Popular Posts
What Is the Intraday Intensity Index and How Do You Interpret Its Values?
Understanding market volatility and momentum is crucial for traders and investors aiming to make informed decisions. One technical analysis tool gaining popularity in recent years is the Intraday Intensity Index (I3). Originally developed for traditional stock markets, this index has found a significant role in cryptocurrency trading due to its ability to capture rapid price movements within a single trading day. This article explores what the I3 is, how it’s calculated, and how traders can interpret its values effectively.
What Is the Intraday Intensity Index?
The Intraday Intensity Index (I3) measures the intensity of price movements during a trading day. Unlike traditional indicators that focus on closing prices or daily averages, I3 emphasizes intraday fluctuations—specifically, how many times prices exceed certain percentage thresholds within a single session. It provides insights into market volatility and momentum by quantifying how active or subdued intraday price changes are.
In practical terms, traders analyze multiple short-term price bars—such as 1-minute or 5-minute intervals—and count those that surpass predefined percentage changes (like 1%, 2%, or more). The resulting data can be visualized as histograms or line charts that highlight periods of heightened activity versus calmer phases during the trading day.
How Is the I3 Calculated?
Calculating the Intraday Intensity Index involves several steps:
- Defining Thresholds: Traders select specific percentage change levels (e.g., 1%, 2%, 5%) based on their trading style and asset characteristics.
- Counting Price Bars: During a given session, they count how many individual bars exceed these thresholds.
- Normalizing Data: The counts are then normalized—often divided by total number of bars—to produce an index value between zero and one.
- Visualization: These values are plotted over time to identify patterns of high or low intraday activity.
Different calculation methods exist; some may incorporate volume data alongside price changes for more nuanced insights. However, most focus on frequency—the number of significant moves—and magnitude—the size of those moves—to gauge overall market intensity.
Interpreting High vs. Low I3 Values
The core utility of the I3 lies in understanding what different values indicate about current market conditions:
High I3 Values: When this index shows elevated readings, it suggests increased intraday volatility with frequent large price swings. Such periods often reflect heightened trader activity driven by news events, economic releases, or speculative interest—especially prevalent in cryptocurrency markets where rapid shifts are common.
Low I3 Values: Conversely, lower readings imply subdued market activity with fewer significant intraday moves. This environment might indicate consolidation phases where prices stabilize before potential breakouts or breakdowns occur.
Traders often use these signals to adjust their strategies—for example:
During high I3 periods: Consider short-term trades capitalizing on quick reversals but remain cautious about increased risk.
During low I3 periods: Focus on longer-term positions waiting for clearer breakout signals once volatility picks up again.
Practical Applications in Trading Strategies
Integrating the Intraday Intensity Index into your trading toolkit can enhance decision-making:
Entry & Exit Points: Sharp increases in I3 may signal upcoming trend reversals or continuation patterns worth acting upon quickly.
Risk Management: Recognizing high-volatility phases helps set appropriate stop-loss levels to protect against sudden adverse moves.
Market Sentiment Analysis: When combined with other indicators like volume analysis or moving averages, it offers deeper insights into overall market sentiment—whether buyers dominate sellers during volatile swings or vice versa.
In cryptocurrency markets especially—which exhibit frequent rapid fluctuations—the adaptation of traditional tools like the I3 has proven valuable for algorithmic systems aiming at real-time decision-making without human bias.
Recent Trends & Developments
Since its inception around 2010–2012 for stock markets and later adaptation around 2017–2018 for cryptocurrencies, interest in using indices like the I3 has surged amid evolving digital assets landscapes. Modern platforms now incorporate automated algorithms that monitor real-time intra-day data through indices such as this one to execute trades swiftly based on detected volatility spikes.
Furthermore:
Many crypto exchanges have integrated customized versions of similar indices tailored specifically for digital assets’ unique behavior.
Combining multiple technical indicators—including relative strength indexes (RSI), Bollinger Bands®, along with intra-day intensity metrics—has become standard practice among professional traders seeking comprehensive insight.
Limitations & Cautions When Using The Index
While powerful when used correctly, relying solely on any single indicator carries risks:
Over-trading: Excessive focus during high-I3 periods might lead traders into overtrading due to perceived opportunities but ignoring underlying fundamentals could increase losses.
False Signals: Sudden spikes may sometimes be false alarms caused by temporary liquidity issues rather than genuine trend shifts—a phenomenon common in thinly traded crypto tokens too small to sustain large swings sustainably.
Therefore:
- Always combine your analysis with broader context including fundamental factors,
- Use proper risk management techniques,
- And consider multiple timeframes before making decisive trades.
Final Thoughts
The Intraday Intensity Index offers valuable insights into intra-session market dynamics by quantifying how intense recent price movements are within a single day. Its interpretation hinges largely on recognizing whether current conditions suggest heightened volatility—or relative calm—and adjusting strategies accordingly. As both stock and crypto markets continue evolving toward faster-paced environments fueled by technological advances like algorithmic trading platforms — tools such as this index will likely grow even more integral for proactive traders seeking an edge amidst rapid fluctuations.
Keywords: Intraday Intensity Index explanation | interpreting intraday volatility | intra-day trading signals | crypto market analysis tools | technical analysis indices


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-09 21:12
What is the Intraday Intensity Index and how do you interpret its values?
What Is the Intraday Intensity Index and How Do You Interpret Its Values?
Understanding market volatility and momentum is crucial for traders and investors aiming to make informed decisions. One technical analysis tool gaining popularity in recent years is the Intraday Intensity Index (I3). Originally developed for traditional stock markets, this index has found a significant role in cryptocurrency trading due to its ability to capture rapid price movements within a single trading day. This article explores what the I3 is, how it’s calculated, and how traders can interpret its values effectively.
What Is the Intraday Intensity Index?
The Intraday Intensity Index (I3) measures the intensity of price movements during a trading day. Unlike traditional indicators that focus on closing prices or daily averages, I3 emphasizes intraday fluctuations—specifically, how many times prices exceed certain percentage thresholds within a single session. It provides insights into market volatility and momentum by quantifying how active or subdued intraday price changes are.
In practical terms, traders analyze multiple short-term price bars—such as 1-minute or 5-minute intervals—and count those that surpass predefined percentage changes (like 1%, 2%, or more). The resulting data can be visualized as histograms or line charts that highlight periods of heightened activity versus calmer phases during the trading day.
How Is the I3 Calculated?
Calculating the Intraday Intensity Index involves several steps:
- Defining Thresholds: Traders select specific percentage change levels (e.g., 1%, 2%, 5%) based on their trading style and asset characteristics.
- Counting Price Bars: During a given session, they count how many individual bars exceed these thresholds.
- Normalizing Data: The counts are then normalized—often divided by total number of bars—to produce an index value between zero and one.
- Visualization: These values are plotted over time to identify patterns of high or low intraday activity.
Different calculation methods exist; some may incorporate volume data alongside price changes for more nuanced insights. However, most focus on frequency—the number of significant moves—and magnitude—the size of those moves—to gauge overall market intensity.
Interpreting High vs. Low I3 Values
The core utility of the I3 lies in understanding what different values indicate about current market conditions:
High I3 Values: When this index shows elevated readings, it suggests increased intraday volatility with frequent large price swings. Such periods often reflect heightened trader activity driven by news events, economic releases, or speculative interest—especially prevalent in cryptocurrency markets where rapid shifts are common.
Low I3 Values: Conversely, lower readings imply subdued market activity with fewer significant intraday moves. This environment might indicate consolidation phases where prices stabilize before potential breakouts or breakdowns occur.
Traders often use these signals to adjust their strategies—for example:
During high I3 periods: Consider short-term trades capitalizing on quick reversals but remain cautious about increased risk.
During low I3 periods: Focus on longer-term positions waiting for clearer breakout signals once volatility picks up again.
Practical Applications in Trading Strategies
Integrating the Intraday Intensity Index into your trading toolkit can enhance decision-making:
Entry & Exit Points: Sharp increases in I3 may signal upcoming trend reversals or continuation patterns worth acting upon quickly.
Risk Management: Recognizing high-volatility phases helps set appropriate stop-loss levels to protect against sudden adverse moves.
Market Sentiment Analysis: When combined with other indicators like volume analysis or moving averages, it offers deeper insights into overall market sentiment—whether buyers dominate sellers during volatile swings or vice versa.
In cryptocurrency markets especially—which exhibit frequent rapid fluctuations—the adaptation of traditional tools like the I3 has proven valuable for algorithmic systems aiming at real-time decision-making without human bias.
Recent Trends & Developments
Since its inception around 2010–2012 for stock markets and later adaptation around 2017–2018 for cryptocurrencies, interest in using indices like the I3 has surged amid evolving digital assets landscapes. Modern platforms now incorporate automated algorithms that monitor real-time intra-day data through indices such as this one to execute trades swiftly based on detected volatility spikes.
Furthermore:
Many crypto exchanges have integrated customized versions of similar indices tailored specifically for digital assets’ unique behavior.
Combining multiple technical indicators—including relative strength indexes (RSI), Bollinger Bands®, along with intra-day intensity metrics—has become standard practice among professional traders seeking comprehensive insight.
Limitations & Cautions When Using The Index
While powerful when used correctly, relying solely on any single indicator carries risks:
Over-trading: Excessive focus during high-I3 periods might lead traders into overtrading due to perceived opportunities but ignoring underlying fundamentals could increase losses.
False Signals: Sudden spikes may sometimes be false alarms caused by temporary liquidity issues rather than genuine trend shifts—a phenomenon common in thinly traded crypto tokens too small to sustain large swings sustainably.
Therefore:
- Always combine your analysis with broader context including fundamental factors,
- Use proper risk management techniques,
- And consider multiple timeframes before making decisive trades.
Final Thoughts
The Intraday Intensity Index offers valuable insights into intra-session market dynamics by quantifying how intense recent price movements are within a single day. Its interpretation hinges largely on recognizing whether current conditions suggest heightened volatility—or relative calm—and adjusting strategies accordingly. As both stock and crypto markets continue evolving toward faster-paced environments fueled by technological advances like algorithmic trading platforms — tools such as this index will likely grow even more integral for proactive traders seeking an edge amidst rapid fluctuations.
Keywords: Intraday Intensity Index explanation | interpreting intraday volatility | intra-day trading signals | crypto market analysis tools | technical analysis indices
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is Out-of-Sample Validation in Machine Learning?
Out-of-sample validation is a fundamental process in machine learning that assesses how well a model performs on data it has never seen before. Unlike training data, which the model learns from, out-of-sample data acts as a test to evaluate the model’s ability to generalize beyond its initial training environment. This step is crucial because it provides insights into how the model might perform in real-world scenarios, where new and unseen data are common.
In practice, out-of-sample validation helps prevent overfitting—a situation where a model performs exceptionally well on training data but poorly on new inputs. Overfitting occurs when the model captures noise or irrelevant patterns rather than underlying trends. By testing models against unseen datasets, practitioners can identify whether their models are truly capturing meaningful signals or just memorizing specific examples.
Why Is Out-of-Sample Validation Important?
The primary goal of machine learning is to develop models that generalize well to new data. Relying solely on performance metrics calculated from training datasets can be misleading because these metrics often reflect how well the model learned the specifics of that dataset rather than its predictive power overall.
Out-of-sample validation offers an unbiased estimate of this generalization capability. It ensures that models are not just fitting historical data but are also capable of making accurate predictions when deployed in real-world applications such as fraud detection, medical diagnosis, or customer segmentation. Without proper validation techniques, there’s a significant risk of deploying models that underperform once they face fresh input—potentially leading to costly errors and loss of trust.
Best Practices for Implementing Out-of-Sample Validation
To maximize reliability and robustness in your machine learning projects, following established best practices for out-of-sample validation is essential:
1. Data Splitting Strategies
Train-Test Split: The simplest approach involves dividing your dataset into two parts: one for training and one for testing (commonly 70/30 or 80/20 splits). The training set trains your model while the test set evaluates its performance on unseen data.
Holdout Method: Similar to train-test splitting but often reserved for final evaluation after tuning other parameters elsewhere during development phases.
2. Cross-Validation Techniques
K-Fold Cross-Validation: This method divides your dataset into ‘k’ equal parts (folds). The model trains on k−1 folds and tests on the remaining fold; this process repeats k times with each fold serving as a test once. Averaging results across all folds yields more stable estimates.
Stratified K-Fold: Particularly useful for classification problems with imbalanced classes; it maintains class proportions across folds ensuring representative sampling.
3. Hyperparameter Tuning Using Validation Sets
Using separate validation sets or cross-validation during hyperparameter tuning helps optimize parameters like regularization strength or tree depth without biasing performance estimates derived from final testing procedures.
4. Selecting Appropriate Evaluation Metrics
Choosing relevant metrics aligned with your problem type enhances interpretability:
- For classification: accuracy, precision, recall, F1 score
- For regression: mean squared error (MSE), mean absolute error (MAE)
Using multiple metrics provides comprehensive insights into different aspects like false positives/negatives or prediction errors' magnitude.
5. Regularization and Ensemble Methods
Applying regularization techniques such as L1/L2 penalties discourages overly complex models prone to overfitting during out-of-sample evaluation stages.
Ensemble methods—like bagging (e.g., Random Forest) or boosting (e.g., Gradient Boosting)—combine multiple weak learners into stronger ones capable of better generalization across diverse datasets tested outside initial training samples.
Recent Developments Enhancing Out-of-Sample Validation
The landscape of machine learning continually evolves with innovations aimed at improving out-of-sample robustness:
Deep Learning & Transfer Learning
Transfer learning leverages pre-trained neural networks trained on large datasets like ImageNet before fine-tuning them for specific tasks such as medical imaging diagnostics or natural language processing applications—substantially reducing required labeled data while enhancing out-of-sample performance by building upon generalized features learned previously.
Automated Machine Learning (AutoML)
AutoML platforms automate tasks including feature engineering, algorithm selection, hyperparameter tuning—and importantly—validation processes using sophisticated cross-validation schemes—making robust out-of-sample evaluation accessible even for non-experts.
Explainability & Model Interpretability
Advances in explainable AI help users understand why certain predictions occur—a key aspect when validating whether models rely too heavily on spurious correlations present only within their original datasets versus genuine signals expected elsewhere.
Robustness Against Adversarial Attacks
Testing models against adversarial inputs ensures they remain reliable under malicious attempts at fooling them—a form of rigorous out-of-sample testing critical in security-sensitive domains like finance and healthcare.
Ethical Considerations & Bias Detection
Outlier detection methods combined with fairness assessments help identify biases within datasets before deployment—ensuring validated models do not perpetuate discrimination when applied broadly.
