidelity or PayPal offering integrated services.
- Sharp declines during market corrections or adverse regulatory developments (e.g., dropping below $30K during late-2022).
Technological Innovations
Advancements continue at pace:
- Layer two solutions such as Lightning Network aim at scaling capabilities—enabling faster transactions with lower fees suitable for everyday use.
- Efforts toward integrating smart contract functionalities into existing protocols are ongoing through proposals like RSK (Rootstock), which seeks compatibility with Ethereum-based smart contracts while leveraging Bitcoin’s security model.
Potential Risks Facing Cryptocurrency
While innovation propels adoption forward, several risks threaten long-term stability:
Regulatory Risks: Uncertain legal frameworks could lead governments worldwide either embracing or restricting usage altogether—impacting investor confidence significantly.
Security Concerns: Despite robust cryptography securing most operations today—including high-profile hacks such as Mt Gox—the threat persists from potential attacks like “51% attacks,” where malicious actors gain majority control over mining power enabling double-spending frauds if unchecked.
Environmental Impact: The energy-intensive nature of proof-of-work mining has sparked debates about sustainability; some advocate transitioning toward greener alternatives without compromising decentralization principles fully yet remain cautious about environmental costs associated with current practices.
Market Volatility & Future Outlook
Price fluctuations remain characteristic features influencing both retail investors and institutional players alike—from rapid bull runs followed by sharp corrections—as seen during recent years including dips below $30K amid broader economic uncertainties in late 2022.
Despite these challenges—and ongoing discussions about regulation—the overall trajectory indicates growing acceptance across sectors worldwide coupled with technological innovations aimed at scalability and sustainability.
Understanding these elements provides crucial insights into what shapes bitcoin’s past evolution—and what might influence its future path amidst evolving global financial landscapes.
By examining who created bitcoin along with key milestones since inception—including technological advances and regulatory shifts—we gain comprehensive perspective essential for anyone interested in cryptocurrency markets today.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Are Creator Royalties Enforced in the NFT Ecosystem?
Understanding how creator royalties are enforced in the NFT ecosystem is crucial for artists, collectors, and marketplace operators alike. As NFTs continue to revolutionize digital ownership and art sales, ensuring that creators receive fair compensation through automatic royalty payments has become a key concern. This article explores the mechanisms behind enforcing creator royalties, highlighting technological solutions, legal considerations, and industry practices.
What Are Creator Royalties in NFTs?
Creator royalties are a percentage of an NFT’s sale price that goes directly to the original artist or creator whenever their work is resold on secondary markets. Similar to traditional art royalties—where artists earn from subsequent sales—NFT creator royalties aim to provide ongoing revenue streams for digital creators. These percentages typically range from 5% to 10%, though they can be higher or lower depending on individual agreements.
The core idea is straightforward: when an NFT changes hands multiple times across different platforms or owners, the original artist continues to benefit financially. This system incentivizes creators by offering potential long-term earnings beyond their initial sale.
How Blockchain Technology Facilitates Royalty Enforcement
Blockchain technology underpins most NFTs and plays a vital role in enforcing royalty payments. Platforms like Ethereum store NFTs as unique tokens with transparent transaction histories recorded immutably on the blockchain. This transparency allows anyone to verify ownership history and transaction details at any time.
Smart contracts—self-executing code embedded within blockchain transactions—are central to automating royalty enforcement. When an NFT is sold via a marketplace supporting royalties, these smart contracts automatically deduct a predetermined percentage of the sale price and transfer it directly into the creator’s wallet without manual intervention.
This automation reduces reliance on trust-based agreements or third-party enforcement mechanisms; instead, it leverages blockchain's inherent security features for reliable execution of royalty terms.
Role of Popular Marketplaces in Enforcing Royalties
Major NFT marketplaces such as OpenSea and Rarible have integrated features that enable creators to set their preferred royalty rates during minting or listing processes:
OpenSea: In 2023, OpenSea updated its policies allowing creators full control over setting secondary sale royalties for each collection they list. The platform enforces these rates through smart contract interactions during transactions.
Rarible: Rarible introduced dynamic royalty settings where artists can adjust their rates based on factors like sale price or other criteria. Their platform also supports programmable royalties via customizable smart contracts.
These marketplaces act as intermediaries that facilitate enforceable payments by embedding royalty logic into transaction protocols supported by blockchain standards such as ERC-721 (for non-fungible tokens) and ERC-1155 (multi-token standard).
However, enforcement depends heavily on whether marketplaces honor these settings consistently across all transactions—a challenge given differing policies among platforms.
Challenges Due to Lack of Standardization
One significant obstacle in enforcing creator royalties stems from inconsistent standards across various platforms:
- Some marketplaces honor setroyalty percentages strictly.
- Others may ignore them entirely if not embedded properly within smart contracts.
This inconsistency leads to confusion among buyers who might expect certain fees but encounter situations where sellers bypass or disable automatic payments—a practice sometimes called "royalty bypassing" or "resale loopholes."
Furthermore, some platforms do not support programmable royalties at all—or only partially enforce them—making universal enforcement difficult without industry-wide standardization efforts.
Legal Considerations Surrounding Royalty Enforcement
While technically feasible through smart contracts and blockchain transparency, legal issues complicate enforcement:
Contractual Nature: Many argue that automated royalities should be legally binding contractual obligations; however,
Terms of Service vs Contract Law: Some dispute whether marketplace policies constitute legally enforceable agreements versus mere terms of service.
Jurisdictional Variability: Different countries have varying laws regarding digital assets’ contractual enforceability which adds complexity when disputes arise over unpaid royalties.
Ongoing discussions focus on establishing clearer legal frameworks that recognize automated smart contract obligations related to intellectual property rights within digital ecosystems.
Recent Industry Developments Supporting Enforcement
The industry has seen notable advancements aimed at strengthening royaltiy enforcement:
OpenSea’s Policy Update (2023) – Allowed creators greater control over setting secondary sale commissions directly linked with underlying smart contracts.
Rarible’s Dynamic Royalties – Enabled flexible rate adjustments based on specific conditions like resale value thresholds.
Emergence of DAO Governance Models – Decentralized Autonomous Organizations are being proposed as governance bodies overseeing collective management of funds—including enforcing rules around creator compensation—to promote fairness across communities.
These developments reflect growing recognition within the community about protecting artists' rights while leveraging technological innovations for better compliance management.
Industry Support & Community Engagement
Major marketplaces actively promote tools enabling easy setup and management of royalty payments:
- User-friendly interfaces allow artists without technical expertise to embed desired rates during minting processes.
- Community forums foster discussions about fair compensation practices—and many advocate increasing default rates or improving transparency around payment flows.
This engagement helps build trust between creators and buyers while encouraging adoption of best practices aligned with evolving standards for fair remuneration.
Future Directions Toward Standardized Enforcement
Looking ahead, several initiatives aim toward creating uniformity:
- Developing cross-platform standards using common protocols such as EIP (Ethereum Improvement Proposals) related specifically to royalty enforcement
- Establishing regulatory frameworks recognizing automated payment commitments
- Promoting industry-wide agreements among major players ensuring consistent adherence
Technological advancements will likely lead toward more sophisticated solutions—for example:
- Blockchain interoperability allowing seamless tracking across multiple chains
- Smart contract templates designed explicitly for enforceable copyright terms
Such innovations could significantly reduce disputes related to unpaid dues while reinforcing trustworthiness within this rapidly expanding market segment.
Final Thoughts
Enforcing creator royalties effectively remains a multifaceted challenge involving technological innovation, legal clarity, market cooperation—and active community participation. While current systems leverage blockchain's transparency coupled with programmable smart contracts successfully in many cases—including leading marketplaces—the lack of universal standardization continues posing hurdles worldwide.
As adoption grows alongside ongoing regulatory discussions and technological improvements — including decentralized governance models — we can expect more robust mechanisms ensuring fair compensation for digital artists moving forward.
By understanding these dynamics, artists, collectors, marketplace operators, and regulators can better navigate this evolving landscape—ensuring creativity remains rewarded fairly amid rapid innovation.*