Common Pitfalls That Can Undermine Out-of-Sample Validation
Despite best practices being widely adopted, several pitfalls can compromise effective validation:
Overfitting Due To Data Leakage: When information from test sets inadvertently influences training processes—for example through improper feature scaling—it leads to overly optimistic performance estimates that don’t hold up outside controlled environments.
Insufficient Data Diversity: If both training and testing sets lack diversity—for instance if they originate from similar sources—the resulting performance metrics may not reflect real-world variability accurately.
Poor Data Quality: No matter how rigorous your validation strategy is; if underlying data contains errors or biases—as missing values unaddressed—the validity of any assessment diminishes significantly.
Model Drift Over Time: As real-world conditions change over time—a phenomenon known as concept drift—the original evaluation may become outdated unless continuous monitoring through ongoing out-of-sample checks occurs.
Understanding these potential issues emphasizes why ongoing vigilance—including periodic revalidation—is vital throughout a machine learning project lifecycle.
Ensuring Reliable Model Deployment Through Effective Validation
Implementing thorough out-of-sample validation isn’t merely about achieving high scores—it’s about building trustworthy systems capable of sustained accuracy under changing conditions and diverse scenarios. Combining traditional techniques like train-test splits with advanced strategies such as cross-validation ensures comprehensive assessment coverage.
Furthermore, integrating recent developments—including transfer learning approaches suited for deep neural networks—and leveraging AutoML tools streamlines this process while maintaining rigor standards necessary for responsible AI deployment.
By prioritizing robust external evaluations alongside ethical considerations around bias detection and adversarial resilience measures—which increasingly influence regulatory frameworks—you position yourself at the forefront of responsible AI development rooted firmly in sound scientific principles.
This overview underscores that effective out-of-sampling strategies form an essential backbone supporting reliable machine learning applications today—and tomorrow—with continuous innovation driving better practices worldwide


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-09 11:58
What are best practices for out-of-sample validation?
What Is Out-of-Sample Validation in Machine Learning?
Out-of-sample validation is a fundamental process in machine learning that assesses how well a model performs on data it has never seen before. Unlike training data, which the model learns from, out-of-sample data acts as a test to evaluate the model’s ability to generalize beyond its initial training environment. This step is crucial because it provides insights into how the model might perform in real-world scenarios, where new and unseen data are common.
In practice, out-of-sample validation helps prevent overfitting—a situation where a model performs exceptionally well on training data but poorly on new inputs. Overfitting occurs when the model captures noise or irrelevant patterns rather than underlying trends. By testing models against unseen datasets, practitioners can identify whether their models are truly capturing meaningful signals or just memorizing specific examples.
Why Is Out-of-Sample Validation Important?
The primary goal of machine learning is to develop models that generalize well to new data. Relying solely on performance metrics calculated from training datasets can be misleading because these metrics often reflect how well the model learned the specifics of that dataset rather than its predictive power overall.
Out-of-sample validation offers an unbiased estimate of this generalization capability. It ensures that models are not just fitting historical data but are also capable of making accurate predictions when deployed in real-world applications such as fraud detection, medical diagnosis, or customer segmentation. Without proper validation techniques, there’s a significant risk of deploying models that underperform once they face fresh input—potentially leading to costly errors and loss of trust.
Best Practices for Implementing Out-of-Sample Validation
To maximize reliability and robustness in your machine learning projects, following established best practices for out-of-sample validation is essential:
1. Data Splitting Strategies
Train-Test Split: The simplest approach involves dividing your dataset into two parts: one for training and one for testing (commonly 70/30 or 80/20 splits). The training set trains your model while the test set evaluates its performance on unseen data.
Holdout Method: Similar to train-test splitting but often reserved for final evaluation after tuning other parameters elsewhere during development phases.
2. Cross-Validation Techniques
K-Fold Cross-Validation: This method divides your dataset into ‘k’ equal parts (folds). The model trains on k−1 folds and tests on the remaining fold; this process repeats k times with each fold serving as a test once. Averaging results across all folds yields more stable estimates.
Stratified K-Fold: Particularly useful for classification problems with imbalanced classes; it maintains class proportions across folds ensuring representative sampling.
3. Hyperparameter Tuning Using Validation Sets
Using separate validation sets or cross-validation during hyperparameter tuning helps optimize parameters like regularization strength or tree depth without biasing performance estimates derived from final testing procedures.
4. Selecting Appropriate Evaluation Metrics
Choosing relevant metrics aligned with your problem type enhances interpretability:
- For classification: accuracy, precision, recall, F1 score
- For regression: mean squared error (MSE), mean absolute error (MAE)
Using multiple metrics provides comprehensive insights into different aspects like false positives/negatives or prediction errors' magnitude.
5. Regularization and Ensemble Methods
Applying regularization techniques such as L1/L2 penalties discourages overly complex models prone to overfitting during out-of-sample evaluation stages.
Ensemble methods—like bagging (e.g., Random Forest) or boosting (e.g., Gradient Boosting)—combine multiple weak learners into stronger ones capable of better generalization across diverse datasets tested outside initial training samples.
Recent Developments Enhancing Out-of-Sample Validation
The landscape of machine learning continually evolves with innovations aimed at improving out-of-sample robustness:
Deep Learning & Transfer Learning
Transfer learning leverages pre-trained neural networks trained on large datasets like ImageNet before fine-tuning them for specific tasks such as medical imaging diagnostics or natural language processing applications—substantially reducing required labeled data while enhancing out-of-sample performance by building upon generalized features learned previously.
Automated Machine Learning (AutoML)
AutoML platforms automate tasks including feature engineering, algorithm selection, hyperparameter tuning—and importantly—validation processes using sophisticated cross-validation schemes—making robust out-of-sample evaluation accessible even for non-experts.
Explainability & Model Interpretability
Advances in explainable AI help users understand why certain predictions occur—a key aspect when validating whether models rely too heavily on spurious correlations present only within their original datasets versus genuine signals expected elsewhere.
Robustness Against Adversarial Attacks
Testing models against adversarial inputs ensures they remain reliable under malicious attempts at fooling them—a form of rigorous out-of-sample testing critical in security-sensitive domains like finance and healthcare.
Ethical Considerations & Bias Detection
Outlier detection methods combined with fairness assessments help identify biases within datasets before deployment—ensuring validated models do not perpetuate discrimination when applied broadly.
Common Pitfalls That Can Undermine Out-of-Sample Validation
Despite best practices being widely adopted, several pitfalls can compromise effective validation:
Overfitting Due To Data Leakage: When information from test sets inadvertently influences training processes—for example through improper feature scaling—it leads to overly optimistic performance estimates that don’t hold up outside controlled environments.
Insufficient Data Diversity: If both training and testing sets lack diversity—for instance if they originate from similar sources—the resulting performance metrics may not reflect real-world variability accurately.
Poor Data Quality: No matter how rigorous your validation strategy is; if underlying data contains errors or biases—as missing values unaddressed—the validity of any assessment diminishes significantly.
Model Drift Over Time: As real-world conditions change over time—a phenomenon known as concept drift—the original evaluation may become outdated unless continuous monitoring through ongoing out-of-sample checks occurs.
Understanding these potential issues emphasizes why ongoing vigilance—including periodic revalidation—is vital throughout a machine learning project lifecycle.
Ensuring Reliable Model Deployment Through Effective Validation
Implementing thorough out-of-sample validation isn’t merely about achieving high scores—it’s about building trustworthy systems capable of sustained accuracy under changing conditions and diverse scenarios. Combining traditional techniques like train-test splits with advanced strategies such as cross-validation ensures comprehensive assessment coverage.
Furthermore, integrating recent developments—including transfer learning approaches suited for deep neural networks—and leveraging AutoML tools streamlines this process while maintaining rigor standards necessary for responsible AI deployment.
By prioritizing robust external evaluations alongside ethical considerations around bias detection and adversarial resilience measures—which increasingly influence regulatory frameworks—you position yourself at the forefront of responsible AI development rooted firmly in sound scientific principles.
This overview underscores that effective out-of-sampling strategies form an essential backbone supporting reliable machine learning applications today—and tomorrow—with continuous innovation driving better practices worldwide
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
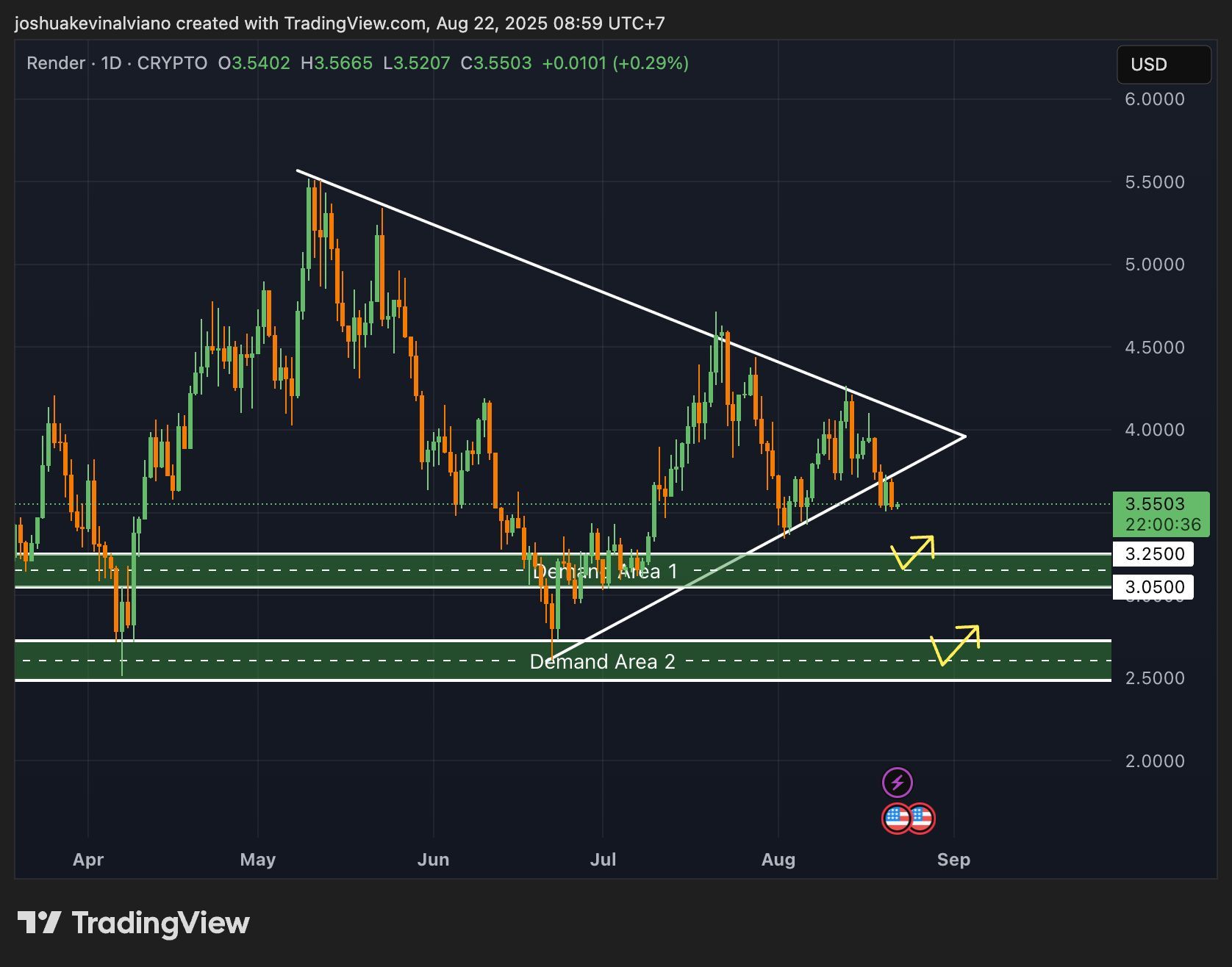
#Render glisse sous sa structure en triangle et approche la zone de demande $3.05–$3.25.
📊 Scénarios à surveiller : ✅ Si ça tient → possible rebond court terme vers $4.00+ 🚀 ❌ Si ça casse → chute probable vers la zone $2.50–$2.70 ⚠️
👉 Selon vous, $RNDR prépare un rebond solide ou une plongée plus profonde ?
#RNDR #AI #CryptoMarkets


Carmelita
2025-08-22 11:50
$RNDR en zone critique : rebond ou cassure ?
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is a Paper Wallet and How Does It Work?
A paper wallet is a physical document or card that stores the essential information needed to access and manage cryptocurrency holdings. Unlike digital wallets stored on computers or smartphones, paper wallets provide a tangible form of crypto storage, making them appealing for users seeking offline security. Typically, a paper wallet contains two critical components: the public address and the private key. The public address functions like an account number, allowing others to send cryptocurrency to your wallet. Conversely, the private key grants full control over those funds and must be kept secret at all costs.
Most paper wallets are printed with these details in human-readable text or QR codes—scannable images that facilitate quick transactions without exposing sensitive data directly on screen. This physical approach aims to reduce exposure to online hacking threats but introduces new risks related to physical security.
Types of Paper Wallets
There are several variations designed to cater to different user preferences and security needs:
- QR Code Wallets: These utilize QR codes for both public addresses and private keys, enabling fast scanning during transactions while minimizing manual entry errors.
- Printed Wallets: Traditional sheets of paper with printed keys and addresses; often generated using dedicated software.
- Card-Based Wallets: Made from durable plastic cards embedded with cryptographic information—more resistant to wear and tear than standard paper.
Each type offers unique advantages in terms of durability, ease of use, and security features.
Historical Context: The Origins of Paper Wallets
The concept emerged early in Bitcoin’s history around 2011 when enthusiasts sought secure ways to store their digital assets offline. A notable discussion thread on Bitcoin Forum highlighted the potential benefits of physically safeguarding private keys through printouts[1]. As awareness grew about hacking vulnerabilities associated with online storage solutions, many users adopted paper wallets as an alternative method for cold storage—a practice that remains relevant today among certain segments of crypto investors.
Security Challenges Associated With Paper Wallets
While offering robust protection against cyberattacks when properly managed, paper wallets are not without significant risks:
- Physical Loss or Theft: Since they exist outside digital environments, losing access means losing funds permanently unless backups exist elsewhere.
- Counterfeit or Fake Paper Wallets: Unscrupulous actors have created counterfeit versions designed solely for theft[2]. Verifying authenticity requires trust in reputable sources.
- Human Error During Generation & Storage: Mistakes such as generating weak keys or improper handling can compromise security[5].
Furthermore, if someone gains physical access—through theft or accidental discovery—they can transfer all associated funds instantly if they possess the private key.
Recent Security Improvements & Their Impact
Advancements over recent years aim at mitigating some traditional vulnerabilities:
- Multi-Signature Support: Some modern implementations incorporate multi-signature schemes requiring multiple approvals before spending funds[3]. This adds layers of authorization beyond just one private key.
- Enhanced QR Code Security: Improved printing techniques make it harder for malicious actors to scan QR codes surreptitiously; some systems employ encryption within QR codes themselves[4].
Despite these innovations enhancing safety measures significantly compared with earlier versions, they do not eliminate inherent risks entirely.
Risks Still Persist Despite Advances
Even with improved technology standards:
Human mistakes remain common—such as generating weak cryptographic material or misplacing backup copies—which can lead directly to loss.
Counterfeiting continues as a concern; counterfeit papers may look authentic but contain compromised data designed explicitly for theft[6].
Therefore, users must exercise caution by sourcing tools from trusted providers and following best practices during creation and storage processes.
Is Using a Paper Wallet Still Safe Today?
The safety profile of paper wallets depends heavily on how they’re used. For individuals who understand proper generation procedures—including secure offline environments—and take meticulous care in storing their printouts securely (e.g., safes), they can serve as reliable long-term cold storage options[^7^]. However,
they are not suitable for frequent transactions due to their static nature; updating requires regenerating new printouts each time you need access changes.
Moreover,
Given persistent risks like physical damage (fire/water), loss through misplacement, human error during setup/handling—and ongoing threats from counterfeit products—their safety is conditional upon rigorous management practices.[^7^]
Alternatives & Best Practices
For those considering alternative methods while maintaining high-security standards:
Use hardware wallets (e.g., Ledger Nano S/X) which combine offline cold storage with user-friendly interfaces
Employ multi-signature setups involving multiple devices/accounts
Regularly back up seed phrases securely stored offline
When opting for a paper wallet specifically,
always generate it using reputable open-source tools, preferably in air-gapped environments (offline computers disconnected from internet). Store printed copies securely away from environmental hazards like moisture or fire hazards.[^7^]
Final Thoughts on Physical Cryptocurrency Storage Methods
Paper wallets represent an enduring method rooted in simplicity yet fraught with practical challenges requiring diligent management. They offer excellent protection against online threats but demand careful handling due to their susceptibility toward physical damage—or theft if improperly secured.[^7^] As part of comprehensive crypto asset management strategies,
combining multiple approaches—including hardware devices backed by strong passwords—is advisable for optimal security[^7^].
By understanding both their strengths and limitations within current technological contexts—and adhering strictly to best practices—you can leverage what makes paper wallets appealing while minimizing associated dangers.
References
- Bitcoin Forum Thread (2011) - "Paper Wallets"
- Counterfeit Paper Wallets (2020) - "Cryptocurrency Scams"
- Multi-Signature Wallets (2022) - "Enhanced Security Measures"
- QR Code Security (2023) - "Advanced QR Code Technology"
- Human Error (2022) - "Common Mistakes in Cryptocurrency Storage"
- Counterfeiting Risks (2023) - "Protecting Against Counterfeit Paper Wallets"
- Usage Statistics (2023) - "Cryptocurrency User Behavior"
This comprehensive overview aims at equipping readers—from beginners exploring secure crypto storage options—to seasoned investors seeking nuanced insights into managing digital assets safely through various methods including traditional papers-based solutions amidst evolving technological landscapes


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-22 17:17
What is a paper wallet, and is it still a safe option?
What Is a Paper Wallet and How Does It Work?
A paper wallet is a physical document or card that stores the essential information needed to access and manage cryptocurrency holdings. Unlike digital wallets stored on computers or smartphones, paper wallets provide a tangible form of crypto storage, making them appealing for users seeking offline security. Typically, a paper wallet contains two critical components: the public address and the private key. The public address functions like an account number, allowing others to send cryptocurrency to your wallet. Conversely, the private key grants full control over those funds and must be kept secret at all costs.
Most paper wallets are printed with these details in human-readable text or QR codes—scannable images that facilitate quick transactions without exposing sensitive data directly on screen. This physical approach aims to reduce exposure to online hacking threats but introduces new risks related to physical security.
Types of Paper Wallets
There are several variations designed to cater to different user preferences and security needs:
- QR Code Wallets: These utilize QR codes for both public addresses and private keys, enabling fast scanning during transactions while minimizing manual entry errors.
- Printed Wallets: Traditional sheets of paper with printed keys and addresses; often generated using dedicated software.
- Card-Based Wallets: Made from durable plastic cards embedded with cryptographic information—more resistant to wear and tear than standard paper.
Each type offers unique advantages in terms of durability, ease of use, and security features.
Historical Context: The Origins of Paper Wallets
The concept emerged early in Bitcoin’s history around 2011 when enthusiasts sought secure ways to store their digital assets offline. A notable discussion thread on Bitcoin Forum highlighted the potential benefits of physically safeguarding private keys through printouts[1]. As awareness grew about hacking vulnerabilities associated with online storage solutions, many users adopted paper wallets as an alternative method for cold storage—a practice that remains relevant today among certain segments of crypto investors.
Security Challenges Associated With Paper Wallets
While offering robust protection against cyberattacks when properly managed, paper wallets are not without significant risks:
- Physical Loss or Theft: Since they exist outside digital environments, losing access means losing funds permanently unless backups exist elsewhere.
- Counterfeit or Fake Paper Wallets: Unscrupulous actors have created counterfeit versions designed solely for theft[2]. Verifying authenticity requires trust in reputable sources.
- Human Error During Generation & Storage: Mistakes such as generating weak keys or improper handling can compromise security[5].
Furthermore, if someone gains physical access—through theft or accidental discovery—they can transfer all associated funds instantly if they possess the private key.
Recent Security Improvements & Their Impact
Advancements over recent years aim at mitigating some traditional vulnerabilities:
- Multi-Signature Support: Some modern implementations incorporate multi-signature schemes requiring multiple approvals before spending funds[3]. This adds layers of authorization beyond just one private key.
- Enhanced QR Code Security: Improved printing techniques make it harder for malicious actors to scan QR codes surreptitiously; some systems employ encryption within QR codes themselves[4].
Despite these innovations enhancing safety measures significantly compared with earlier versions, they do not eliminate inherent risks entirely.
Risks Still Persist Despite Advances
Even with improved technology standards:
Human mistakes remain common—such as generating weak cryptographic material or misplacing backup copies—which can lead directly to loss.
Counterfeiting continues as a concern; counterfeit papers may look authentic but contain compromised data designed explicitly for theft[6].
Therefore, users must exercise caution by sourcing tools from trusted providers and following best practices during creation and storage processes.
Is Using a Paper Wallet Still Safe Today?
The safety profile of paper wallets depends heavily on how they’re used. For individuals who understand proper generation procedures—including secure offline environments—and take meticulous care in storing their printouts securely (e.g., safes), they can serve as reliable long-term cold storage options[^7^]. However,
they are not suitable for frequent transactions due to their static nature; updating requires regenerating new printouts each time you need access changes.
Moreover,
Given persistent risks like physical damage (fire/water), loss through misplacement, human error during setup/handling—and ongoing threats from counterfeit products—their safety is conditional upon rigorous management practices.[^7^]
Alternatives & Best Practices
For those considering alternative methods while maintaining high-security standards:
Use hardware wallets (e.g., Ledger Nano S/X) which combine offline cold storage with user-friendly interfaces
Employ multi-signature setups involving multiple devices/accounts
Regularly back up seed phrases securely stored offline
When opting for a paper wallet specifically,
always generate it using reputable open-source tools, preferably in air-gapped environments (offline computers disconnected from internet). Store printed copies securely away from environmental hazards like moisture or fire hazards.[^7^]
Final Thoughts on Physical Cryptocurrency Storage Methods
Paper wallets represent an enduring method rooted in simplicity yet fraught with practical challenges requiring diligent management. They offer excellent protection against online threats but demand careful handling due to their susceptibility toward physical damage—or theft if improperly secured.[^7^] As part of comprehensive crypto asset management strategies,
combining multiple approaches—including hardware devices backed by strong passwords—is advisable for optimal security[^7^].
By understanding both their strengths and limitations within current technological contexts—and adhering strictly to best practices—you can leverage what makes paper wallets appealing while minimizing associated dangers.
References
- Bitcoin Forum Thread (2011) - "Paper Wallets"
- Counterfeit Paper Wallets (2020) - "Cryptocurrency Scams"
- Multi-Signature Wallets (2022) - "Enhanced Security Measures"
- QR Code Security (2023) - "Advanced QR Code Technology"
- Human Error (2022) - "Common Mistakes in Cryptocurrency Storage"
- Counterfeiting Risks (2023) - "Protecting Against Counterfeit Paper Wallets"
- Usage Statistics (2023) - "Cryptocurrency User Behavior"
This comprehensive overview aims at equipping readers—from beginners exploring secure crypto storage options—to seasoned investors seeking nuanced insights into managing digital assets safely through various methods including traditional papers-based solutions amidst evolving technological landscapes
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Are Donchian Channels?
Donchian Channels are a popular technical analysis tool used by traders to identify market trends and potential breakout points. Developed by Richard Donchian in the 1950s, these channels provide a visual representation of price volatility and trend direction, making them valuable for both novice and experienced traders across various financial markets, including stocks, commodities, forex, and cryptocurrencies.
How Do Donchian Channels Work?
At their core, Donchian Channels consist of three lines plotted on a price chart:
- Upper Band: Represents the highest high over a specified period (commonly n days).
- Lower Band: Represents the lowest low over the same period.
- Middle Line: Usually a simple moving average (SMA) of the upper and lower bands or sometimes omitted depending on trading strategy.
The primary idea behind these channels is that when prices break above the upper band or below the lower band, it signals potential trend reversals or continuations. For example, if prices move above the upper band consistently, it may indicate an emerging bullish trend. Conversely, breaking below the lower band could signal bearish momentum.
The width between these bands reflects market volatility; wider channels suggest higher volatility with larger price swings. Traders often monitor changes in channel width to gauge market conditions—narrowing channels might indicate consolidation phases before significant moves.
Calculating Donchian Channels
Calculating Donchian Channels is straightforward:
- Determine Period Length (n): Decide on how many periods you want to analyze—common choices include 20-day or 55-day periods.
- Calculate Upper Band: Find the highest high within those n periods.
- Calculate Lower Band: Find the lowest low within those same n periods.
- Compute Middle Line (Optional): Take an average of these two values or use another moving average method for trend confirmation.
This simplicity makes Donchian Channels accessible for traders without complex calculations but still effective in capturing essential market dynamics.
Practical Uses in Trading Strategies
Traders leverage Donchian Channels primarily for identifying entry and exit points based on trend strength and breakouts:
- When prices cross above the upper band consistently with increasing volume or momentum indicators like RSI or MACD, it can be interpreted as a buy signal.
- Conversely, crossing below the lower band may suggest selling opportunities.
Additionally, some traders use channel width as an indicator of volatility; expanding channels can precede significant price movements while narrowing ones might signal consolidation phases before breakout events occur.
Combining Donchian Channel signals with other technical tools enhances decision-making accuracy—for instance: using volume analysis alongside channel breakouts provides more reliable trade entries.
Advantages of Using Donchian Channels
One reason why many traders favor this indicator is its simplicity combined with effectiveness:
- Easy to understand and implement without advanced mathematical skills
- Provides clear visual cues about trending markets versus consolidations
- Useful across different asset classes due to its universal calculation method
- Can be integrated seamlessly into automated trading systems owing to straightforward rules
Furthermore, because they focus solely on historical highs and lows rather than complex indicators like oscillators or overlays requiring multiple inputs—they serve as robust foundational tools for developing broader trading strategies.
Limitations To Keep In Mind
Despite their advantages, there are notable limitations associated with relying solely on Donchian Channels:
They are lagging indicators since they depend entirely on past data; thus,
- They might generate delayed signals during fast-moving markets
- False breakouts can occur during choppy sideways movements
Market conditions such as sudden news events can cause abrupt price shifts that don’t immediately reflect in channel positioning
The absence of volume consideration means that some signals could be less reliable without supplementary analysis
Regulatory changes affecting specific assets—like cryptocurrencies—may influence how effectively these channels work due to altered trading hours or liquidity issues
To mitigate these drawbacks—and improve overall accuracy—traders often combine them with other technical tools such as volume indicators or fundamental analysis insights.
The Role of Modern Technology & Crypto Adoption
In recent years—and especially within cryptocurrency markets—Donchian Channels have gained renewed popularity thanks to their adaptability across volatile assets like Bitcoin and altcoins. Crypto traders frequently utilize shorter-period settings due to rapid price fluctuations characteristic of digital assets.
Moreover, advancements in AI-driven trading platforms have integrated machine learning algorithms with traditional indicators like Donchians to enhance predictive capabilities further:
- Real-time data processing allows quicker detection of breakout signals
- Machine learning models help filter false positives by analyzing multiple factors simultaneously
This technological evolution has made it easier for retail investors—and institutional players alike—to incorporate sophisticated strategies involving classic tools such as Donchin’s channels into their automated systems.
Community Engagement & Strategy Sharing
Online forums dedicated to technical analysis often feature discussions around effective uses of Donichan’s methodology:
- Traders share customized settings tailored for specific assets
- Backtesting results demonstrate performance under different market conditions
Such community engagement fosters continuous learning while helping new users understand best practices when deploying this indicator within broader trading frameworks.
Final Thoughts: Staying Ahead With Technical Analysis Tools
While no single indicator guarantees success—a principle true across all forms of technical analysis—the simplicity combined with versatility makes Donichian Channels an enduring choice among traders worldwide. Their ability to visually depict trends alongside volatility offers valuable insights into market behavior that can inform timely decisions when used correctly alongside other analytical methods.
By understanding how they function—including calculation methods—and recognizing their strengths along with limitations—you position yourself better equipped for navigating diverse financial landscapes—from stocks through commodities all the way into cryptocurrencies—informed by proven techniques rooted in decades-old research yet continually adapted through modern technology advances.


kai
2025-05-20 01:26
What are Donchian Channels?
What Are Donchian Channels?
Donchian Channels are a popular technical analysis tool used by traders to identify market trends and potential breakout points. Developed by Richard Donchian in the 1950s, these channels provide a visual representation of price volatility and trend direction, making them valuable for both novice and experienced traders across various financial markets, including stocks, commodities, forex, and cryptocurrencies.
How Do Donchian Channels Work?
At their core, Donchian Channels consist of three lines plotted on a price chart:
- Upper Band: Represents the highest high over a specified period (commonly n days).
- Lower Band: Represents the lowest low over the same period.
- Middle Line: Usually a simple moving average (SMA) of the upper and lower bands or sometimes omitted depending on trading strategy.
The primary idea behind these channels is that when prices break above the upper band or below the lower band, it signals potential trend reversals or continuations. For example, if prices move above the upper band consistently, it may indicate an emerging bullish trend. Conversely, breaking below the lower band could signal bearish momentum.