kai
2025-05-22 11:39
How are creator royalties enforced in the NFT ecosystem?
How Are Creator Royalties Enforced in the NFT Ecosystem?
Understanding how creator royalties are enforced in the NFT ecosystem is crucial for artists, collectors, and marketplace operators alike. As NFTs continue to revolutionize digital ownership and art sales, ensuring that creators receive fair compensation through automatic royalty payments has become a key concern. This article explores the mechanisms behind enforcing creator royalties, highlighting technological solutions, legal considerations, and industry practices.
What Are Creator Royalties in NFTs?
Creator royalties are a percentage of an NFT’s sale price that goes directly to the original artist or creator whenever their work is resold on secondary markets. Similar to traditional art royalties—where artists earn from subsequent sales—NFT creator royalties aim to provide ongoing revenue streams for digital creators. These percentages typically range from 5% to 10%, though they can be higher or lower depending on individual agreements.
The core idea is straightforward: when an NFT changes hands multiple times across different platforms or owners, the original artist continues to benefit financially. This system incentivizes creators by offering potential long-term earnings beyond their initial sale.
How Blockchain Technology Facilitates Royalty Enforcement
Blockchain technology underpins most NFTs and plays a vital role in enforcing royalty payments. Platforms like Ethereum store NFTs as unique tokens with transparent transaction histories recorded immutably on the blockchain. This transparency allows anyone to verify ownership history and transaction details at any time.
Smart contracts—self-executing code embedded within blockchain transactions—are central to automating royalty enforcement. When an NFT is sold via a marketplace supporting royalties, these smart contracts automatically deduct a predetermined percentage of the sale price and transfer it directly into the creator’s wallet without manual intervention.
This automation reduces reliance on trust-based agreements or third-party enforcement mechanisms; instead, it leverages blockchain's inherent security features for reliable execution of royalty terms.
Role of Popular Marketplaces in Enforcing Royalties
Major NFT marketplaces such as OpenSea and Rarible have integrated features that enable creators to set their preferred royalty rates during minting or listing processes:
OpenSea: In 2023, OpenSea updated its policies allowing creators full control over setting secondary sale royalties for each collection they list. The platform enforces these rates through smart contract interactions during transactions.
Rarible: Rarible introduced dynamic royalty settings where artists can adjust their rates based on factors like sale price or other criteria. Their platform also supports programmable royalties via customizable smart contracts.
These marketplaces act as intermediaries that facilitate enforceable payments by embedding royalty logic into transaction protocols supported by blockchain standards such as ERC-721 (for non-fungible tokens) and ERC-1155 (multi-token standard).
However, enforcement depends heavily on whether marketplaces honor these settings consistently across all transactions—a challenge given differing policies among platforms.
Challenges Due to Lack of Standardization
One significant obstacle in enforcing creator royalties stems from inconsistent standards across various platforms:
- Some marketplaces honor setroyalty percentages strictly.
- Others may ignore them entirely if not embedded properly within smart contracts.
This inconsistency leads to confusion among buyers who might expect certain fees but encounter situations where sellers bypass or disable automatic payments—a practice sometimes called "royalty bypassing" or "resale loopholes."
Furthermore, some platforms do not support programmable royalties at all—or only partially enforce them—making universal enforcement difficult without industry-wide standardization efforts.
Legal Considerations Surrounding Royalty Enforcement
While technically feasible through smart contracts and blockchain transparency, legal issues complicate enforcement:
Contractual Nature: Many argue that automated royalities should be legally binding contractual obligations; however,
Terms of Service vs Contract Law: Some dispute whether marketplace policies constitute legally enforceable agreements versus mere terms of service.
Jurisdictional Variability: Different countries have varying laws regarding digital assets’ contractual enforceability which adds complexity when disputes arise over unpaid royalties.
Ongoing discussions focus on establishing clearer legal frameworks that recognize automated smart contract obligations related to intellectual property rights within digital ecosystems.
Recent Industry Developments Supporting Enforcement
The industry has seen notable advancements aimed at strengthening royaltiy enforcement:
OpenSea’s Policy Update (2023) – Allowed creators greater control over setting secondary sale commissions directly linked with underlying smart contracts.
Rarible’s Dynamic Royalties – Enabled flexible rate adjustments based on specific conditions like resale value thresholds.
Emergence of DAO Governance Models – Decentralized Autonomous Organizations are being proposed as governance bodies overseeing collective management of funds—including enforcing rules around creator compensation—to promote fairness across communities.
These developments reflect growing recognition within the community about protecting artists' rights while leveraging technological innovations for better compliance management.
Industry Support & Community Engagement
Major marketplaces actively promote tools enabling easy setup and management of royalty payments:
- User-friendly interfaces allow artists without technical expertise to embed desired rates during minting processes.
- Community forums foster discussions about fair compensation practices—and many advocate increasing default rates or improving transparency around payment flows.
This engagement helps build trust between creators and buyers while encouraging adoption of best practices aligned with evolving standards for fair remuneration.
Future Directions Toward Standardized Enforcement
Looking ahead, several initiatives aim toward creating uniformity:
- Developing cross-platform standards using common protocols such as EIP (Ethereum Improvement Proposals) related specifically to royalty enforcement
- Establishing regulatory frameworks recognizing automated payment commitments
- Promoting industry-wide agreements among major players ensuring consistent adherence
Technological advancements will likely lead toward more sophisticated solutions—for example:
- Blockchain interoperability allowing seamless tracking across multiple chains
- Smart contract templates designed explicitly for enforceable copyright terms
Such innovations could significantly reduce disputes related to unpaid dues while reinforcing trustworthiness within this rapidly expanding market segment.
Final Thoughts
Enforcing creator royalties effectively remains a multifaceted challenge involving technological innovation, legal clarity, market cooperation—and active community participation. While current systems leverage blockchain's transparency coupled with programmable smart contracts successfully in many cases—including leading marketplaces—the lack of universal standardization continues posing hurdles worldwide.
As adoption grows alongside ongoing regulatory discussions and technological improvements — including decentralized governance models — we can expect more robust mechanisms ensuring fair compensation for digital artists moving forward.
By understanding these dynamics, artists, collectors, marketplace operators, and regulators can better navigate this evolving landscape—ensuring creativity remains rewarded fairly amid rapid innovation.*
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Error executing ChatgptTask


kai
2025-05-22 09:54
What’s the difference between custodial and non-custodial wallets?
Error executing ChatgptTask
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is the Difference Between a Coin and a Token in Cryptocurrency?
Understanding the fundamental differences between coins and tokens is essential for anyone interested in cryptocurrency investing, development, or regulation. While these terms are often used interchangeably by newcomers, they represent distinct concepts with unique roles within the blockchain ecosystem. Clarifying these differences helps users make informed decisions and navigate the evolving crypto landscape more effectively.
Coins: The Native Digital Currencies
A coin in cryptocurrency refers to a digital currency that operates on its own independent blockchain network. These coins are designed primarily as mediums of exchange, stores of value, or units of account within their respective ecosystems. For example, Bitcoin (BTC) is built on its own blockchain and was created to serve as a decentralized digital currency that can be used for peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries.
Similarly, Ethereum (ETH), while often associated with smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps), functions as both a platform token and a coin—its native currency used to pay transaction fees on its network. Coins typically have their own consensus mechanisms such as proof-of-work (PoW) or proof-of-stake (PoS), which secure their networks against malicious activities.
Because they operate independently, coins tend to be more decentralized than tokens. They also usually have broader acceptance across exchanges and wallets due to their status as primary currencies within their blockchains.
Tokens: Assets Built on Existing Blockchains
In contrast, tokens are digital assets issued on top of existing blockchain platforms through smart contracts. Unlike coins, tokens do not have their own dedicated blockchain but rely entirely on another network’s infrastructure for validation and security.
Tokens can represent an array of assets or rights—utility tokens grant access to specific services; security tokens symbolize ownership stakes similar to traditional securities; non-fungible tokens (NFTs) represent unique digital items like art or collectibles; governance tokens enable holders to participate in decision-making processes within decentralized organizations.
Most popular platforms for creating tokens include Ethereum’s ERC-20 standard for fungible assets and ERC-721/ERC-1155 standards for NFTs. Because they depend on existing blockchains like Ethereum or Binance Smart Chain (BSC), token transactions benefit from established security protocols but may also inherit limitations related to scalability or centralization concerns associated with those networks.
Key Differences Summarized
| Aspect | Coins | Tokens |
|---|---|---|
| Blockchain Origin | Own blockchain | Existing blockchain platform |
| Purpose | Medium of exchange / store of value | Asset representation / utility / governance |
| Consensus Mechanism | Own mechanism (e.g., PoW/PoS) | Underlying network’s mechanism |
| Decentralization Level | Generally more decentralized | Less decentralized due to reliance |
Recent Trends Shaping Coins & Tokens
The crypto industry continues evolving rapidly with new developments impacting how coins and tokens are perceived and utilized:
Stablecoins like USD1 linked directly with fiat currencies are gaining prominence for financial stability during volatile market conditions. For instance, World Liberty Financial's USD1 stablecoin was recently adopted as an official settlement tool amid rising institutional interest.
Meme Coins such as $TRUMP exemplify high volatility driven by social media hype rather than intrinsic utility—delays in token unlocks highlight regulatory scrutiny faced by such assets.
Major tech companies like Meta exploring stablecoins aim at integrating them into mainstream payment systems — this signals increasing acceptance but also raises questions about centralization risks.
Regulatory debates surrounding cryptocurrencies continue intensively; authorities scrutinize whether certain tokens should be classified as securities under laws similar to those governing traditional finance markets—a process that could significantly influence future adoption patterns.
Potential Challenges & Risks
As cryptocurrencies grow more complex through innovations involving both coins and tokens, several challenges emerge:
Regulatory Uncertainty: Differentiating between what constitutes a coin versus a security token remains ambiguous in many jurisdictions—leading regulators like the SEC scrutinizing various projects closely.
Market Volatility: Meme-based projects demonstrate how sentiment-driven trading can cause dramatic price swings—posing risks especially when investors lack comprehensive understanding.
Adoption Barriers: While stablecoins facilitate smoother integration into traditional finance systems via partnerships with corporations like Meta—or even central banks—their centralized nature raises concerns over potential manipulation or censorship vulnerabilities.
By understanding these distinctions thoroughly—and staying updated about ongoing developments—you position yourself better whether you're investing strategically or developing innovative solutions within this space.
Understanding Cryptocurrencies: Why Differentiating Between Coins And Tokens Matters
Grasping what sets apart cryptocurrencies’ core components is vital not only from an investment perspective but also from regulatory compliance angles. Recognizing whether an asset is classified primarily as a coin—or if it functions solely as a token representing other assets—is key when evaluating risk profiles, technological capabilities, legal considerations—and ultimately making smarter decisions aligned with your goals in this dynamic environment.
Final Thoughts
The distinction between coins and tokens forms the foundation upon which much of cryptocurrency's innovation rests today—from establishing new financial instruments via stablecoins to creating vibrant ecosystems around NFTs or governance models through various token standards. As regulations tighten globally amid rapid technological advances—including initiatives by major corporations exploring crypto integrations—it becomes increasingly important for users at all levels—from casual investors to developers—to understand these fundamental differences clearly.
Staying informed about recent trends such as regulatory shifts affecting meme coins’ legitimacy—or institutional moves toward adopting stablecoins—can help you navigate potential opportunities while managing inherent risks effectively within this fast-changing domain.