The width between these bands reflects market volatility; wider channels suggest higher volatility with larger price swings. Traders often monitor changes in channel width to gauge market conditions—narrowing channels might indicate consolidation phases before significant moves.
Calculating Donchian Channels
Calculating Donchian Channels is straightforward:
- Determine Period Length (n): Decide on how many periods you want to analyze—common choices include 20-day or 55-day periods.
- Calculate Upper Band: Find the highest high within those n periods.
- Calculate Lower Band: Find the lowest low within those same n periods.
- Compute Middle Line (Optional): Take an average of these two values or use another moving average method for trend confirmation.
This simplicity makes Donchian Channels accessible for traders without complex calculations but still effective in capturing essential market dynamics.
Practical Uses in Trading Strategies
Traders leverage Donchian Channels primarily for identifying entry and exit points based on trend strength and breakouts:
- When prices cross above the upper band consistently with increasing volume or momentum indicators like RSI or MACD, it can be interpreted as a buy signal.
- Conversely, crossing below the lower band may suggest selling opportunities.
Additionally, some traders use channel width as an indicator of volatility; expanding channels can precede significant price movements while narrowing ones might signal consolidation phases before breakout events occur.
Combining Donchian Channel signals with other technical tools enhances decision-making accuracy—for instance: using volume analysis alongside channel breakouts provides more reliable trade entries.
Advantages of Using Donchian Channels
One reason why many traders favor this indicator is its simplicity combined with effectiveness:
- Easy to understand and implement without advanced mathematical skills
- Provides clear visual cues about trending markets versus consolidations
- Useful across different asset classes due to its universal calculation method
- Can be integrated seamlessly into automated trading systems owing to straightforward rules
Furthermore, because they focus solely on historical highs and lows rather than complex indicators like oscillators or overlays requiring multiple inputs—they serve as robust foundational tools for developing broader trading strategies.
Limitations To Keep In Mind
Despite their advantages, there are notable limitations associated with relying solely on Donchian Channels:
They are lagging indicators since they depend entirely on past data; thus,
- They might generate delayed signals during fast-moving markets
- False breakouts can occur during choppy sideways movements
Market conditions such as sudden news events can cause abrupt price shifts that don’t immediately reflect in channel positioning
The absence of volume consideration means that some signals could be less reliable without supplementary analysis
Regulatory changes affecting specific assets—like cryptocurrencies—may influence how effectively these channels work due to altered trading hours or liquidity issues
To mitigate these drawbacks—and improve overall accuracy—traders often combine them with other technical tools such as volume indicators or fundamental analysis insights.
The Role of Modern Technology & Crypto Adoption
In recent years—and especially within cryptocurrency markets—Donchian Channels have gained renewed popularity thanks to their adaptability across volatile assets like Bitcoin and altcoins. Crypto traders frequently utilize shorter-period settings due to rapid price fluctuations characteristic of digital assets.
Moreover, advancements in AI-driven trading platforms have integrated machine learning algorithms with traditional indicators like Donchians to enhance predictive capabilities further:
- Real-time data processing allows quicker detection of breakout signals
- Machine learning models help filter false positives by analyzing multiple factors simultaneously
This technological evolution has made it easier for retail investors—and institutional players alike—to incorporate sophisticated strategies involving classic tools such as Donchin’s channels into their automated systems.
Community Engagement & Strategy Sharing
Online forums dedicated to technical analysis often feature discussions around effective uses of Donichan’s methodology:
- Traders share customized settings tailored for specific assets
- Backtesting results demonstrate performance under different market conditions
Such community engagement fosters continuous learning while helping new users understand best practices when deploying this indicator within broader trading frameworks.
Final Thoughts: Staying Ahead With Technical Analysis Tools
While no single indicator guarantees success—a principle true across all forms of technical analysis—the simplicity combined with versatility makes Donichian Channels an enduring choice among traders worldwide. Their ability to visually depict trends alongside volatility offers valuable insights into market behavior that can inform timely decisions when used correctly alongside other analytical methods.
By understanding how they function—including calculation methods—and recognizing their strengths along with limitations—you position yourself better equipped for navigating diverse financial landscapes—from stocks through commodities all the way into cryptocurrencies—informed by proven techniques rooted in decades-old research yet continually adapted through modern technology advances.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Is Volume Shown on Charts?
Understanding how volume is displayed on financial charts is essential for traders and investors aiming to interpret market activity accurately. Volume provides insight into the strength behind price movements, helping to confirm trends or signal potential reversals. In this article, we explore the various ways volume is visualized on charts, its significance in technical analysis, and how traders can leverage this information for better decision-making.
What Does Volume Look Like on Financial Charts?
On most trading platforms and charting tools, volume is represented as a histogram or bar chart positioned below the main price chart. Each bar corresponds to a specific time period—such as minutes, hours, days, or weeks—and indicates the total number of shares or contracts traded during that interval. The height of each bar reflects trading activity: taller bars mean higher volumes, while shorter bars suggest lower participation.
This visual setup allows traders to quickly assess periods of heightened market interest versus times of relative inactivity. For example, a sudden spike in volume often coincides with significant news events or breakouts from key support/resistance levels. Conversely, low-volume periods may indicate indecision among market participants.
Types of Volume Indicators Displayed on Charts
While basic volume bars are common across most platforms due to their simplicity and clarity, advanced technical analysis employs various indicators that incorporate volume data:
- Simple Volume: The raw count of shares traded within each period; straightforward but sometimes less informative without context.
- On-Balance Volume (OBV): A cumulative indicator that adds or subtracts volume based on whether prices close higher or lower than previous periods. It helps identify potential trend strength by showing whether buying pressure outweighs selling pressure.
- Money Flow Index (MFI): Combines price and volume data into an oscillator that signals overbought or oversold conditions by analyzing money flow into and out of an asset.
These indicators are typically plotted alongside the main price chart but can also be displayed separately for detailed analysis.
Interpreting How Volume Is Shown
The way volume appears visually aids traders in making quick assessments about market sentiment:
- Confirmation: When rising prices are accompanied by increasing volumes—represented by taller bars—it suggests strong buying interest supporting an uptrend.
- Divergence: If prices move upward but volumes decline (shorter bars), it might indicate weakening momentum and possible reversal.
- Breakouts: High-volume spikes during breakouts above resistance levels often confirm genuine moves rather than false signals caused by low liquidity.
Many trading platforms allow customization so users can set alerts when unusual volume occurs at specific levels—helping them react swiftly to emerging opportunities.
Recent Trends in Visualizing Trading Volumes
With technological advancements and growing popularity of cryptocurrencies as alternative assets, visualization methods have evolved further:
- Real-time dynamic charts now display live updates with high precision.
- Customizable overlays enable combining multiple indicators like OBV with other oscillators for comprehensive insights.
- Interactive dashboards allow traders to analyze historical patterns alongside current data seamlessly.
These developments make it easier for both novice and experienced traders to incorporate volume analysis into their strategies effectively.
Potential Risks Associated With Visualizing Volume Data
Despite its usefulness, interpreting visualized volume data requires caution:
- Market Manipulation – Large institutional players may artificially inflate trading volumes through practices like wash trading to create misleading signals.
- Liquidity Concerns – Low-volume securities can produce exaggerated movement patterns where small trades cause significant apparent changes in activity.
- False Breakouts – High-volume spikes do not always guarantee sustained moves; they could be traps set by market makers aiming to induce herd behavior.
Therefore, combining volumetric insights with other technical tools such as trendlines or momentum indicators enhances reliability while reducing risk exposure.
Practical Examples Showing How Charted Volumes Signal Market Moves
To illustrate these concepts practically:
Deutsche Post AG (DHL.DE): As reported recently around May 2025, increased short-term volatility was observed alongside rising trade volumes—a sign that investors were actively repositioning before a forecasted decline[5]. Recognizing such patterns enables timely entry or exit decisions based on confirmed activity shifts.
X5 Retail Group N.V.: Significant upticks in daily trading volumes indicated heightened investor interest[4], which could precede major sector-wide movements if corroborated with other technical signals like breakout confirmations.
By studying these examples within real-market contexts—where high-volume days align with notable price changes—traders develop sharper intuition about what volumetric cues imply regarding future trends.
How Traders Use Charted Volumes Effectively
Successful application involves integrating visualized volumetric data into broader analytical frameworks:
Confirm trend directionality — Rising prices supported by increasing volumes reinforce bullish outlooks; declining prices amid high volumes suggest bearish sentiment.
Detect potential reversals — Divergences between price action and volumetric trends serve as early warning signs for upcoming shifts;
Validate breakouts — Confirm high-volume surges during breakout attempts ensure authenticity rather than false alarms caused by manipulative tactics.
Incorporating these principles enhances decision-making accuracy while minimizing risks associated with misinterpretation.
Final Thoughts
Visual representation of trading volume plays a vital role in understanding market dynamics beyond mere price movements alone. Whether through simple histograms beneath candlestick charts or sophisticated indicators like OBV and MFI integrated into modern platforms—all serve as powerful tools enabling informed investment choices. As markets evolve—with crypto assets gaining prominence—the importance of accurately interpreting how much activity occurs at any given moment continues to grow exponentially.
By mastering how charted volumes are shown—and recognizing their implications—traders gain deeper insights into underlying supply-demand forces shaping asset prices today’s volatile markets demand vigilant analysis backed by clear visual cues.
References:
- Perplexity Finance: Aftermath Silver Ltd., Price & Performance
- Perplexity Finance: Renergen Limited Price & Performance
- Perplexity Finance: Bittium Oyj Price & Forecast
- Perplexity Finance: X5 Retail Group N.V., Price & Performance
- Perplexity Finance: Deutsche Post AG Price & Performance


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-19 20:15
How is volume shown on charts?
How Is Volume Shown on Charts?
Understanding how volume is displayed on financial charts is essential for traders and investors aiming to interpret market activity accurately. Volume provides insight into the strength behind price movements, helping to confirm trends or signal potential reversals. In this article, we explore the various ways volume is visualized on charts, its significance in technical analysis, and how traders can leverage this information for better decision-making.
What Does Volume Look Like on Financial Charts?
On most trading platforms and charting tools, volume is represented as a histogram or bar chart positioned below the main price chart. Each bar corresponds to a specific time period—such as minutes, hours, days, or weeks—and indicates the total number of shares or contracts traded during that interval. The height of each bar reflects trading activity: taller bars mean higher volumes, while shorter bars suggest lower participation.
This visual setup allows traders to quickly assess periods of heightened market interest versus times of relative inactivity. For example, a sudden spike in volume often coincides with significant news events or breakouts from key support/resistance levels. Conversely, low-volume periods may indicate indecision among market participants.
Types of Volume Indicators Displayed on Charts
While basic volume bars are common across most platforms due to their simplicity and clarity, advanced technical analysis employs various indicators that incorporate volume data:
- Simple Volume: The raw count of shares traded within each period; straightforward but sometimes less informative without context.
- On-Balance Volume (OBV): A cumulative indicator that adds or subtracts volume based on whether prices close higher or lower than previous periods. It helps identify potential trend strength by showing whether buying pressure outweighs selling pressure.
- Money Flow Index (MFI): Combines price and volume data into an oscillator that signals overbought or oversold conditions by analyzing money flow into and out of an asset.
These indicators are typically plotted alongside the main price chart but can also be displayed separately for detailed analysis.
Interpreting How Volume Is Shown
The way volume appears visually aids traders in making quick assessments about market sentiment:
- Confirmation: When rising prices are accompanied by increasing volumes—represented by taller bars—it suggests strong buying interest supporting an uptrend.
- Divergence: If prices move upward but volumes decline (shorter bars), it might indicate weakening momentum and possible reversal.
- Breakouts: High-volume spikes during breakouts above resistance levels often confirm genuine moves rather than false signals caused by low liquidity.
Many trading platforms allow customization so users can set alerts when unusual volume occurs at specific levels—helping them react swiftly to emerging opportunities.
Recent Trends in Visualizing Trading Volumes
With technological advancements and growing popularity of cryptocurrencies as alternative assets, visualization methods have evolved further:
- Real-time dynamic charts now display live updates with high precision.
- Customizable overlays enable combining multiple indicators like OBV with other oscillators for comprehensive insights.
- Interactive dashboards allow traders to analyze historical patterns alongside current data seamlessly.
These developments make it easier for both novice and experienced traders to incorporate volume analysis into their strategies effectively.
Potential Risks Associated With Visualizing Volume Data
Despite its usefulness, interpreting visualized volume data requires caution:
- Market Manipulation – Large institutional players may artificially inflate trading volumes through practices like wash trading to create misleading signals.
- Liquidity Concerns – Low-volume securities can produce exaggerated movement patterns where small trades cause significant apparent changes in activity.
- False Breakouts – High-volume spikes do not always guarantee sustained moves; they could be traps set by market makers aiming to induce herd behavior.
Therefore, combining volumetric insights with other technical tools such as trendlines or momentum indicators enhances reliability while reducing risk exposure.
Practical Examples Showing How Charted Volumes Signal Market Moves
To illustrate these concepts practically:
Deutsche Post AG (DHL.DE): As reported recently around May 2025, increased short-term volatility was observed alongside rising trade volumes—a sign that investors were actively repositioning before a forecasted decline[5]. Recognizing such patterns enables timely entry or exit decisions based on confirmed activity shifts.
X5 Retail Group N.V.: Significant upticks in daily trading volumes indicated heightened investor interest[4], which could precede major sector-wide movements if corroborated with other technical signals like breakout confirmations.
By studying these examples within real-market contexts—where high-volume days align with notable price changes—traders develop sharper intuition about what volumetric cues imply regarding future trends.
How Traders Use Charted Volumes Effectively
Successful application involves integrating visualized volumetric data into broader analytical frameworks:
Confirm trend directionality — Rising prices supported by increasing volumes reinforce bullish outlooks; declining prices amid high volumes suggest bearish sentiment.
Detect potential reversals — Divergences between price action and volumetric trends serve as early warning signs for upcoming shifts;
Validate breakouts — Confirm high-volume surges during breakout attempts ensure authenticity rather than false alarms caused by manipulative tactics.
Incorporating these principles enhances decision-making accuracy while minimizing risks associated with misinterpretation.
Final Thoughts
Visual representation of trading volume plays a vital role in understanding market dynamics beyond mere price movements alone. Whether through simple histograms beneath candlestick charts or sophisticated indicators like OBV and MFI integrated into modern platforms—all serve as powerful tools enabling informed investment choices. As markets evolve—with crypto assets gaining prominence—the importance of accurately interpreting how much activity occurs at any given moment continues to grow exponentially.
By mastering how charted volumes are shown—and recognizing their implications—traders gain deeper insights into underlying supply-demand forces shaping asset prices today’s volatile markets demand vigilant analysis backed by clear visual cues.