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-22 02:34
What is the difference between a coin and a token?
What Is the Difference Between a Coin and a Token in Cryptocurrency?
Understanding the fundamental differences between coins and tokens is essential for anyone interested in cryptocurrency investing, development, or regulation. While these terms are often used interchangeably by newcomers, they represent distinct concepts with unique roles within the blockchain ecosystem. Clarifying these differences helps users make informed decisions and navigate the evolving crypto landscape more effectively.
Coins: The Native Digital Currencies
A coin in cryptocurrency refers to a digital currency that operates on its own independent blockchain network. These coins are designed primarily as mediums of exchange, stores of value, or units of account within their respective ecosystems. For example, Bitcoin (BTC) is built on its own blockchain and was created to serve as a decentralized digital currency that can be used for peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries.
Similarly, Ethereum (ETH), while often associated with smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps), functions as both a platform token and a coin—its native currency used to pay transaction fees on its network. Coins typically have their own consensus mechanisms such as proof-of-work (PoW) or proof-of-stake (PoS), which secure their networks against malicious activities.
Because they operate independently, coins tend to be more decentralized than tokens. They also usually have broader acceptance across exchanges and wallets due to their status as primary currencies within their blockchains.
Tokens: Assets Built on Existing Blockchains
In contrast, tokens are digital assets issued on top of existing blockchain platforms through smart contracts. Unlike coins, tokens do not have their own dedicated blockchain but rely entirely on another network’s infrastructure for validation and security.
Tokens can represent an array of assets or rights—utility tokens grant access to specific services; security tokens symbolize ownership stakes similar to traditional securities; non-fungible tokens (NFTs) represent unique digital items like art or collectibles; governance tokens enable holders to participate in decision-making processes within decentralized organizations.
Most popular platforms for creating tokens include Ethereum’s ERC-20 standard for fungible assets and ERC-721/ERC-1155 standards for NFTs. Because they depend on existing blockchains like Ethereum or Binance Smart Chain (BSC), token transactions benefit from established security protocols but may also inherit limitations related to scalability or centralization concerns associated with those networks.
Key Differences Summarized
| Aspect | Coins | Tokens |
|---|---|---|
| Blockchain Origin | Own blockchain | Existing blockchain platform |
| Purpose | Medium of exchange / store of value | Asset representation / utility / governance |
| Consensus Mechanism | Own mechanism (e.g., PoW/PoS) | Underlying network’s mechanism |
| Decentralization Level | Generally more decentralized | Less decentralized due to reliance |
Recent Trends Shaping Coins & Tokens
The crypto industry continues evolving rapidly with new developments impacting how coins and tokens are perceived and utilized:
Stablecoins like USD1 linked directly with fiat currencies are gaining prominence for financial stability during volatile market conditions. For instance, World Liberty Financial's USD1 stablecoin was recently adopted as an official settlement tool amid rising institutional interest.
Meme Coins such as $TRUMP exemplify high volatility driven by social media hype rather than intrinsic utility—delays in token unlocks highlight regulatory scrutiny faced by such assets.
Major tech companies like Meta exploring stablecoins aim at integrating them into mainstream payment systems — this signals increasing acceptance but also raises questions about centralization risks.
Regulatory debates surrounding cryptocurrencies continue intensively; authorities scrutinize whether certain tokens should be classified as securities under laws similar to those governing traditional finance markets—a process that could significantly influence future adoption patterns.
Potential Challenges & Risks
As cryptocurrencies grow more complex through innovations involving both coins and tokens, several challenges emerge:
Regulatory Uncertainty: Differentiating between what constitutes a coin versus a security token remains ambiguous in many jurisdictions—leading regulators like the SEC scrutinizing various projects closely.
Market Volatility: Meme-based projects demonstrate how sentiment-driven trading can cause dramatic price swings—posing risks especially when investors lack comprehensive understanding.
Adoption Barriers: While stablecoins facilitate smoother integration into traditional finance systems via partnerships with corporations like Meta—or even central banks—their centralized nature raises concerns over potential manipulation or censorship vulnerabilities.
By understanding these distinctions thoroughly—and staying updated about ongoing developments—you position yourself better whether you're investing strategically or developing innovative solutions within this space.
Understanding Cryptocurrencies: Why Differentiating Between Coins And Tokens Matters
Grasping what sets apart cryptocurrencies’ core components is vital not only from an investment perspective but also from regulatory compliance angles. Recognizing whether an asset is classified primarily as a coin—or if it functions solely as a token representing other assets—is key when evaluating risk profiles, technological capabilities, legal considerations—and ultimately making smarter decisions aligned with your goals in this dynamic environment.
Final Thoughts
The distinction between coins and tokens forms the foundation upon which much of cryptocurrency's innovation rests today—from establishing new financial instruments via stablecoins to creating vibrant ecosystems around NFTs or governance models through various token standards. As regulations tighten globally amid rapid technological advances—including initiatives by major corporations exploring crypto integrations—it becomes increasingly important for users at all levels—from casual investors to developers—to understand these fundamental differences clearly.
Staying informed about recent trends such as regulatory shifts affecting meme coins’ legitimacy—or institutional moves toward adopting stablecoins—can help you navigate potential opportunities while managing inherent risks effectively within this fast-changing domain.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is a High-Wave Candle?
A High-Wave Candle is a distinctive candlestick pattern used in technical analysis to interpret market sentiment and potential future price movements. It is characterized by a small real body with long upper shadows, often resembling a doji but with more prominent upper wicks. This pattern typically appears during periods of high volatility, reflecting significant price swings within the trading session.
The defining feature of a High-Wave Candle is its long upper shadow, which indicates that buyers pushed prices higher during the session but were ultimately met with selling pressure that drove prices back down near the opening level. The short lower shadow suggests limited downward movement, emphasizing indecision among traders. Because of these characteristics, traders view this pattern as an indicator of market uncertainty or potential reversals.
Significance in Technical Analysis
High-Wave Candles are valuable tools for traders because they provide insights into market psychology at specific points in time. Their formation often signals that neither buyers nor sellers have full control over the market direction at that moment. As such, these candles can serve as warning signs or confirmation signals depending on their context within broader chart patterns.
In technical analysis, candlestick patterns like the High-Wave are used alongside other indicators such as moving averages, RSI (Relative Strength Index), and volume data to improve decision-making accuracy. When combined effectively, they help traders identify whether current trends are likely to continue or reverse.
Market Contexts Where High-Wave Candles Appear
The interpretation of a High-Wave Candle depends heavily on where it appears within the overall trend:
At Market Bottoms (Bullish Reversal Signal): When this pattern forms after a downtrend, especially if it occurs near support levels or after declining prices, it may suggest weakening selling pressure and an impending reversal to an uptrend.
At Market Tops (Bearish Reversal Signal): Conversely, if seen after an uptrend at resistance levels or following rapid price increases, it could indicate that buying momentum is waning and sellers might soon take control.
In Sideways Markets: During periods without clear directional movement—often called consolidation phases—the appearance of high-wick candles like this can reflect trader indecision rather than definitive trend shifts.
Understanding these contexts helps traders avoid false signals and better align their strategies with prevailing market conditions.
How Does Volatility Influence High-Wave Candles?
High volatility environments tend to produce more frequent and pronounced candlestick patterns like the High-Wave Candle. Large price swings within short periods lead to extended shadows on candles due to rapid buying and selling activity. This heightened volatility makes these candles particularly relevant for day traders and scalpers who seek quick entries based on short-term momentum shifts.
However, increased volatility also raises risks; false signals become more common when markets fluctuate wildly without clear directional bias. Therefore, it's crucial for traders not only to recognize high-wave patterns but also to confirm them through additional indicators such as volume spikes or trendlines before acting upon them.
Practical Uses in Trading Strategies
Traders incorporate High-Wave Candles into their strategies primarily for identifying potential reversals or confirming ongoing trends:
Reversal Indicators: A high-wick candle appearing after prolonged declines might signal exhaustion among sellers—potentially marking an entry point for bullish trades.
Confirmation Tools: When combined with other technical signals—like divergence in RSI or MACD—a High-Wave Candle can strengthen confidence in upcoming trend changes.
Risk Management: Recognizing these candles helps set stop-loss levels just beyond recent highs/lows associated with the pattern’s shadows—limiting downside risk if predictions prove wrong.
Many online trading platforms now include automated detection features for candlestick patterns like this one—making it easier even for less experienced traders to spot opportunities quickly while maintaining disciplined risk controls.
Recent Trends: Cryptocurrency Markets & Technical Analysis Tools
Over recent years — especially during major crypto bull runs — cryptocurrency markets have exhibited increased instances of high-volatility events marked by prominent candle formations including High-Waves. For example:
- During Bitcoin's 2021 rally toward new all-time highs,
- Several instances appeared where large upper shadows signaled hesitation before breakouts,
- Or reversals when similar patterns formed at key resistance zones.
This has led many crypto traders to adopt advanced charting tools capable of automatically detecting such patterns across multiple assets simultaneously using platforms like TradingView or Binance’s proprietary software solutions.
Furthermore,
- The proliferation of real-time data feeds
- Enhanced analytical algorithmsare empowering both retail investors and professional fund managers aliketo make quicker decisions based on candlestick cues including high-waves amidst volatile markets.
Limitations & Risks Associated With Using These Patterns
Despite their usefulness,
it’s important not to rely solely on candlestick formations like the High Wave without considering broader analysis frameworks:
- False Signals: Not every appearance leads to actual reversals; some may be mere noise caused by random trading activity.
- Market Sentiment Impact: External factors such as news events can override technical indications provided by candle patterns.
- Confirmation Needed: Always corroborate findings from candlesticks with other indicators—for example,
- Volume analysis
- Trendline breaks
- Momentum oscillators
This comprehensive approach reduces chances of making costly mistakes based solely on isolated candle formations.
How Traders Can Use This Pattern Effectively
To maximize its utility,
traders should consider:
– Monitoring multiple timeframes: Short-term charts (e.g., 5-minute) reveal immediate moves while daily charts provide longer-term context.– Combining with support/resistance levels: Confirm whether high-wicks occur near key zones where reversals are likely.– Watching volume spikes: Elevated volume accompanying a high-wave candle adds credibility regarding potential trend shifts.– Setting appropriate stop-loss orders: Placing stops beyond shadow extremes minimizes losses if trade assumptions prove incorrect.
Final Thoughts
The High Wave Candle remains an essential element within modern technical analysis toolkits due to its ability to highlight moments of indecision amid strong price movements. While not infallible—as all trading indicators carry inherent risks—it offers valuable insights when interpreted correctly alongside other analytical methods.
By understanding its formation dynamics across different market environments—including cryptocurrencies—and leveraging advanced charting tools available today users can enhance their decision-making process significantly while managing associated risks effectively.
Keywords: what is high-wave candle | candlestick pattern | technical analysis | market reversal | cryptocurrency trading | volatility indicator | trading strategy


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-19 06:21
What is High-Wave Candle?
What Is a High-Wave Candle?
A High-Wave Candle is a distinctive candlestick pattern used in technical analysis to interpret market sentiment and potential future price movements. It is characterized by a small real body with long upper shadows, often resembling a doji but with more prominent upper wicks. This pattern typically appears during periods of high volatility, reflecting significant price swings within the trading session.
The defining feature of a High-Wave Candle is its long upper shadow, which indicates that buyers pushed prices higher during the session but were ultimately met with selling pressure that drove prices back down near the opening level. The short lower shadow suggests limited downward movement, emphasizing indecision among traders. Because of these characteristics, traders view this pattern as an indicator of market uncertainty or potential reversals.
Significance in Technical Analysis
High-Wave Candles are valuable tools for traders because they provide insights into market psychology at specific points in time. Their formation often signals that neither buyers nor sellers have full control over the market direction at that moment. As such, these candles can serve as warning signs or confirmation signals depending on their context within broader chart patterns.
In technical analysis, candlestick patterns like the High-Wave are used alongside other indicators such as moving averages, RSI (Relative Strength Index), and volume data to improve decision-making accuracy. When combined effectively, they help traders identify whether current trends are likely to continue or reverse.
Market Contexts Where High-Wave Candles Appear
The interpretation of a High-Wave Candle depends heavily on where it appears within the overall trend:
At Market Bottoms (Bullish Reversal Signal): When this pattern forms after a downtrend, especially if it occurs near support levels or after declining prices, it may suggest weakening selling pressure and an impending reversal to an uptrend.
At Market Tops (Bearish Reversal Signal): Conversely, if seen after an uptrend at resistance levels or following rapid price increases, it could indicate that buying momentum is waning and sellers might soon take control.
In Sideways Markets: During periods without clear directional movement—often called consolidation phases—the appearance of high-wick candles like this can reflect trader indecision rather than definitive trend shifts.
Understanding these contexts helps traders avoid false signals and better align their strategies with prevailing market conditions.
How Does Volatility Influence High-Wave Candles?
High volatility environments tend to produce more frequent and pronounced candlestick patterns like the High-Wave Candle. Large price swings within short periods lead to extended shadows on candles due to rapid buying and selling activity. This heightened volatility makes these candles particularly relevant for day traders and scalpers who seek quick entries based on short-term momentum shifts.
However, increased volatility also raises risks; false signals become more common when markets fluctuate wildly without clear directional bias. Therefore, it's crucial for traders not only to recognize high-wave patterns but also to confirm them through additional indicators such as volume spikes or trendlines before acting upon them.
Practical Uses in Trading Strategies
Traders incorporate High-Wave Candles into their strategies primarily for identifying potential reversals or confirming ongoing trends:
Reversal Indicators: A high-wick candle appearing after prolonged declines might signal exhaustion among sellers—potentially marking an entry point for bullish trades.
Confirmation Tools: When combined with other technical signals—like divergence in RSI or MACD—a High-Wave Candle can strengthen confidence in upcoming trend changes.
Risk Management: Recognizing these candles helps set stop-loss levels just beyond recent highs/lows associated with the pattern’s shadows—limiting downside risk if predictions prove wrong.
Many online trading platforms now include automated detection features for candlestick patterns like this one—making it easier even for less experienced traders to spot opportunities quickly while maintaining disciplined risk controls.
Recent Trends: Cryptocurrency Markets & Technical Analysis Tools
Over recent years — especially during major crypto bull runs — cryptocurrency markets have exhibited increased instances of high-volatility events marked by prominent candle formations including High-Waves. For example:
- During Bitcoin's 2021 rally toward new all-time highs,
- Several instances appeared where large upper shadows signaled hesitation before breakouts,
- Or reversals when similar patterns formed at key resistance zones.
This has led many crypto traders to adopt advanced charting tools capable of automatically detecting such patterns across multiple assets simultaneously using platforms like TradingView or Binance’s proprietary software solutions.
Furthermore,
- The proliferation of real-time data feeds
- Enhanced analytical algorithmsare empowering both retail investors and professional fund managers aliketo make quicker decisions based on candlestick cues including high-waves amidst volatile markets.
Limitations & Risks Associated With Using These Patterns
Despite their usefulness,
it’s important not to rely solely on candlestick formations like the High Wave without considering broader analysis frameworks:
- False Signals: Not every appearance leads to actual reversals; some may be mere noise caused by random trading activity.
- Market Sentiment Impact: External factors such as news events can override technical indications provided by candle patterns.
- Confirmation Needed: Always corroborate findings from candlesticks with other indicators—for example,
- Volume analysis
- Trendline breaks
- Momentum oscillators
This comprehensive approach reduces chances of making costly mistakes based solely on isolated candle formations.
How Traders Can Use This Pattern Effectively
To maximize its utility,
traders should consider:
– Monitoring multiple timeframes: Short-term charts (e.g., 5-minute) reveal immediate moves while daily charts provide longer-term context.– Combining with support/resistance levels: Confirm whether high-wicks occur near key zones where reversals are likely.– Watching volume spikes: Elevated volume accompanying a high-wave candle adds credibility regarding potential trend shifts.– Setting appropriate stop-loss orders: Placing stops beyond shadow extremes minimizes losses if trade assumptions prove incorrect.
Final Thoughts
The High Wave Candle remains an essential element within modern technical analysis toolkits due to its ability to highlight moments of indecision amid strong price movements. While not infallible—as all trading indicators carry inherent risks—it offers valuable insights when interpreted correctly alongside other analytical methods.
By understanding its formation dynamics across different market environments—including cryptocurrencies—and leveraging advanced charting tools available today users can enhance their decision-making process significantly while managing associated risks effectively.
Keywords: what is high-wave candle | candlestick pattern | technical analysis | market reversal | cryptocurrency trading | volatility indicator | trading strategy
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is Adaptive Moving Average (AMA)?
The Adaptive Moving Average (AMA) is a sophisticated technical indicator used by traders and investors to analyze market trends more accurately. Unlike traditional moving averages, which use a fixed period, AMA dynamically adjusts its calculation based on recent market volatility. This feature allows it to respond swiftly during volatile periods and smooth out noise during calmer times, making it a valuable tool for navigating complex financial markets such as cryptocurrencies and stocks.
How Does the Adaptive Moving Average Work?
At its core, the AMA begins with an initial fixed period similar to a Simple Moving Average (SMA). However, what sets it apart is its ability to adapt this period over time. The adjustment process involves analyzing recent price changes: when prices exhibit high volatility—meaning large swings—the AMA shortens its period to become more sensitive; conversely, during low volatility phases with minimal price fluctuations, it lengthens the period for smoother signals.
This dynamic adjustment helps traders identify trend shifts more effectively. For example, if the AMA crosses above or below the current price or other indicators like RSI or MACD, traders interpret these as potential buy or sell signals. Because of this adaptability, AMA can better capture real-time market movements compared to static moving averages.
Historical Context of Adaptive Moving Averages
Introduced in the 1990s by technical analysts seeking improved trend-following tools, AMA gained traction among professional traders who needed more responsive indicators in volatile markets. Its popularity surged in the early 2000s as trading platforms integrated advanced algorithms capable of calculating adaptive averages efficiently.
Initially used primarily in stock markets and forex trading environments where volatility could be predictable within certain ranges, AMA's flexibility made it especially appealing for commodities and futures trading as well. Over time, with technological advancements and increased computational power available on trading platforms—and later through algorithmic trading—AMA became accessible even for retail investors.
Advantages of Using an Adaptive Moving Average
One significant benefit of using an AMA lies in its responsiveness; because it adjusts according to recent market conditions rather than sticking rigidly to a preset window size:
- Enhanced Responsiveness: It reacts quickly during sudden price movements.
- Better Trend Detection: It adapts smoothly between trending phases and sideways consolidations.
- Versatility Across Markets: Suitable for various asset classes including cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum due to their high volatility.
Additionally, combining AMA with other technical indicators such as Bollinger Bands or RSI can improve trade accuracy by confirming signals generated through multiple analysis layers.
Limitations & Challenges
Despite its advantages, there are some limitations that traders should consider:
- Complexity: Understanding how adaptive periods are calculated requires familiarity with advanced mathematical concepts.
- Overfitting Risks: Excessive sensitivity might lead some traders into reacting prematurely or chasing false signals caused by short-term noise.
- Market Conditions Dependency: In extremely unpredictable markets—like crypto during sudden crashes—AMA may generate conflicting signals that need careful interpretation alongside fundamental analysis.
Therefore, while powerful when used correctly within comprehensive strategies—including risk management practices—it’s essential not solely rely on AMAs but incorporate them into broader analytical frameworks.
Recent Trends: Cryptocurrency Trading & Beyond
In recent years especially within cryptocurrency markets characterized by extreme volatility—such as Bitcoin’s rapid swings—the adoption of adaptive tools like AMA has increased significantly. Traders appreciate how quickly AMAs adjust their sensitivity levels without manual intervention—a crucial feature amid fast-changing crypto landscapes.
Many experienced crypto traders combine AMAs with momentum indicators like MACD or oscillators such as RSI for confirmation purposes before executing trades. This multi-layered approach helps mitigate false positives often associated with single-indicator strategies while leveraging AMAs’ responsiveness for timely entries and exits.
Beyond cryptocurrencies — traditional assets including stocks and forex also benefit from using AMAs within algorithmic trading systems designed for high-frequency decision-making processes that require rapid adaptation to shifting trends.
Practical Tips When Using an Adaptive Moving Average
To maximize effectiveness when incorporating AMP into your strategy:
- Use alongside other technical tools: Confirm signals from multiple sources before acting.
- Adjust parameters cautiously: Understand how different settings influence sensitivity levels.
- Backtest thoroughly: Test your setup across historical data relevant to your preferred assets.
- Keep abreast of market news: Technical analysis works best when complemented by fundamental insights about macroeconomic factors impacting asset prices.
- Avoid overreliance: Remember that no indicator guarantees success; always practice sound risk management principles like stop-loss orders.
Why Traders Should Consider Incorporating AMP Into Their Strategy
Given its ability to adapt dynamically based on real-time data fluctuations—and particularly useful in highly volatile environments—AMP offers several strategic advantages over traditional static moving averages:
- Better detection of trend reversals
- Reduced lag compared to simple moving averages
- Flexibility across different asset classes
However—as part of any robust investment approach—it should be combined thoughtfully with fundamental analysis techniques and other technical tools rather than used exclusively.
Final Thoughts on Adaptive Moving Averages
The Adaptive Moving Average stands out among technical indicators because of its unique capacity for self-adjustment according to prevailing market conditions—a feature increasingly valued amidst today's fast-paced financial landscape involving cryptocurrencies' wild swings along with traditional assets' evolving dynamics.
While mastering AMP requires understanding both mathematical foundations and practical application nuances—including avoiding pitfalls like overfitting—it remains a potent addition tailored toward proactive trend-following strategies suited both beginners seeking enhanced responsiveness—and seasoned professionals aiming at refined entry/exit points amid complex markets.
Keywords:Adaptive Moving Average (AMA), dynamic moving average , trend-following indicator , cryptocurrency trading , technical analysis tools , volatility adaptation , flexible indicator , signal confirmation , crypto market trends