References:
- Perplexity Finance: Aftermath Silver Ltd., Price & Performance
- Perplexity Finance: Renergen Limited Price & Performance
- Perplexity Finance: Bittium Oyj Price & Forecast
- Perplexity Finance: X5 Retail Group N.V., Price & Performance
- Perplexity Finance: Deutsche Post AG Price & Performance
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is a Doji in Technical Analysis?
A doji is a distinctive candlestick pattern widely recognized in technical analysis, especially within stock trading, forex markets, and cryptocurrency exchanges. It forms when the opening and closing prices of an asset are virtually equal or very close, resulting in a small real body on the candlestick chart. This pattern is characterized by long wicks or shadows extending above and below the small body, indicating that during the trading period, buyers and sellers were in equilibrium. The presence of a doji suggests market indecision—a moment where neither bulls nor bears have gained control—making it an important signal for traders seeking to understand potential trend reversals or continuations.
Understanding what a doji represents requires grasping its visual appearance on charts. Typically, it appears as a thin line with minimal real body size but with extended upper and lower shadows. Depending on its specific form—such as gravestone or dragonfly—the implications can vary slightly but generally point to market uncertainty at that particular point.
Why Do Traders Pay Attention to Dojis?
In trading strategies rooted in technical analysis, dojis serve as crucial indicators of market sentiment shifts. Because they reflect indecision among traders—where buying pressure equals selling pressure—they often appear at critical junctures like trend reversals or pauses during strong trends. For example, if an uptrend encounters a doji near its peak price level, it might signal that bullish momentum is weakening and that sellers could soon take control.
However, it's essential to interpret dojis within context rather than relying solely on their appearance. When combined with other technical tools such as moving averages, Relative Strength Index (RSI), volume data, or support/resistance levels—as part of comprehensive chart analysis—they can significantly improve prediction accuracy regarding future price movements.
Types of Dojis
There are several variations of doji patterns used by traders to refine their analysis:
- Standard Doji: Features almost equal opening and closing prices with long wicks on both sides; indicates high market indecision.
- Gravestone Doji: Has no lower wick (or very minimal) with a long upper shadow; often signals potential bearish reversal after an uptrend.
- Dragonfly Doji: Exhibits no upper wick (or very minimal) with long lower shadows; may suggest bullish reversal following downtrends.
- Long-Legged Doji: Characterized by very long upper and lower wicks relative to the small body; signifies extreme indecision during volatile periods.
Each type provides nuanced insights into trader sentiment depending on where they appear within price trends.
Do Dojis Signal Reversals or Continuations?
The significance of a doji largely depends on its position within prevailing trends:
When appearing after an extended upward movement (an uptrend), especially near resistance levels—a doji can indicate hesitation among buyers—and potentially foreshadow a reversal downward.
Conversely, following prolonged declines (a downtrend), spotting a doji might suggest selling exhaustion and possible upward reversal if confirmed by subsequent candles.
Nevertheless, because dojis are neutral signals themselves—they merely reflect indecision—their predictive power increases when confirmed by additional indicators such as volume spikes or subsequent candle patterns like engulfing candles.
Recent Trends: Cryptocurrencies & Stock Markets
In recent years—particularly amid heightened volatility seen during major events like Bitcoin’s 2021 surge—dojis have gained prominence among crypto traders aiming to anticipate sudden reversals amidst rapid price swings. During Bitcoin's rally phases in 2021 leading up to all-time highs followed by corrections — numerous traders identified multiple dojis signaling potential trend pauses before continuation or reversal occurred.
Similarly in traditional stock markets—including notable periods like the 2008 financial crisis—dojii patterns appeared frequently at points where investor uncertainty was high. These patterns served as early warning signs for significant upcoming moves once confirmed through other technical signals or fundamental developments.
Risks & Limitations
While useful tools within technical analysis arsenals — particularly when combined with other indicators — reliance solely on dojii patterns carries risks:
False Signals: Not every dojo leads to actual reversals; some may simply be pauses before continued trends.
Market Context Dependency: The effectiveness varies depending on overall market conditions; during highly volatile times like cryptocurrencies' boom-bust cycles—or macroeconomic shocks—the reliability diminishes without corroborating evidence.
Confirmation Needed: To mitigate false positives’ impact—and enhance decision-making—it’s advisable always to seek confirmation from additional technical signals such as volume increase or subsequent candle formations indicating momentum shifts.
How Traders Use Dojis Effectively
Successful incorporation of dojo patterns into trading strategies involves understanding their limitations while leveraging their strengths:
- Identify key support/resistance levels where dojii tend to appear more reliably.
- Combine dojo detection with trend-following tools like moving averages for better context.
- Watch for confirmation candles post-dojo—for example,
- Engulfing candles
- Hammer
- Shooting star
- Monitor volume changes around dojo formations for added insight into trader conviction.
Historical Examples & Practical Insights
During Bitcoin's historic rise in 2021—from around $30K early that year toward over $60K—multiple dojii appeared at critical junctures suggesting temporary pauses before further gains—or warnings ahead of corrections when paired with other bearish signals emerged simultaneously.
In traditional markets such as equities leading up to the 2008 financial crisis—a series of dojii formed across various indices indicated growing uncertainty among investors about economic stability which eventually culminated into sharp declines once broader systemic issues surfaced.
Integrating Knowledge Into Your Trading Approach
For both novice and experienced traders aiming for informed decision-making:
Recognize that no single pattern guarantees future moves but serves best when integrated into comprehensive analyses.
Practice identifying different types of dojii across various timeframes—from daily charts for swing trades down to intraday setups—to understand how they behave under different conditions.
Stay updated about recent developments affecting markets you trade—in cryptocurrencies’ case especially—to interpret pattern significance accurately amid high volatility environments.
Understanding what constitutes a valid dojo pattern—and how it fits into broader analytical frameworks—is vital for enhancing your ability not only to spot potential turning points but also manage risk effectively amidst unpredictable markets.
By mastering these insights about dojii candlestick patterns—including their formation types, contextual relevance,and strategic application—you equip yourself better for navigating complex financial landscapes whether you're trading stocks , forex ,or digital assets .


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-19 20:00
What's a doji?
What Is a Doji in Technical Analysis?
A doji is a distinctive candlestick pattern widely recognized in technical analysis, especially within stock trading, forex markets, and cryptocurrency exchanges. It forms when the opening and closing prices of an asset are virtually equal or very close, resulting in a small real body on the candlestick chart. This pattern is characterized by long wicks or shadows extending above and below the small body, indicating that during the trading period, buyers and sellers were in equilibrium. The presence of a doji suggests market indecision—a moment where neither bulls nor bears have gained control—making it an important signal for traders seeking to understand potential trend reversals or continuations.
Understanding what a doji represents requires grasping its visual appearance on charts. Typically, it appears as a thin line with minimal real body size but with extended upper and lower shadows. Depending on its specific form—such as gravestone or dragonfly—the implications can vary slightly but generally point to market uncertainty at that particular point.
Why Do Traders Pay Attention to Dojis?
In trading strategies rooted in technical analysis, dojis serve as crucial indicators of market sentiment shifts. Because they reflect indecision among traders—where buying pressure equals selling pressure—they often appear at critical junctures like trend reversals or pauses during strong trends. For example, if an uptrend encounters a doji near its peak price level, it might signal that bullish momentum is weakening and that sellers could soon take control.
However, it's essential to interpret dojis within context rather than relying solely on their appearance. When combined with other technical tools such as moving averages, Relative Strength Index (RSI), volume data, or support/resistance levels—as part of comprehensive chart analysis—they can significantly improve prediction accuracy regarding future price movements.
Types of Dojis
There are several variations of doji patterns used by traders to refine their analysis:
- Standard Doji: Features almost equal opening and closing prices with long wicks on both sides; indicates high market indecision.
- Gravestone Doji: Has no lower wick (or very minimal) with a long upper shadow; often signals potential bearish reversal after an uptrend.
- Dragonfly Doji: Exhibits no upper wick (or very minimal) with long lower shadows; may suggest bullish reversal following downtrends.
- Long-Legged Doji: Characterized by very long upper and lower wicks relative to the small body; signifies extreme indecision during volatile periods.
Each type provides nuanced insights into trader sentiment depending on where they appear within price trends.
Do Dojis Signal Reversals or Continuations?
The significance of a doji largely depends on its position within prevailing trends:
When appearing after an extended upward movement (an uptrend), especially near resistance levels—a doji can indicate hesitation among buyers—and potentially foreshadow a reversal downward.
Conversely, following prolonged declines (a downtrend), spotting a doji might suggest selling exhaustion and possible upward reversal if confirmed by subsequent candles.
Nevertheless, because dojis are neutral signals themselves—they merely reflect indecision—their predictive power increases when confirmed by additional indicators such as volume spikes or subsequent candle patterns like engulfing candles.
Recent Trends: Cryptocurrencies & Stock Markets
In recent years—particularly amid heightened volatility seen during major events like Bitcoin’s 2021 surge—dojis have gained prominence among crypto traders aiming to anticipate sudden reversals amidst rapid price swings. During Bitcoin's rally phases in 2021 leading up to all-time highs followed by corrections — numerous traders identified multiple dojis signaling potential trend pauses before continuation or reversal occurred.
Similarly in traditional stock markets—including notable periods like the 2008 financial crisis—dojii patterns appeared frequently at points where investor uncertainty was high. These patterns served as early warning signs for significant upcoming moves once confirmed through other technical signals or fundamental developments.
Risks & Limitations
While useful tools within technical analysis arsenals — particularly when combined with other indicators — reliance solely on dojii patterns carries risks:
False Signals: Not every dojo leads to actual reversals; some may simply be pauses before continued trends.
Market Context Dependency: The effectiveness varies depending on overall market conditions; during highly volatile times like cryptocurrencies' boom-bust cycles—or macroeconomic shocks—the reliability diminishes without corroborating evidence.
Confirmation Needed: To mitigate false positives’ impact—and enhance decision-making—it’s advisable always to seek confirmation from additional technical signals such as volume increase or subsequent candle formations indicating momentum shifts.
How Traders Use Dojis Effectively
Successful incorporation of dojo patterns into trading strategies involves understanding their limitations while leveraging their strengths:
- Identify key support/resistance levels where dojii tend to appear more reliably.
- Combine dojo detection with trend-following tools like moving averages for better context.
- Watch for confirmation candles post-dojo—for example,
- Engulfing candles
- Hammer
- Shooting star
- Monitor volume changes around dojo formations for added insight into trader conviction.
Historical Examples & Practical Insights
During Bitcoin's historic rise in 2021—from around $30K early that year toward over $60K—multiple dojii appeared at critical junctures suggesting temporary pauses before further gains—or warnings ahead of corrections when paired with other bearish signals emerged simultaneously.
In traditional markets such as equities leading up to the 2008 financial crisis—a series of dojii formed across various indices indicated growing uncertainty among investors about economic stability which eventually culminated into sharp declines once broader systemic issues surfaced.
Integrating Knowledge Into Your Trading Approach
For both novice and experienced traders aiming for informed decision-making:
Recognize that no single pattern guarantees future moves but serves best when integrated into comprehensive analyses.
Practice identifying different types of dojii across various timeframes—from daily charts for swing trades down to intraday setups—to understand how they behave under different conditions.
Stay updated about recent developments affecting markets you trade—in cryptocurrencies’ case especially—to interpret pattern significance accurately amid high volatility environments.
Understanding what constitutes a valid dojo pattern—and how it fits into broader analytical frameworks—is vital for enhancing your ability not only to spot potential turning points but also manage risk effectively amidst unpredictable markets.
By mastering these insights about dojii candlestick patterns—including their formation types, contextual relevance,and strategic application—you equip yourself better for navigating complex financial landscapes whether you're trading stocks , forex ,or digital assets .
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Is Cryptocurrency Used for Cross-Border Remittances?
Understanding the Role of Cryptocurrency in International Money Transfers
Cryptocurrency has increasingly become a viable alternative to traditional cross-border remittance methods. For individuals and businesses sending money across countries, cryptocurrencies offer a faster, cheaper, and more secure option compared to conventional services like wire transfers or money transfer operators such as Western Union and MoneyGram. This shift is driven by blockchain technology’s unique features, which address many limitations of traditional remittance channels.
Traditional cross-border remittances often involve high fees, lengthy processing times—sometimes taking several days—and risks related to fraud or transaction errors. These issues are especially problematic for migrant workers and families relying on timely financial support. Cryptocurrencies aim to mitigate these challenges by leveraging decentralized ledger technology that ensures transparency and security.
Blockchain Technology: The Backbone of Crypto Remittances
At the core of cryptocurrency’s utility in international transfers is blockchain technology—a distributed ledger system that records all transactions across a network of computers. Unlike centralized banking systems, blockchain operates without a single controlling authority, making it resistant to tampering or censorship.
When someone sends cryptocurrency like Bitcoin or Ethereum across borders, the transaction is validated by network participants (miners) within minutes rather than days. Once confirmed, the transaction becomes immutable—meaning it cannot be altered or reversed—adding an extra layer of security against fraud.
Key Benefits of Using Cryptocurrency for Cross-Border Payments
- Speed: Traditional bank wires can take anywhere from one to five business days depending on the countries involved; cryptocurrencies typically settle within minutes.
- Lower Costs: Transaction fees are generally lower than those charged by banks or money transfer services. Sending $200 via Bitcoin might cost around 1-2%, whereas conventional providers could charge up to 7%.
- Enhanced Security: Blockchain’s cryptographic protocols make transactions tamper-proof and reduce risks associated with hacking or unauthorized access.
- Accessibility: With just an internet connection and digital wallet, users can send funds without needing access to formal banking infrastructure—a significant advantage in regions with limited banking services.
Recent Trends & Developments in Crypto-Based Remittances
Over recent years, there has been notable progress toward mainstream adoption:
Regulatory Clarity
Governments are increasingly establishing frameworks for crypto use in financial transactions. For example, in 2023, U.S. authorities issued guidelines emphasizing compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations when using cryptocurrencies for remittance purposes. Clearer rules help legitimize crypto activities while protecting consumers.Partnerships & Platform Integrations
Major financial institutions have begun integrating cryptocurrencies into their platforms:- PayPal enabled users worldwide since 2020 to buy,sell,and hold cryptocurrencies.
- Several fintech firms now facilitate crypto-based remittances directly through user-friendly apps.
Growing Adoption Rates
Regions with limited access to traditional banking see rapid growth:- Countries like Kenya have embraced mobile-based crypto solutions due to existing mobile money infrastructure.
- The Philippines remains one of the leading markets where diaspora communities utilize cryptocurrencies for sending funds home efficiently.
Challenges Facing Crypto Remittances
Despite promising advantages, several hurdles remain:
- Price Volatility: Cryptocurrencies are known for their price swings; sudden drops can diminish transferred value before recipients withdraw funds.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Lack of comprehensive regulation creates legal ambiguities; non-compliance risks include fines or account freezes if exchanges violate AML/KYC laws.
- Scalability Limitations: Current blockchain networks face congestion issues during peak periods which slow down transactions further—an obstacle when handling large volumes typical in commercial remittance flows.
Potential Risks & Future Outlook
The volatility inherent in many cryptocurrencies poses significant risk; fluctuations can impact both senders’ costs and recipients’ purchasing power if not managed properly through stablecoins (cryptocurrencies pegged-to fiat currencies). Regulatory developments will also shape future adoption: stricter rules may limit certain uses but could enhance legitimacy overall.
Looking ahead towards 2025 and beyond:
- Increased infrastructure improvements aim at enhancing scalability
- Broader regulatory clarity will foster safer environments
- Growing acceptance among merchants will expand usability beyond peer-to-peer transfers
This evolving landscape suggests that cryptocurrency's role within cross-border remittance ecosystems will continue expanding as technological innovations address current limitations while regulatory frameworks mature globally.
How Cryptocurrency Enhances Financial Inclusion Across Borders
One notable benefit is its potential impact on underserved populations lacking access to traditional banking systems — especially migrants working abroad who rely heavily on remitting small amounts regularly back home . Digital wallets paired with cryptocurrency enable these users bypass costly intermediaries , reducing transfer costs significantly . Moreover , simplified onboarding processes mean even those unfamiliar with complex finance procedures can participate .
Risks To Consider When Using Cryptocurrency For Cross-Border Transfers
While promising , adopting crypto solutions requires awareness about potential pitfalls :
- Price volatility affecting transferred amounts
- Regulatory changes impacting legality
- Limited merchant acceptance outside niche markets
- Technical barriers such as wallet management complexities
By understanding these factors , users can better navigate this emerging space safely .
Final Thoughts: The Future Of Crypto In International Money Transfers
Cryptocurrency presents a compelling alternative that addresses many inefficiencies associated with traditional cross-border payments . As technological advancements continue alongside clearer regulations , its integration into global financial systems appears inevitable . Stakeholders—including regulators , service providers , consumers —must collaborate closely ensuring safety standards while fostering innovation . Ultimately , embracing this digital evolution could lead toward more inclusive global finance where transferring money across borders becomes faster , cheaper , more secure—and accessible—to all.
Keywords: cryptocurrency cross-border payments | international money transfer | blockchain technology | crypto remittance solutions | digital wallets | low-cost international transfers


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-15 02:19
How is cryptocurrency used for cross-border remittances?
How Is Cryptocurrency Used for Cross-Border Remittances?
Understanding the Role of Cryptocurrency in International Money Transfers
Cryptocurrency has increasingly become a viable alternative to traditional cross-border remittance methods. For individuals and businesses sending money across countries, cryptocurrencies offer a faster, cheaper, and more secure option compared to conventional services like wire transfers or money transfer operators such as Western Union and MoneyGram. This shift is driven by blockchain technology’s unique features, which address many limitations of traditional remittance channels.
Traditional cross-border remittances often involve high fees, lengthy processing times—sometimes taking several days—and risks related to fraud or transaction errors. These issues are especially problematic for migrant workers and families relying on timely financial support. Cryptocurrencies aim to mitigate these challenges by leveraging decentralized ledger technology that ensures transparency and security.
Blockchain Technology: The Backbone of Crypto Remittances
At the core of cryptocurrency’s utility in international transfers is blockchain technology—a distributed ledger system that records all transactions across a network of computers. Unlike centralized banking systems, blockchain operates without a single controlling authority, making it resistant to tampering or censorship.
When someone sends cryptocurrency like Bitcoin or Ethereum across borders, the transaction is validated by network participants (miners) within minutes rather than days. Once confirmed, the transaction becomes immutable—meaning it cannot be altered or reversed—adding an extra layer of security against fraud.
Key Benefits of Using Cryptocurrency for Cross-Border Payments
- Speed: Traditional bank wires can take anywhere from one to five business days depending on the countries involved; cryptocurrencies typically settle within minutes.
- Lower Costs: Transaction fees are generally lower than those charged by banks or money transfer services. Sending $200 via Bitcoin might cost around 1-2%, whereas conventional providers could charge up to 7%.
- Enhanced Security: Blockchain’s cryptographic protocols make transactions tamper-proof and reduce risks associated with hacking or unauthorized access.
- Accessibility: With just an internet connection and digital wallet, users can send funds without needing access to formal banking infrastructure—a significant advantage in regions with limited banking services.
Recent Trends & Developments in Crypto-Based Remittances
Over recent years, there has been notable progress toward mainstream adoption:
Regulatory Clarity
Governments are increasingly establishing frameworks for crypto use in financial transactions. For example, in 2023, U.S. authorities issued guidelines emphasizing compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations when using cryptocurrencies for remittance purposes. Clearer rules help legitimize crypto activities while protecting consumers.Partnerships & Platform Integrations
Major financial institutions have begun integrating cryptocurrencies into their platforms:- PayPal enabled users worldwide since 2020 to buy,sell,and hold cryptocurrencies.
- Several fintech firms now facilitate crypto-based remittances directly through user-friendly apps.
Growing Adoption Rates
Regions with limited access to traditional banking see rapid growth:- Countries like Kenya have embraced mobile-based crypto solutions due to existing mobile money infrastructure.
- The Philippines remains one of the leading markets where diaspora communities utilize cryptocurrencies for sending funds home efficiently.
Challenges Facing Crypto Remittances
Despite promising advantages, several hurdles remain:
- Price Volatility: Cryptocurrencies are known for their price swings; sudden drops can diminish transferred value before recipients withdraw funds.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Lack of comprehensive regulation creates legal ambiguities; non-compliance risks include fines or account freezes if exchanges violate AML/KYC laws.
- Scalability Limitations: Current blockchain networks face congestion issues during peak periods which slow down transactions further—an obstacle when handling large volumes typical in commercial remittance flows.
Potential Risks & Future Outlook
The volatility inherent in many cryptocurrencies poses significant risk; fluctuations can impact both senders’ costs and recipients’ purchasing power if not managed properly through stablecoins (cryptocurrencies pegged-to fiat currencies). Regulatory developments will also shape future adoption: stricter rules may limit certain uses but could enhance legitimacy overall.
Looking ahead towards 2025 and beyond:
- Increased infrastructure improvements aim at enhancing scalability
- Broader regulatory clarity will foster safer environments
- Growing acceptance among merchants will expand usability beyond peer-to-peer transfers
This evolving landscape suggests that cryptocurrency's role within cross-border remittance ecosystems will continue expanding as technological innovations address current limitations while regulatory frameworks mature globally.
How Cryptocurrency Enhances Financial Inclusion Across Borders
One notable benefit is its potential impact on underserved populations lacking access to traditional banking systems — especially migrants working abroad who rely heavily on remitting small amounts regularly back home . Digital wallets paired with cryptocurrency enable these users bypass costly intermediaries , reducing transfer costs significantly . Moreover , simplified onboarding processes mean even those unfamiliar with complex finance procedures can participate .
Risks To Consider When Using Cryptocurrency For Cross-Border Transfers
While promising , adopting crypto solutions requires awareness about potential pitfalls :
- Price volatility affecting transferred amounts
- Regulatory changes impacting legality
- Limited merchant acceptance outside niche markets
- Technical barriers such as wallet management complexities
By understanding these factors , users can better navigate this emerging space safely .
Final Thoughts: The Future Of Crypto In International Money Transfers
Cryptocurrency presents a compelling alternative that addresses many inefficiencies associated with traditional cross-border payments . As technological advancements continue alongside clearer regulations , its integration into global financial systems appears inevitable . Stakeholders—including regulators , service providers , consumers —must collaborate closely ensuring safety standards while fostering innovation . Ultimately , embracing this digital evolution could lead toward more inclusive global finance where transferring money across borders becomes faster , cheaper , more secure—and accessible—to all.
Keywords: cryptocurrency cross-border payments | international money transfer | blockchain technology | crypto remittance solutions | digital wallets | low-cost international transfers
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Tether USDt (USDT) Integration with CBDC Pilots Is Transforming Cross-Border Settlement
Understanding the Role of USDT in Modern Cross-Border Transactions
Tether USDt (USDT) is a widely used stablecoin pegged to the US dollar, offering stability and liquidity that are crucial for international financial transactions. Its primary appeal lies in its ability to maintain a consistent value, making it an attractive option for cross-border settlements where currency fluctuations can pose significant risks. Unlike traditional cryptocurrencies, USDT is backed by reserves claimed by Tether Limited, which holds fiat currency equivalents to support each token issued. This backing provides users with confidence in its stability, facilitating smoother and more predictable international transfers.
The Rise of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) represent a digital form of fiat money issued and regulated by national central banks. They aim to modernize monetary systems by providing secure, efficient, and transparent means for managing monetary policies and conducting transactions. Unlike cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum, CBDCs are centralized and backed directly by government authorities. Their development reflects efforts to enhance financial inclusion, reduce transaction costs, and improve the speed of settlement processes across borders.
How USDT Is Being Integrated into CBDC Pilot Programs
The integration of USDT into CBDC pilots marks an innovative step toward bridging traditional digital assets with state-backed currencies. This approach leverages the stability features of USDT alongside the regulatory oversight associated with CBDCs to streamline cross-border payments.
In 2022, Singapore’s Monetary Authority launched Project Ubin—a pioneering initiative exploring how a digital Singapore dollar could facilitate international transactions. Notably, this pilot included testing stablecoins like USDT as part of its settlement mechanisms to evaluate their effectiveness in real-world scenarios.
Similarly, China’s PBOC has been actively developing its own digital currency—DCEP or e-CNY—and has conducted cross-border transaction tests that could potentially incorporate stablecoins such as USDT in future phases.
Partnerships Between Stablecoin Providers and Financial Networks
A significant recent development involves Tether's partnership with SWIFT—the global messaging network connecting thousands of financial institutions worldwide. Announced in 2023, this collaboration aims to integrate USDT into SWIFT’s infrastructure—making it easier for banks and payment providers to utilize stablecoins for cross-border settlements efficiently.
Other central banks have shown interest too; some are researching how stablecoins can complement existing payment rails or serve as bridges during transition phases toward fully digitalized monetary systems.
Regulatory Environment Impacting Stablecoin Integration
As these technological advancements unfold, regulatory considerations remain at the forefront. Authorities such as the U.S Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) issued guidelines on stablecoin regulation in 2023—aimed at ensuring transparency around reserve backing and compliance with AML/KYC standards.
Global organizations like FATF have also emphasized strict anti-money laundering measures for crypto assets involved in cross-border payments. These regulations influence how entities can deploy stablecoins like USDT within official pilot programs while maintaining legal compliance across jurisdictions.
Benefits: Speeding Up Cross-Border Payments With Stablecoins
One key advantage offered by integrating USDT into CBDC pilots is significantly faster transaction processing times compared to traditional methods involving correspondent banking networks—which often take days due to multiple intermediaries handling conversions between different currencies.
Blockchain technology underpins these innovations; it enables near-instantaneous settlement confirmation while reducing reliance on manual reconciliation processes that typically slow down international transfers.
Cost Efficiency Through Reduced Transaction Fees
Traditional cross-border payments incur high fees because they involve multiple currency conversions along with intermediary charges from correspondent banks or remittance services. Using stablecoins like USDT minimizes these costs since transactions occur directly on blockchain networks without needing extensive intermediaries or foreign exchange conversions—resulting in substantial savings especially beneficial for businesses engaged in frequent international trade or remittances.
Enhanced Security & Transparency Features
Blockchain's inherent security features—including cryptographic validation—provide increased protection against fraud while ensuring transparency through publicly accessible ledgers visible during each transaction process. This transparency helps regulators monitor compliance more effectively while giving users confidence that their funds are secure throughout settlement procedures involving both CBDCs and stablecoins like USDT.
Challenges Facing Integration Efforts
Despite promising developments, several hurdles must be addressed before widespread adoption becomes feasible:
- Regulatory Uncertainty: The evolving legal landscape surrounding cryptocurrencies poses risks related to compliance requirements.
- Security Risks: While blockchain offers security benefits; vulnerabilities such as hacking incidents targeting exchanges or wallets remain concerns.
- Market Volatility: Although pegged stability reduces risk compared to other cryptos — fluctuations still exist due to market dynamics affecting reserve backing.
- Interoperability Issues: Ensuring seamless operation between different platforms supporting various tokens requires standardized protocols—a work-in-progress area within blockchain development communities.
Implications For Global Finance Ecosystems
Integrating stablecoins like USDT within CBDC frameworks signifies a shift towards hybrid models combining private sector innovation with public sector regulation—a move likely influencing future policy decisions worldwide:
- Increased Competition: Traditional banking systems may face pressure from new entrants leveraging blockchain-based solutions.
- Greater Financial Inclusion: Faster settlements could enable underserved regions access affordable remittance services.
- Policy Evolution: Governments might develop new regulations balancing innovation incentives against systemic risks posed by unregulated crypto assets.
Future Outlook And Strategic Considerations
Looking ahead beyond current pilots:
- Broader Adoption Scenarios – As successful case studies emerge from projects involving both CBDCs and stablecoins such as USDT,
- Expect wider acceptance among multinational corporations seeking efficient settlement options
- Potential expansion into retail-level cross-border payments
- Technological Advancements – Continued improvements will focus on:
- Enhancing interoperability standards
- Strengthening security protocols3.. Regulatory Harmonization – International cooperation will be vital:
- Developing unified guidelines governing crypto-assets used alongside national currencies
- Facilitating smoother integration across jurisdictions
Why It Matters For Stakeholders
For central banks aiming at modernizing monetary infrastructure,
this integration offers opportunities but also necessitates careful navigation through complex regulatory landscapes—to harness benefits without exposing systemic vulnerabilities.
Financial institutions stand at a crossroads where embracing innovative solutions could lead either toward competitive advantage or operational risk if not managed properly.
Businesses engaged in global trade should monitor these developments closely—they stand poised either benefit from reduced costs & faster settlements—or face disruptions if regulatory barriers tighten unexpectedly.
Final Thoughts
The ongoing efforts integrating Tether USDt within CBDC pilots highlight an important evolution towards more efficient global payment systems rooted firmly at the intersection between private innovation and public regulation — promising faster transactions combined with enhanced security but requiring vigilant management of emerging risks.
By understanding these dynamics today,stakeholders can better prepare themselves for tomorrow's increasingly digitized financial landscape—and contribute meaningfully towards shaping resilient future frameworks that support seamless international commerce.
Keywords: Cross-Border Payments | Stablecoin Integration | Blockchain Technology | Digital Currency | Central Bank Digital Currency | International Settlement | Cryptocurrency Regulation


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-14 20:21
How does Tether USDt (USDT) integration with CBDC pilots affect cross-border settlement?