kai
2025-05-19 04:27
What is Adaptive Moving Average (AMA)?
What Is Adaptive Moving Average (AMA)?
The Adaptive Moving Average (AMA) is a sophisticated technical indicator used by traders and investors to analyze market trends more accurately. Unlike traditional moving averages, which use a fixed period, AMA dynamically adjusts its calculation based on recent market volatility. This feature allows it to respond swiftly during volatile periods and smooth out noise during calmer times, making it a valuable tool for navigating complex financial markets such as cryptocurrencies and stocks.
How Does the Adaptive Moving Average Work?
At its core, the AMA begins with an initial fixed period similar to a Simple Moving Average (SMA). However, what sets it apart is its ability to adapt this period over time. The adjustment process involves analyzing recent price changes: when prices exhibit high volatility—meaning large swings—the AMA shortens its period to become more sensitive; conversely, during low volatility phases with minimal price fluctuations, it lengthens the period for smoother signals.
This dynamic adjustment helps traders identify trend shifts more effectively. For example, if the AMA crosses above or below the current price or other indicators like RSI or MACD, traders interpret these as potential buy or sell signals. Because of this adaptability, AMA can better capture real-time market movements compared to static moving averages.
Historical Context of Adaptive Moving Averages
Introduced in the 1990s by technical analysts seeking improved trend-following tools, AMA gained traction among professional traders who needed more responsive indicators in volatile markets. Its popularity surged in the early 2000s as trading platforms integrated advanced algorithms capable of calculating adaptive averages efficiently.
Initially used primarily in stock markets and forex trading environments where volatility could be predictable within certain ranges, AMA's flexibility made it especially appealing for commodities and futures trading as well. Over time, with technological advancements and increased computational power available on trading platforms—and later through algorithmic trading—AMA became accessible even for retail investors.
Advantages of Using an Adaptive Moving Average
One significant benefit of using an AMA lies in its responsiveness; because it adjusts according to recent market conditions rather than sticking rigidly to a preset window size:
- Enhanced Responsiveness: It reacts quickly during sudden price movements.
- Better Trend Detection: It adapts smoothly between trending phases and sideways consolidations.
- Versatility Across Markets: Suitable for various asset classes including cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum due to their high volatility.
Additionally, combining AMA with other technical indicators such as Bollinger Bands or RSI can improve trade accuracy by confirming signals generated through multiple analysis layers.
Limitations & Challenges
Despite its advantages, there are some limitations that traders should consider:
- Complexity: Understanding how adaptive periods are calculated requires familiarity with advanced mathematical concepts.
- Overfitting Risks: Excessive sensitivity might lead some traders into reacting prematurely or chasing false signals caused by short-term noise.
- Market Conditions Dependency: In extremely unpredictable markets—like crypto during sudden crashes—AMA may generate conflicting signals that need careful interpretation alongside fundamental analysis.
Therefore, while powerful when used correctly within comprehensive strategies—including risk management practices—it’s essential not solely rely on AMAs but incorporate them into broader analytical frameworks.
Recent Trends: Cryptocurrency Trading & Beyond
In recent years especially within cryptocurrency markets characterized by extreme volatility—such as Bitcoin’s rapid swings—the adoption of adaptive tools like AMA has increased significantly. Traders appreciate how quickly AMAs adjust their sensitivity levels without manual intervention—a crucial feature amid fast-changing crypto landscapes.
Many experienced crypto traders combine AMAs with momentum indicators like MACD or oscillators such as RSI for confirmation purposes before executing trades. This multi-layered approach helps mitigate false positives often associated with single-indicator strategies while leveraging AMAs’ responsiveness for timely entries and exits.
Beyond cryptocurrencies — traditional assets including stocks and forex also benefit from using AMAs within algorithmic trading systems designed for high-frequency decision-making processes that require rapid adaptation to shifting trends.
Practical Tips When Using an Adaptive Moving Average
To maximize effectiveness when incorporating AMP into your strategy:
- Use alongside other technical tools: Confirm signals from multiple sources before acting.
- Adjust parameters cautiously: Understand how different settings influence sensitivity levels.
- Backtest thoroughly: Test your setup across historical data relevant to your preferred assets.
- Keep abreast of market news: Technical analysis works best when complemented by fundamental insights about macroeconomic factors impacting asset prices.
- Avoid overreliance: Remember that no indicator guarantees success; always practice sound risk management principles like stop-loss orders.
Why Traders Should Consider Incorporating AMP Into Their Strategy
Given its ability to adapt dynamically based on real-time data fluctuations—and particularly useful in highly volatile environments—AMP offers several strategic advantages over traditional static moving averages:
- Better detection of trend reversals
- Reduced lag compared to simple moving averages
- Flexibility across different asset classes
However—as part of any robust investment approach—it should be combined thoughtfully with fundamental analysis techniques and other technical tools rather than used exclusively.
Final Thoughts on Adaptive Moving Averages
The Adaptive Moving Average stands out among technical indicators because of its unique capacity for self-adjustment according to prevailing market conditions—a feature increasingly valued amidst today's fast-paced financial landscape involving cryptocurrencies' wild swings along with traditional assets' evolving dynamics.
While mastering AMP requires understanding both mathematical foundations and practical application nuances—including avoiding pitfalls like overfitting—it remains a potent addition tailored toward proactive trend-following strategies suited both beginners seeking enhanced responsiveness—and seasoned professionals aiming at refined entry/exit points amid complex markets.
Keywords:Adaptive Moving Average (AMA), dynamic moving average , trend-following indicator , cryptocurrency trading , technical analysis tools , volatility adaptation , flexible indicator , signal confirmation , crypto market trends
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is a Blockchain Oracle Network and How Is Decentralization Ensured?
Understanding Blockchain Oracle Networks
A blockchain oracle network is a vital infrastructure component that connects smart contracts with external data sources. In the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem, smart contracts are self-executing agreements that automatically trigger actions based on predefined conditions. However, these contracts cannot inherently access real-world information such as weather data, stock prices, or sports results. This is where blockchain oracle networks come into play—they serve as bridges that securely fetch and deliver external data to smart contracts.
The core function of an oracle network is to provide accurate, reliable, and tamper-proof data inputs for blockchain applications. Without oracles, the potential of smart contracts would be limited to on-chain information only—rendering many DeFi applications impractical or impossible. For example, decentralized insurance platforms rely heavily on real-world event verification; without trustworthy oracles delivering this data, claims processing could become unreliable.
How Do Blockchain Oracles Work?
The operation of a blockchain oracle network involves several key steps:
- Data Collection: External sources such as APIs from financial markets, sensors in IoT devices, or public databases gather relevant information.
- Relay Nodes: These nodes act as intermediaries that transmit collected data into the oracle network.
- Verification Process: Multiple nodes verify the accuracy and integrity of incoming data through consensus mechanisms.
- Feeding Data into Smart Contracts: Once verified, the trusted data is fed into specific smart contracts on the blockchain platform for execution.
This process ensures that only validated information influences contract outcomes—an essential feature for maintaining trustworthiness in decentralized systems.
Ensuring Decentralization in Oracle Networks
Decentralization remains at the heart of blockchain technology’s appeal because it reduces reliance on single points of failure and mitigates risks associated with centralized control. Achieving decentralization within oracle networks involves several strategies:
Distributed Architecture: Instead of relying on a single node or entity to provide external data, multiple independent nodes participate in collecting and verifying information. This distribution prevents any one party from manipulating outcomes.
Consensus Mechanisms: Protocols like proof-of-stake (PoS) or proof-of-work (PoW) are employed among relay nodes to agree upon which data should be accepted by smart contracts. These mechanisms ensure collective validation rather than trusting individual sources blindly.
Multi-Signature Security: Some networks implement multi-signature wallets requiring multiple signatures before feeding data into a contract—adding an extra layer of security against malicious actors.
Open-Source Development: Many oracle solutions operate under open-source licenses allowing community audits and contributions—further enhancing transparency and decentralization by enabling continuous security improvements.
Recent Innovations in Blockchain Oracles
Over recent years, notable developments have advanced how decentralized oracles operate across different blockchains:
In 2020, Chainlink emerged as one of the most prominent players by introducing its hybrid model combining both off-chain (external API calls) and on-chain components to improve reliability while maintaining decentralization standards.
The following year saw Polkadot launching its own dedicated oracle solution designed for interoperability between various blockchains—a crucial step toward seamless cross-chain communication essential for complex DeFi ecosystems.
Cosmos joined this movement in 2022 by developing its own robust decentralized oracle service utilizing Tendermint Core consensus algorithms aimed at fostering secure inter-blockchain communication within its ecosystem.
Despite these advancements’ benefits—such as increased accuracy and interoperability—the space has also faced challenges related to security vulnerabilities exposed through attacks targeting certain protocols’ codebases.
Security Concerns & Risks
While blockchain oracles enable powerful functionalities within DeFi platforms—and beyond—they introduce unique security considerations:
External Data Manipulation: Malicious actors may attempt to feed false information if not properly verified.
Hacking Attacks: Vulnerabilities within relay nodes’ code can be exploited leading to compromised datasets; recent incidents have resulted in significant financial losses during 2023 due to such breaches.
These risks underscore why continuous security audits are critical alongside implementing multi-layered verification processes—a necessity reinforced by ongoing research into resilient consensus algorithms tailored specifically for decentralized oracles.
Potential Challenges Facing Oracle Networks
As demand grows for real-time accurate external data across diverse applications—from gaming platforms to supply chain management—the scalability limitations become apparent:
- Increased latency can delay transaction execution
- Higher throughput requirements strain existing infrastructure
- Maintaining trustworthiness amid rapid updates demands sophisticated validation techniques
Addressing these issues requires ongoing innovation around protocol design—including off-chain computation solutions—and collaborative efforts among developers worldwide aiming at creating more resilient architectures capable of handling future growth efficiently.
The Role Of Blockchain Oracles In Decentralized Ecosystems
Blockchain oracle networks underpin many innovative use cases beyond simple financial transactions—they enable complex interactions involving real-world events seamlessly integrated with digital assets:
Decentralized Insurance: Claims processing based on verified weather reportsPrediction Markets: Accurate event outcome reportingSupply Chain Management: Authenticity verification via sensor-based tracking
By providing trustworthy external inputs while preserving decentralization principles through distributed architecture models—which prevent single points of failure—these networks foster greater trustworthiness across entire ecosystems.
Future Outlook And Industry Trends
Looking ahead from 2024 onward,the importance of secure , scalable ,and interoperableoracle solutions will intensify given their central role in expanding DeFi capabilities globally . Emerging trends include:
- Adoption of cross-chain compatible protocols facilitating broader interoperability
- Enhanced focus on cybersecurity measures including formal verification methods
- Integration with AI-driven analytics for smarter decision-making
Moreover,the evolution toward fully autonomous “oracle-as-a-service” models promises simplified deployment coupled with improved resilience against attacks—all contributing towards more robust decentralized applications.
Building Trust Through Transparency And Security Standards
Maintaining user confidence hinges upon rigorous transparency practices:
- Open-source codebases allow community review
- Regular third-party audits identify vulnerabilities proactively
- Clear governance frameworks define responsibility sharing
Such measures align with industry best practices aimed at reinforcing trustworthiness—a critical factor given increasing regulatory scrutiny over DeFi operations.
Final Thoughts
Blockchain oracle networks stand at a pivotal intersection where technological innovation meets fundamental principles like decentralization and security . As they continue evolving amidst emerging threats—and opportunities—they will remain indispensable tools powering next-generation decentralized applications across finance,supply chains,and beyond . Ensuring their robustness through transparent development practices will be key drivers shaping their future trajectory.
Keywords: Blockchain Oracle Network | Decentralized Data Feeds | Smart Contract Integration | Cross-chain Compatibility | Security Audits | Open-source Protocols