How Tether USDt (USDT) Integration with CBDC Pilots Is Transforming Cross-Border Settlement
Understanding the Role of USDT in Modern Cross-Border Transactions
Tether USDt (USDT) is a widely used stablecoin pegged to the US dollar, offering stability and liquidity that are crucial for international financial transactions. Its primary appeal lies in its ability to maintain a consistent value, making it an attractive option for cross-border settlements where currency fluctuations can pose significant risks. Unlike traditional cryptocurrencies, USDT is backed by reserves claimed by Tether Limited, which holds fiat currency equivalents to support each token issued. This backing provides users with confidence in its stability, facilitating smoother and more predictable international transfers.
The Rise of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) represent a digital form of fiat money issued and regulated by national central banks. They aim to modernize monetary systems by providing secure, efficient, and transparent means for managing monetary policies and conducting transactions. Unlike cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum, CBDCs are centralized and backed directly by government authorities. Their development reflects efforts to enhance financial inclusion, reduce transaction costs, and improve the speed of settlement processes across borders.
How USDT Is Being Integrated into CBDC Pilot Programs
The integration of USDT into CBDC pilots marks an innovative step toward bridging traditional digital assets with state-backed currencies. This approach leverages the stability features of USDT alongside the regulatory oversight associated with CBDCs to streamline cross-border payments.
In 2022, Singapore’s Monetary Authority launched Project Ubin—a pioneering initiative exploring how a digital Singapore dollar could facilitate international transactions. Notably, this pilot included testing stablecoins like USDT as part of its settlement mechanisms to evaluate their effectiveness in real-world scenarios.
Similarly, China’s PBOC has been actively developing its own digital currency—DCEP or e-CNY—and has conducted cross-border transaction tests that could potentially incorporate stablecoins such as USDT in future phases.
Partnerships Between Stablecoin Providers and Financial Networks
A significant recent development involves Tether's partnership with SWIFT—the global messaging network connecting thousands of financial institutions worldwide. Announced in 2023, this collaboration aims to integrate USDT into SWIFT’s infrastructure—making it easier for banks and payment providers to utilize stablecoins for cross-border settlements efficiently.
Other central banks have shown interest too; some are researching how stablecoins can complement existing payment rails or serve as bridges during transition phases toward fully digitalized monetary systems.
Regulatory Environment Impacting Stablecoin Integration
As these technological advancements unfold, regulatory considerations remain at the forefront. Authorities such as the U.S Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) issued guidelines on stablecoin regulation in 2023—aimed at ensuring transparency around reserve backing and compliance with AML/KYC standards.
Global organizations like FATF have also emphasized strict anti-money laundering measures for crypto assets involved in cross-border payments. These regulations influence how entities can deploy stablecoins like USDT within official pilot programs while maintaining legal compliance across jurisdictions.
Benefits: Speeding Up Cross-Border Payments With Stablecoins
One key advantage offered by integrating USDT into CBDC pilots is significantly faster transaction processing times compared to traditional methods involving correspondent banking networks—which often take days due to multiple intermediaries handling conversions between different currencies.
Blockchain technology underpins these innovations; it enables near-instantaneous settlement confirmation while reducing reliance on manual reconciliation processes that typically slow down international transfers.
Cost Efficiency Through Reduced Transaction Fees
Traditional cross-border payments incur high fees because they involve multiple currency conversions along with intermediary charges from correspondent banks or remittance services. Using stablecoins like USDT minimizes these costs since transactions occur directly on blockchain networks without needing extensive intermediaries or foreign exchange conversions—resulting in substantial savings especially beneficial for businesses engaged in frequent international trade or remittances.
Enhanced Security & Transparency Features
Blockchain's inherent security features—including cryptographic validation—provide increased protection against fraud while ensuring transparency through publicly accessible ledgers visible during each transaction process. This transparency helps regulators monitor compliance more effectively while giving users confidence that their funds are secure throughout settlement procedures involving both CBDCs and stablecoins like USDT.
Challenges Facing Integration Efforts
Despite promising developments, several hurdles must be addressed before widespread adoption becomes feasible:
- Regulatory Uncertainty: The evolving legal landscape surrounding cryptocurrencies poses risks related to compliance requirements.
- Security Risks: While blockchain offers security benefits; vulnerabilities such as hacking incidents targeting exchanges or wallets remain concerns.
- Market Volatility: Although pegged stability reduces risk compared to other cryptos — fluctuations still exist due to market dynamics affecting reserve backing.
- Interoperability Issues: Ensuring seamless operation between different platforms supporting various tokens requires standardized protocols—a work-in-progress area within blockchain development communities.
Implications For Global Finance Ecosystems
Integrating stablecoins like USDT within CBDC frameworks signifies a shift towards hybrid models combining private sector innovation with public sector regulation—a move likely influencing future policy decisions worldwide:
- Increased Competition: Traditional banking systems may face pressure from new entrants leveraging blockchain-based solutions.
- Greater Financial Inclusion: Faster settlements could enable underserved regions access affordable remittance services.
- Policy Evolution: Governments might develop new regulations balancing innovation incentives against systemic risks posed by unregulated crypto assets.
Future Outlook And Strategic Considerations
Looking ahead beyond current pilots:
- Broader Adoption Scenarios – As successful case studies emerge from projects involving both CBDCs and stablecoins such as USDT,
- Expect wider acceptance among multinational corporations seeking efficient settlement options
- Potential expansion into retail-level cross-border payments
- Technological Advancements – Continued improvements will focus on:
- Enhancing interoperability standards
- Strengthening security protocols3.. Regulatory Harmonization – International cooperation will be vital:
- Developing unified guidelines governing crypto-assets used alongside national currencies
- Facilitating smoother integration across jurisdictions
Why It Matters For Stakeholders
For central banks aiming at modernizing monetary infrastructure,
this integration offers opportunities but also necessitates careful navigation through complex regulatory landscapes—to harness benefits without exposing systemic vulnerabilities.
Financial institutions stand at a crossroads where embracing innovative solutions could lead either toward competitive advantage or operational risk if not managed properly.
Businesses engaged in global trade should monitor these developments closely—they stand poised either benefit from reduced costs & faster settlements—or face disruptions if regulatory barriers tighten unexpectedly.
Final Thoughts
The ongoing efforts integrating Tether USDt within CBDC pilots highlight an important evolution towards more efficient global payment systems rooted firmly at the intersection between private innovation and public regulation — promising faster transactions combined with enhanced security but requiring vigilant management of emerging risks.
By understanding these dynamics today,stakeholders can better prepare themselves for tomorrow's increasingly digitized financial landscape—and contribute meaningfully towards shaping resilient future frameworks that support seamless international commerce.
Keywords: Cross-Border Payments | Stablecoin Integration | Blockchain Technology | Digital Currency | Central Bank Digital Currency | International Settlement | Cryptocurrency Regulation
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Web3: Unlocking the Future of the Internet
Understanding Web3 and Its Potential
Web3 is often described as the next evolution of the internet, promising a more decentralized, transparent, and user-centric digital landscape. Coined by Gavin Wood, co-founder of Ethereum, Web3 leverages blockchain technology to fundamentally change how data is stored, shared, and controlled online. Unlike its predecessors—Web1 (static content) and Web2 (interactive platforms)—Web3 aims to empower users with ownership over their digital identities and assets while reducing reliance on centralized authorities.
This shift is driven by advancements in blockchain technology that enable secure peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries. Smart contracts automate processes and enforce agreements automatically once predefined conditions are met. As a result, Web3 has the potential to redefine online interactions across sectors such as finance, social media, gaming, art, and real estate.
The Evolution from Web1 to Web3
The internet's journey began with static web pages where users primarily consumed content without much interaction. This era was characterized by limited user engagement but offered broad accessibility. The advent of Web2 introduced dynamic content through social media platforms like Facebook and Twitter alongside e-commerce giants such as Amazon. While this era fostered unprecedented connectivity and innovation—enabling sharing of information at scale—it also concentrated power within large corporations that control vast amounts of user data.
Recognizing these issues has fueled interest in decentralization principles underpinning Web3. By distributing data across multiple nodes rather than central servers—and utilizing blockchain for transparency—Web3 seeks to address privacy concerns while giving users more control over their personal information.
Key Technologies Powering Web3
Blockchain Technology: At its core lies distributed ledger technology that ensures security through cryptography while maintaining transparency via public transaction records. Once data enters a blockchain network—such as Bitcoin or Ethereum—it becomes immutable; it cannot be altered or erased later.
Smart Contracts: These are self-executing code snippets embedded within blockchains that facilitate automatic transactions based on predetermined rules without human intervention. They reduce reliance on intermediaries like banks or legal entities for executing agreements securely.
Decentralized Applications (dApps): Built atop blockchain networks, dApps operate without centralized servers—they run on peer-to-peer networks ensuring resilience against censorship or shutdowns.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi): DeFi platforms recreate traditional financial services such as lending or trading using smart contracts on blockchains like Ethereum; they aim to democratize access to financial tools globally.
NFTs & Digital Assets: Non-fungible tokens have revolutionized ownership rights for digital art collectibles but also extend into domains like virtual real estate or gaming assets—all secured via blockchain’s transparency features.
Opportunities Presented by Web3
Enhanced User Control & Privacy
One significant advantage of Web3 is empowering individuals with ownership over their personal data through decentralized identity solutions (DIDs). Users can decide what information they share—and with whom—reducing risks associated with centralized databases prone to breaches. This shift fosters greater trust between users and service providers because transactions are transparent yet privacy-preserving when designed correctly.
Financial Inclusion & Innovation
DeFi applications eliminate barriers posed by traditional banking systems—especially in underserved regions—by providing accessible financial services via smartphones connected directly to blockchain networks. This democratization could lead toward broader economic participation worldwide while fostering innovative business models built around token economies or microtransactions.
Content Ownership & Monetization Opportunities
NFTs enable creators—from artists to musicians—to monetize their work directly without intermediaries like galleries or record labels. Blockchain’s provenance tracking assures buyers about authenticity while enabling new revenue streams through royalties embedded into smart contracts—a game-changer for creative industries adapting to digital transformation trends.
Challenges Facing Widespread Adoption
Despite its promise, several hurdles remain before full-scale adoption becomes mainstream:
Regulatory Uncertainty: Governments worldwide are still formulating policies regarding cryptocurrencies and decentralized applications—which can create legal ambiguities affecting innovation timelines.Scalability Issues: Current blockchain infrastructure faces challenges related to transaction speed and costs; solutions like layer-2 scaling protocols are under development but not yet universally adopted.Security Risks: Smart contract vulnerabilities have led to notable exploits causing significant financial losses; rigorous auditing practices are essential.Digital Divide Concerns
While decentralization offers empowerment opportunities globally—including in developing nations—the technological complexity might widen existing inequalities if access remains limited due to infrastructure gaps or lack of technical literacy among certain populations.Environmental Impact Considerations
Some consensus mechanisms used in popular blockchains consume substantial energy—for example proof-of-work systems—which raises sustainability questions amid growing environmental awareness.Moving Toward Mainstream Adoption
To realize the full potential of Web3:
- Infrastructure must become more scalable—with faster transaction speeds at lower costs.
- Clearer regulatory frameworks should be established globally—to foster innovation while protecting consumers.
- Education initiatives need expansion—to bridge knowledge gaps among general users unfamiliar with complex technologies involved.
- Sustainable consensus mechanisms should be prioritized—to minimize environmental footprints associated with network maintenance efforts.
How Businesses Can Prepare for a Decentralized Future
Organizations aiming for future-proof strategies should consider integrating decentralized principles into their operations gradually:
- Explore partnerships within the crypto ecosystem—for example, adopting NFT-based loyalty programs.
- Invest in employee training focused on understanding blockchain fundamentals.
- Develop pilot projects leveraging smart contracts for supply chain management or payments processing.
- Stay informed about evolving regulations impacting digital assets.
The Role of Regulation in Shaping Wepb’s Future
Regulatory clarity will play a pivotal role in determining how quickly mainstream adoption occurs—and whether innovations flourish sustainably within legal boundaries. Governments worldwide are balancing fostering innovation against consumer protection concerns; some have embraced cryptocurrencies openly whereas others impose restrictions due diligence measures which could influence market growth trajectories.
Final Thoughts
Web3 holds transformative potential across multiple sectors—from redefining ownership rights through NFTs to creating inclusive financial ecosystems via DeFi platforms—all built upon robust security features inherent in blockchain technology. However—as it stands—the path forward requires addressing scalability challenges、regulatory uncertainties、security vulnerabilities、and social equity considerations。 By proactively tackling these issues—with collaboration among technologists、 policymakers、and communities—the vision of an open、transparent,and user-controlled internet can become reality.


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-14 09:40
What potential does Web3 have for the future of the internet?
Web3: Unlocking the Future of the Internet
Understanding Web3 and Its Potential
Web3 is often described as the next evolution of the internet, promising a more decentralized, transparent, and user-centric digital landscape. Coined by Gavin Wood, co-founder of Ethereum, Web3 leverages blockchain technology to fundamentally change how data is stored, shared, and controlled online. Unlike its predecessors—Web1 (static content) and Web2 (interactive platforms)—Web3 aims to empower users with ownership over their digital identities and assets while reducing reliance on centralized authorities.
This shift is driven by advancements in blockchain technology that enable secure peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries. Smart contracts automate processes and enforce agreements automatically once predefined conditions are met. As a result, Web3 has the potential to redefine online interactions across sectors such as finance, social media, gaming, art, and real estate.
The Evolution from Web1 to Web3
The internet's journey began with static web pages where users primarily consumed content without much interaction. This era was characterized by limited user engagement but offered broad accessibility. The advent of Web2 introduced dynamic content through social media platforms like Facebook and Twitter alongside e-commerce giants such as Amazon. While this era fostered unprecedented connectivity and innovation—enabling sharing of information at scale—it also concentrated power within large corporations that control vast amounts of user data.
Recognizing these issues has fueled interest in decentralization principles underpinning Web3. By distributing data across multiple nodes rather than central servers—and utilizing blockchain for transparency—Web3 seeks to address privacy concerns while giving users more control over their personal information.
Key Technologies Powering Web3
Blockchain Technology: At its core lies distributed ledger technology that ensures security through cryptography while maintaining transparency via public transaction records. Once data enters a blockchain network—such as Bitcoin or Ethereum—it becomes immutable; it cannot be altered or erased later.
Smart Contracts: These are self-executing code snippets embedded within blockchains that facilitate automatic transactions based on predetermined rules without human intervention. They reduce reliance on intermediaries like banks or legal entities for executing agreements securely.