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-09 18:08
What is a blockchain oracle network and how is decentralization ensured?
What Is a Blockchain Oracle Network and How Is Decentralization Ensured?
Understanding Blockchain Oracle Networks
A blockchain oracle network is a vital infrastructure component that connects smart contracts with external data sources. In the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem, smart contracts are self-executing agreements that automatically trigger actions based on predefined conditions. However, these contracts cannot inherently access real-world information such as weather data, stock prices, or sports results. This is where blockchain oracle networks come into play—they serve as bridges that securely fetch and deliver external data to smart contracts.
The core function of an oracle network is to provide accurate, reliable, and tamper-proof data inputs for blockchain applications. Without oracles, the potential of smart contracts would be limited to on-chain information only—rendering many DeFi applications impractical or impossible. For example, decentralized insurance platforms rely heavily on real-world event verification; without trustworthy oracles delivering this data, claims processing could become unreliable.
How Do Blockchain Oracles Work?
The operation of a blockchain oracle network involves several key steps:
- Data Collection: External sources such as APIs from financial markets, sensors in IoT devices, or public databases gather relevant information.
- Relay Nodes: These nodes act as intermediaries that transmit collected data into the oracle network.
- Verification Process: Multiple nodes verify the accuracy and integrity of incoming data through consensus mechanisms.
- Feeding Data into Smart Contracts: Once verified, the trusted data is fed into specific smart contracts on the blockchain platform for execution.
This process ensures that only validated information influences contract outcomes—an essential feature for maintaining trustworthiness in decentralized systems.
Ensuring Decentralization in Oracle Networks
Decentralization remains at the heart of blockchain technology’s appeal because it reduces reliance on single points of failure and mitigates risks associated with centralized control. Achieving decentralization within oracle networks involves several strategies:
Distributed Architecture: Instead of relying on a single node or entity to provide external data, multiple independent nodes participate in collecting and verifying information. This distribution prevents any one party from manipulating outcomes.
Consensus Mechanisms: Protocols like proof-of-stake (PoS) or proof-of-work (PoW) are employed among relay nodes to agree upon which data should be accepted by smart contracts. These mechanisms ensure collective validation rather than trusting individual sources blindly.
Multi-Signature Security: Some networks implement multi-signature wallets requiring multiple signatures before feeding data into a contract—adding an extra layer of security against malicious actors.
Open-Source Development: Many oracle solutions operate under open-source licenses allowing community audits and contributions—further enhancing transparency and decentralization by enabling continuous security improvements.
Recent Innovations in Blockchain Oracles
Over recent years, notable developments have advanced how decentralized oracles operate across different blockchains:
In 2020, Chainlink emerged as one of the most prominent players by introducing its hybrid model combining both off-chain (external API calls) and on-chain components to improve reliability while maintaining decentralization standards.
The following year saw Polkadot launching its own dedicated oracle solution designed for interoperability between various blockchains—a crucial step toward seamless cross-chain communication essential for complex DeFi ecosystems.
Cosmos joined this movement in 2022 by developing its own robust decentralized oracle service utilizing Tendermint Core consensus algorithms aimed at fostering secure inter-blockchain communication within its ecosystem.
Despite these advancements’ benefits—such as increased accuracy and interoperability—the space has also faced challenges related to security vulnerabilities exposed through attacks targeting certain protocols’ codebases.
Security Concerns & Risks
While blockchain oracles enable powerful functionalities within DeFi platforms—and beyond—they introduce unique security considerations:
External Data Manipulation: Malicious actors may attempt to feed false information if not properly verified.
Hacking Attacks: Vulnerabilities within relay nodes’ code can be exploited leading to compromised datasets; recent incidents have resulted in significant financial losses during 2023 due to such breaches.
These risks underscore why continuous security audits are critical alongside implementing multi-layered verification processes—a necessity reinforced by ongoing research into resilient consensus algorithms tailored specifically for decentralized oracles.
Potential Challenges Facing Oracle Networks
As demand grows for real-time accurate external data across diverse applications—from gaming platforms to supply chain management—the scalability limitations become apparent:
- Increased latency can delay transaction execution
- Higher throughput requirements strain existing infrastructure
- Maintaining trustworthiness amid rapid updates demands sophisticated validation techniques
Addressing these issues requires ongoing innovation around protocol design—including off-chain computation solutions—and collaborative efforts among developers worldwide aiming at creating more resilient architectures capable of handling future growth efficiently.
The Role Of Blockchain Oracles In Decentralized Ecosystems
Blockchain oracle networks underpin many innovative use cases beyond simple financial transactions—they enable complex interactions involving real-world events seamlessly integrated with digital assets:
Decentralized Insurance: Claims processing based on verified weather reportsPrediction Markets: Accurate event outcome reportingSupply Chain Management: Authenticity verification via sensor-based tracking
By providing trustworthy external inputs while preserving decentralization principles through distributed architecture models—which prevent single points of failure—these networks foster greater trustworthiness across entire ecosystems.
Future Outlook And Industry Trends
Looking ahead from 2024 onward,the importance of secure , scalable ,and interoperableoracle solutions will intensify given their central role in expanding DeFi capabilities globally . Emerging trends include:
- Adoption of cross-chain compatible protocols facilitating broader interoperability
- Enhanced focus on cybersecurity measures including formal verification methods
- Integration with AI-driven analytics for smarter decision-making
Moreover,the evolution toward fully autonomous “oracle-as-a-service” models promises simplified deployment coupled with improved resilience against attacks—all contributing towards more robust decentralized applications.
Building Trust Through Transparency And Security Standards
Maintaining user confidence hinges upon rigorous transparency practices:
- Open-source codebases allow community review
- Regular third-party audits identify vulnerabilities proactively
- Clear governance frameworks define responsibility sharing
Such measures align with industry best practices aimed at reinforcing trustworthiness—a critical factor given increasing regulatory scrutiny over DeFi operations.
Final Thoughts
Blockchain oracle networks stand at a pivotal intersection where technological innovation meets fundamental principles like decentralization and security . As they continue evolving amidst emerging threats—and opportunities—they will remain indispensable tools powering next-generation decentralized applications across finance,supply chains,and beyond . Ensuring their robustness through transparent development practices will be key drivers shaping their future trajectory.
Keywords: Blockchain Oracle Network | Decentralized Data Feeds | Smart Contract Integration | Cross-chain Compatibility | Security Audits | Open-source Protocols
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
👉 Trade Now: https://bit.ly/4eDheON


JuCoin Community
2025-08-06 07:39
📈 Another milestone unlocked! $JU breaks through $13!!
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
📅 August 5 2025
🎉 Stay updated with the latest crypto market trends!
👉 Trade on:https://bit.ly/3DFYq30
👉 X:https://twitter.com/Jucoinex
👉 APP download: https://www.jucoin.com/en/community-downloads
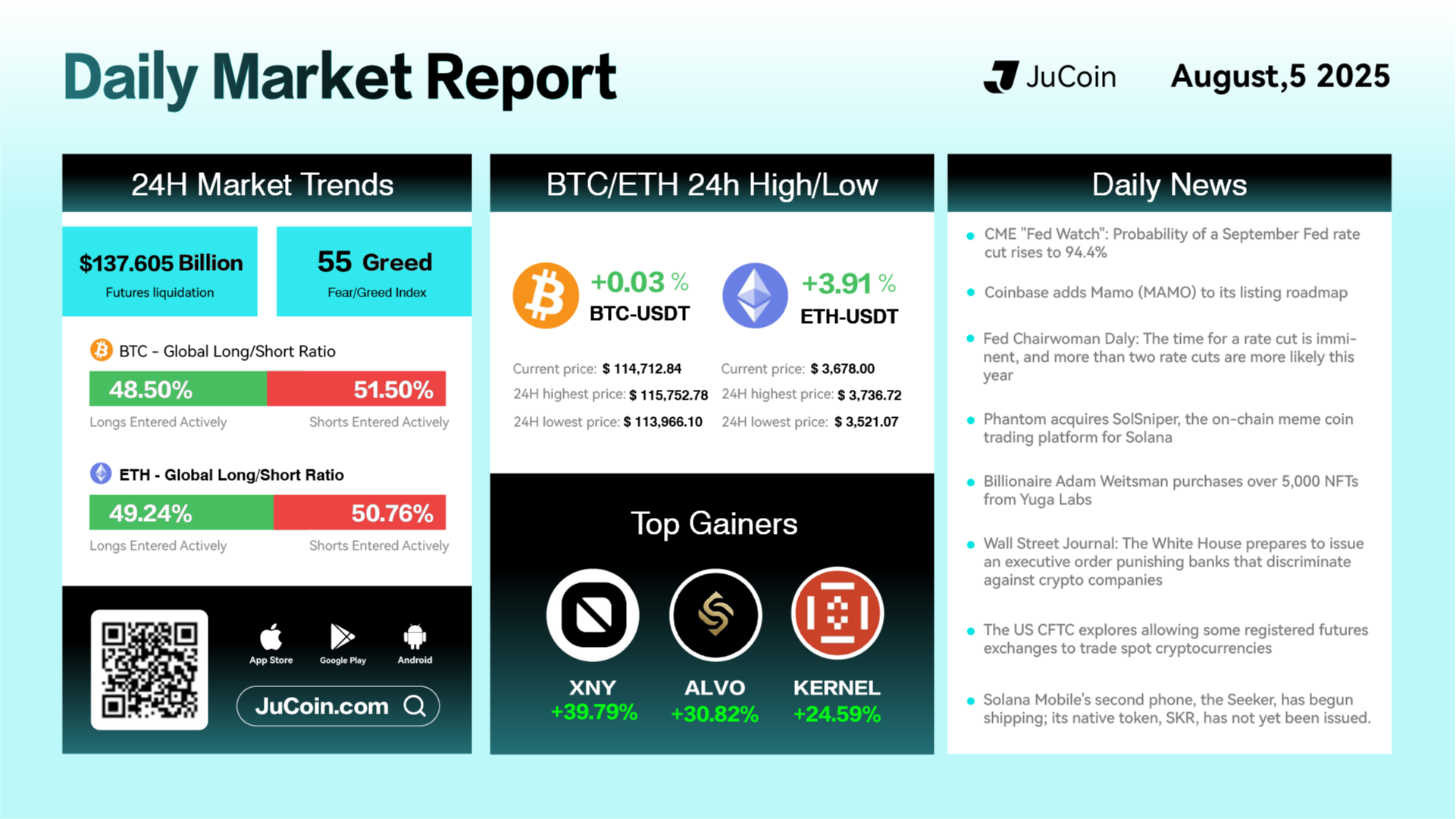


JuCoin Community
2025-08-05 04:32
🚀 #JuCoin Daily Market Report
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
💚12 new spot listings added
💚8 campaigns launched this week
💚Platform token $JU surged over 6.33%
Stay connected with JuCoin and never miss an update!
👉 Register Now:https://www.jucoin.online/en/accounts/register?ref=MR6KTR
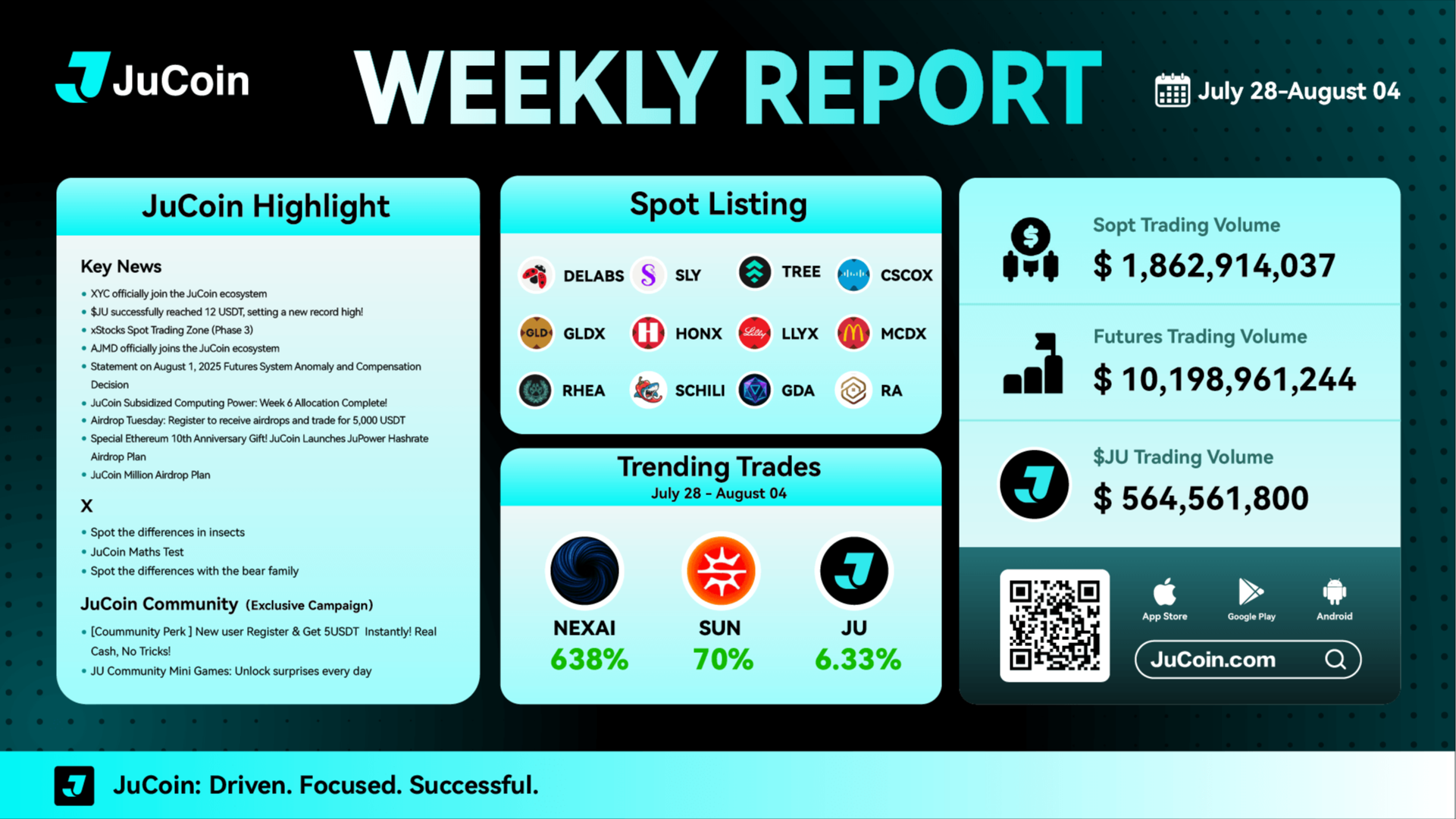


JuCoin Community
2025-08-04 09:41
👌JuCoin Weekly Report | July 28 – August 3 🔥
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Exclusive community benefits are here! Invite 5+ friends to join JuCoin, climb the leaderboard, and earn USDT rewards!
⏰ Event Period:August 4, 08:00 – August 11, 08:00 (UTC)
🏆 Rewards for Top 5:
🥇 1st Place: $50 USDT
🥈 2nd Place: $40 USDT
🥉 3rd Place: $30 USDT
🏅 4th Place: $20 USDT
🏅 5th Place: $10 USDT
✅ How to Participate:
1️⃣ Log in to JuCoin and get your unique referral link.
2️⃣ Share your link – friends must register + complete KYC.
3️⃣ Reach 5+ valid invites to qualify for the leaderboard.
4️⃣ Submit your JuCoin UID to confirm entry:👉 https://forms.gle/vGi6c9LAksggH68D6
❗ Important Notice:
• Fraudulent activity (e.g., fake/bulk accounts) will result in immediate disqualification.
• Rewards will be distributed to winners’ JuCoin accounts after verification.
🚀 Start inviting now – dominate the leaderboard and claim your USDT!



JuCoin Community
2025-08-04 08:40
🔥 JuCoin Community Contest: Invite Friends & Win USDT! 🔥
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
👌JuCoin will list the CMEW/USDT trading pair on August 7, 2025
🔹 Deposit: August 6, 2025 at 04:00 (UTC)
🔹 Trading: August 7, 2025 at 09:00 (UTC)
🔹 Withdrawal: August 8, 2025 at 09:00 (UTC)
🪧More:https://bit.ly/458FkfG



JuCoin Community
2025-08-04 07:45
📢 New Listing|CMEW (CelestialMew) 🔥
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
JuCoin is pleased to announce the launch of xStocks Spot Trading (Phase 4 on Aug. 4, 2025. We welcome all users to participate in trading. Below are the details:
🔹Trading Pairs: ABBVX/USDT、ACNX/USDT、AZNX/USDT、CMCSAX/USDT、CRWDX/USDT、HDX/USDT、KOX/USDT、NFLXX/USDT、PEPX/USDT、PGX/USDT、UNHX/USDT、VTIX/USDT
🔹Trading Time: Aug. 4, 2025 at 07:00 (UTC)
👉 More: https://bit.ly/3U8VIYP



JuCoin Community
2025-08-04 04:34
🚨 xStocks Spot Trading Zone (Phase 4)
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
BTC with his tank, ETH guy chilling, and gold-suit investor pretending all’s fine 😬 Same train, same goal — protect the bag 💼 Different look, same fear
Check out our YouTube Channel 👉
#BitcoinVsGold #AssetProtection #CryptoContrast


JuCoin Media
2025-08-01 11:30
Spot the difference: Bitcoin vs Gold holders 🛤️
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Bitcoin Profit — every bull run cycle hits the same 😅 "This is my last year broke..." Meanwhile the house is collapsing behind you 🫠 Hopium never dies, even when profits do 🙃
Check out our YouTube Channel 👉
#BullRunCycle #BitcoinProfit #HopiumLives


JuCoin Media
2025-08-01 11:13
Hoping for That Bitcoin Profit Every Bull Run Cycle 📈
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Succinct Network combines the world's fastest zkVM (SP1) with a decentralized marketplace for proof generation, making zero-knowledge proofs accessible to mainstream developers without deep cryptographic expertise.
💰 Key Highlights:
-
World's Fastest zkVM: SP1 is 28x faster than competing zkVMs on real-world workloads
PROVE Token Economics: Payment medium + staking security + governance rights
Real-Time Ethereum Proving: Under 40 seconds per block, 93% success rate with 200 RTX 4090s
$55M Series A: Led by Paradigm, demonstrating strong institutional confidence
🎯 Technical Breakthroughs:
-
SP1 Turbo (v4.0.0): Blazing fast performance with precompile-centric architecture
SP1 Hypercube: Sub-12-second Ethereum block proving milestone
Developer-Friendly: Write normal Rust code, automatically generate ZK proofs
100% Open Source: MIT licensed, all constraint logic public
🏆 Market Position:
-
Major Integrations: Polygon, Celestia, Avail, Taiko already using SP1
$1B+ TVL: Securing over $1 billion in total value locked
AggLayer Partnership: Will use SP1 for pessimistic proofs
💡 Use Cases:
-
ZK Rollups: Reduce finality from 7 days to minutes
Cross-Chain Bridges: Trustless blockchain interoperability
Verifiable AI: Cryptographic proof of AI model outputs
Privacy Identity: Verification without revealing sensitive data
Enterprise Auditing: Prove compliance without exposing proprietary data
⏰ Development Timeline:
-
Current: Testnet Stage 2
Coming Soon: Stage 2.5 with competitive auctions
February 10, 2025: "Crisis of Trust" testnet program launch
Future: Mainnet with full PROVE token functionality
⚠️ Investment Risks:
-
Technical competition (RISC Zero, Jolt, Nexus)
Computational resource requirements for real-time proving
Regulatory uncertainty around ZK privacy capabilities
Enterprise adoption timeline dependencies
🔥 Why It Matters: This democratization of ZK technology mirrors how cloud computing made enterprise infrastructure accessible to all developers. SP1's breakthrough performance enables real-time verification for next-gen blockchain applications.
PROVE token launch marks a significant milestone in decentralizing ZK infrastructure, potentially creating the economic foundation for verifiable applications across blockchain and traditional computing.
Read our complete technical analysis and investment guide: 👇
https://blog.jucoin.com/succinct-network-zkvm-prove-token/?utm_source=blog
#SuccinctNetwork #SP1 #PROVE #zkVM #ZeroKnowledge #Blockchain #Scalability #Polygon #Ethereum #Layer2 #ZKRollups #CrossChain #JuCoin #Web3 #Crypto #Decentralized #Paradigm #VerifiableAI #Privacy



JU Blog
2025-08-01 08:49
🚀 Succinct Network: Revolutionary SP1 zkVM & PROVE Token Launch!
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
👌JuCoin to List GDA/HI Trading Pair on August 18, 2025
🔷Deposit Time: August 17, 2025 at 09:00 (UTC)
🔷Trading Time: August 18, 2025 at 09:00 (UTC)
🔷Withdrawal Time: August 19, 2025 at 09:00 (UTC)
👉 More Detail:https://bit.ly/45jcyJv



JuCoin Community
2025-08-01 06:47
📢New Listing
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
🐣 New to Crypto? Start Here!
🔸 1-min to know what #FUD is → https://youtube.com/shorts/i6s2QQ9XEDw?feature=share
📌 Bookmark this thread – your ultimate starter kit👇
#CryptoBeginner #Blockchain101 #LearnWeb3



JuCoin Official
2025-07-31 09:12
🐣 New to Crypto? Start Here!
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