Decentralized Applications (dApps): Built atop blockchain networks, dApps operate without centralized servers—they run on peer-to-peer networks ensuring resilience against censorship or shutdowns.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi): DeFi platforms recreate traditional financial services such as lending or trading using smart contracts on blockchains like Ethereum; they aim to democratize access to financial tools globally.
NFTs & Digital Assets: Non-fungible tokens have revolutionized ownership rights for digital art collectibles but also extend into domains like virtual real estate or gaming assets—all secured via blockchain’s transparency features.
Opportunities Presented by Web3
Enhanced User Control & Privacy
One significant advantage of Web3 is empowering individuals with ownership over their personal data through decentralized identity solutions (DIDs). Users can decide what information they share—and with whom—reducing risks associated with centralized databases prone to breaches. This shift fosters greater trust between users and service providers because transactions are transparent yet privacy-preserving when designed correctly.
Financial Inclusion & Innovation
DeFi applications eliminate barriers posed by traditional banking systems—especially in underserved regions—by providing accessible financial services via smartphones connected directly to blockchain networks. This democratization could lead toward broader economic participation worldwide while fostering innovative business models built around token economies or microtransactions.
Content Ownership & Monetization Opportunities
NFTs enable creators—from artists to musicians—to monetize their work directly without intermediaries like galleries or record labels. Blockchain’s provenance tracking assures buyers about authenticity while enabling new revenue streams through royalties embedded into smart contracts—a game-changer for creative industries adapting to digital transformation trends.
Challenges Facing Widespread Adoption
Despite its promise, several hurdles remain before full-scale adoption becomes mainstream:
Regulatory Uncertainty: Governments worldwide are still formulating policies regarding cryptocurrencies and decentralized applications—which can create legal ambiguities affecting innovation timelines.Scalability Issues: Current blockchain infrastructure faces challenges related to transaction speed and costs; solutions like layer-2 scaling protocols are under development but not yet universally adopted.Security Risks: Smart contract vulnerabilities have led to notable exploits causing significant financial losses; rigorous auditing practices are essential.Digital Divide Concerns
While decentralization offers empowerment opportunities globally—including in developing nations—the technological complexity might widen existing inequalities if access remains limited due to infrastructure gaps or lack of technical literacy among certain populations.Environmental Impact Considerations
Some consensus mechanisms used in popular blockchains consume substantial energy—for example proof-of-work systems—which raises sustainability questions amid growing environmental awareness.Moving Toward Mainstream Adoption
To realize the full potential of Web3:
- Infrastructure must become more scalable—with faster transaction speeds at lower costs.
- Clearer regulatory frameworks should be established globally—to foster innovation while protecting consumers.
- Education initiatives need expansion—to bridge knowledge gaps among general users unfamiliar with complex technologies involved.
- Sustainable consensus mechanisms should be prioritized—to minimize environmental footprints associated with network maintenance efforts.
How Businesses Can Prepare for a Decentralized Future
Organizations aiming for future-proof strategies should consider integrating decentralized principles into their operations gradually:
- Explore partnerships within the crypto ecosystem—for example, adopting NFT-based loyalty programs.
- Invest in employee training focused on understanding blockchain fundamentals.
- Develop pilot projects leveraging smart contracts for supply chain management or payments processing.
- Stay informed about evolving regulations impacting digital assets.
The Role of Regulation in Shaping Wepb’s Future
Regulatory clarity will play a pivotal role in determining how quickly mainstream adoption occurs—and whether innovations flourish sustainably within legal boundaries. Governments worldwide are balancing fostering innovation against consumer protection concerns; some have embraced cryptocurrencies openly whereas others impose restrictions due diligence measures which could influence market growth trajectories.
Final Thoughts
Web3 holds transformative potential across multiple sectors—from redefining ownership rights through NFTs to creating inclusive financial ecosystems via DeFi platforms—all built upon robust security features inherent in blockchain technology. However—as it stands—the path forward requires addressing scalability challenges、regulatory uncertainties、security vulnerabilities、and social equity considerations。 By proactively tackling these issues—with collaboration among technologists、 policymakers、and communities—the vision of an open、transparent,and user-controlled internet can become reality.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Are Real-World Asset Tokens? An In-Depth Explanation
Understanding Real-World Asset Tokens
Real-world asset tokens, often called tokenized assets, are digital representations of physical or financial assets issued on a blockchain. This innovative approach leverages blockchain’s security, transparency, and decentralization features to transform how assets are owned, traded, and managed. Essentially, these tokens serve as digital certificates of ownership or rights to tangible items like real estate or commodities, or financial instruments such as stocks and bonds.
The core idea is to convert physical assets into tradable digital tokens that can be easily transferred across borders without the need for traditional intermediaries. This process not only simplifies transactions but also opens up new opportunities for investors by making previously illiquid markets more accessible.
How Tokenization Works
Tokenizing an asset involves several steps facilitated by blockchain technology:
- Asset Valuation and Verification: The physical or financial asset is appraised and verified for authenticity.
- Creation of Digital Tokens: Using smart contracts—self-executing contracts with coded rules—the asset is represented as a specific number of tokens on the blockchain.
- Issuance and Distribution: These tokens are then issued through a tokenization platform where investors can purchase fractional shares if desired.
- Trading and Management: Once issued, these tokens can be traded peer-to-peer on various platforms with all transactions recorded transparently on the blockchain.
This process ensures that ownership rights are securely stored in a tamper-proof ledger while enabling fractional ownership—meaning investors don’t need to buy entire properties or large quantities of commodities but can instead invest smaller amounts.
Benefits of Tokenizing Real-World Assets
Tokenization offers multiple advantages over traditional methods:
Enhanced Liquidity: By converting assets into smaller units (fractions), tokenized assets allow more participants—including retail investors—to access markets that were once limited to institutional players.
Faster Transactions: Blockchain reduces settlement times from days to minutes compared to conventional processes involving banks or brokers.
Greater Transparency: Every transaction is recorded immutably on the blockchain, providing clear audit trails which reduce fraud risks.
Increased Accessibility: Investors worldwide can participate without geographical barriers thanks to online platforms supporting token trading.
These benefits collectively contribute toward democratizing investment opportunities across various sectors like real estate, commodities, art collectibles, and traditional securities.
Regulatory Landscape Surrounding Asset Tokenization
Despite its promising potential, the regulatory environment remains complex and evolving globally. Different jurisdictions have varying approaches—from clear guidelines in some countries like Switzerland and Singapore to ambiguous regulations elsewhere.
Regulators focus primarily on issues such as securities classification (whether tokens qualify as securities), anti-money laundering (AML) compliance requirements, investor protections, and licensing standards for platforms facilitating trading activities. As this field matures rapidly—with innovations outpacing regulation—stakeholders must stay informed about legal developments affecting their operations or investments in tokenized assets.
Recent Trends Shaping the Market
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated interest in digital solutions including asset tokenization due to increased demand for remote investment options amid economic uncertainty. Additionally:
The rise of decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms has expanded possibilities for lending against tokenized collateral or earning yields through staking these digital representations.
Major industry players have launched projects focusing on real estate crowdfunding via tokenized shares—making property investments more accessible than ever before.
2022 marked significant growth with increased adoption among institutional investors seeking efficient ways to diversify portfolios while maintaining liquidity.
Risks Associated With Real-World Asset Tokens
While promising benefits exist; potential pitfalls should not be overlooked:
Regulatory Risks: Lack of comprehensive regulations could lead to legal uncertainties impacting market stability.
Security Concerns: Blockchain systems are vulnerable if security protocols aren’t robust; hacking incidents could compromise investor holdings.
Market Volatility: The value fluctuations typical in crypto markets may affect even stable-assets if underlying physical assets experience price swings unexpectedly.
Investors should conduct thorough due diligence before engaging with any platform offering asset-backed tokens—and consider consulting legal experts familiar with local laws governing securities issuance.
Examples From Industry Leaders
Several companies exemplify successful implementation of real-world asset tokenization:
– Propellr partnered with property developers allowing fractional ownership in commercial real estate projects—a move that broadens access beyond wealthy institutional clients.
– GrainChain digitizes agricultural commodities such as grains using blockchain-based tracking systems—enhancing transparency from farm-to-market logistics while enabling farmers easier access to global buyers.
– Art marketplaces like Rarible facilitate artists’ ability to tokenize artwork pieces—creating new revenue streams through secondary sales while expanding collector reach globally.
Future Outlook: Opportunities & Challenges Ahead
As technology advances alongside growing regulatory clarity in certain regions—and increasing acceptance among mainstream financial institutions—the landscape for real-world asset tokens appears poised for expansion further into mainstream finance sectors such as banking services and insurance products.
However,
stakeholders must navigate challenges including developing standardized frameworks compatible across jurisdictions; ensuring security measures keep pace with evolving cyber threats; managing market volatility risks; addressing concerns around valuation accuracy; plus fostering consumer trust through transparent practices.
By addressing these issues proactively—with ongoing innovation coupled with responsible regulation—the potential exists not only for democratizing access but also transforming how we perceive ownership itself—from exclusive holdings towards liquid participation enabled by blockchain-powered digitization.
Understanding what constitutes a real-world asset token provides foundational insight into this transformative trend shaping modern finance—and highlights both its promise and complexities within today’s dynamic economic environment


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-11 12:45
What are real-world asset tokens?
What Are Real-World Asset Tokens? An In-Depth Explanation
Understanding Real-World Asset Tokens
Real-world asset tokens, often called tokenized assets, are digital representations of physical or financial assets issued on a blockchain. This innovative approach leverages blockchain’s security, transparency, and decentralization features to transform how assets are owned, traded, and managed. Essentially, these tokens serve as digital certificates of ownership or rights to tangible items like real estate or commodities, or financial instruments such as stocks and bonds.
The core idea is to convert physical assets into tradable digital tokens that can be easily transferred across borders without the need for traditional intermediaries. This process not only simplifies transactions but also opens up new opportunities for investors by making previously illiquid markets more accessible.
How Tokenization Works
Tokenizing an asset involves several steps facilitated by blockchain technology:
- Asset Valuation and Verification: The physical or financial asset is appraised and verified for authenticity.
- Creation of Digital Tokens: Using smart contracts—self-executing contracts with coded rules—the asset is represented as a specific number of tokens on the blockchain.
- Issuance and Distribution: These tokens are then issued through a tokenization platform where investors can purchase fractional shares if desired.
- Trading and Management: Once issued, these tokens can be traded peer-to-peer on various platforms with all transactions recorded transparently on the blockchain.
This process ensures that ownership rights are securely stored in a tamper-proof ledger while enabling fractional ownership—meaning investors don’t need to buy entire properties or large quantities of commodities but can instead invest smaller amounts.
Benefits of Tokenizing Real-World Assets
Tokenization offers multiple advantages over traditional methods:
Enhanced Liquidity: By converting assets into smaller units (fractions), tokenized assets allow more participants—including retail investors—to access markets that were once limited to institutional players.
Faster Transactions: Blockchain reduces settlement times from days to minutes compared to conventional processes involving banks or brokers.
Greater Transparency: Every transaction is recorded immutably on the blockchain, providing clear audit trails which reduce fraud risks.
Increased Accessibility: Investors worldwide can participate without geographical barriers thanks to online platforms supporting token trading.
These benefits collectively contribute toward democratizing investment opportunities across various sectors like real estate, commodities, art collectibles, and traditional securities.
Regulatory Landscape Surrounding Asset Tokenization
Despite its promising potential, the regulatory environment remains complex and evolving globally. Different jurisdictions have varying approaches—from clear guidelines in some countries like Switzerland and Singapore to ambiguous regulations elsewhere.
Regulators focus primarily on issues such as securities classification (whether tokens qualify as securities), anti-money laundering (AML) compliance requirements, investor protections, and licensing standards for platforms facilitating trading activities. As this field matures rapidly—with innovations outpacing regulation—stakeholders must stay informed about legal developments affecting their operations or investments in tokenized assets.
Recent Trends Shaping the Market
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated interest in digital solutions including asset tokenization due to increased demand for remote investment options amid economic uncertainty. Additionally:
The rise of decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms has expanded possibilities for lending against tokenized collateral or earning yields through staking these digital representations.
Major industry players have launched projects focusing on real estate crowdfunding via tokenized shares—making property investments more accessible than ever before.
2022 marked significant growth with increased adoption among institutional investors seeking efficient ways to diversify portfolios while maintaining liquidity.
Risks Associated With Real-World Asset Tokens
While promising benefits exist; potential pitfalls should not be overlooked:
Regulatory Risks: Lack of comprehensive regulations could lead to legal uncertainties impacting market stability.
Security Concerns: Blockchain systems are vulnerable if security protocols aren’t robust; hacking incidents could compromise investor holdings.
Market Volatility: The value fluctuations typical in crypto markets may affect even stable-assets if underlying physical assets experience price swings unexpectedly.
Investors should conduct thorough due diligence before engaging with any platform offering asset-backed tokens—and consider consulting legal experts familiar with local laws governing securities issuance.
Examples From Industry Leaders
Several companies exemplify successful implementation of real-world asset tokenization:
– Propellr partnered with property developers allowing fractional ownership in commercial real estate projects—a move that broadens access beyond wealthy institutional clients.
– GrainChain digitizes agricultural commodities such as grains using blockchain-based tracking systems—enhancing transparency from farm-to-market logistics while enabling farmers easier access to global buyers.
– Art marketplaces like Rarible facilitate artists’ ability to tokenize artwork pieces—creating new revenue streams through secondary sales while expanding collector reach globally.
Future Outlook: Opportunities & Challenges Ahead
As technology advances alongside growing regulatory clarity in certain regions—and increasing acceptance among mainstream financial institutions—the landscape for real-world asset tokens appears poised for expansion further into mainstream finance sectors such as banking services and insurance products.
However,
stakeholders must navigate challenges including developing standardized frameworks compatible across jurisdictions; ensuring security measures keep pace with evolving cyber threats; managing market volatility risks; addressing concerns around valuation accuracy; plus fostering consumer trust through transparent practices.
By addressing these issues proactively—with ongoing innovation coupled with responsible regulation—the potential exists not only for democratizing access but also transforming how we perceive ownership itself—from exclusive holdings towards liquid participation enabled by blockchain-powered digitization.
Understanding what constitutes a real-world asset token provides foundational insight into this transformative trend shaping modern finance—and highlights both its promise and complexities within today’s dynamic economic environment
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Can Users Protect Against Sandwich Attacks in DeFi?
DeFi (Decentralized Finance) has revolutionized the way individuals interact with financial services, offering greater accessibility and control over assets. However, this innovation comes with its own set of security challenges, notably sandwich attacks. Understanding how these attacks work and implementing effective protective measures is essential for users aiming to safeguard their funds. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of strategies users can adopt to defend against sandwich attacks in the DeFi ecosystem.
What Are Sandwich Attacks and Why Do They Matter?
Sandwich attacks exploit vulnerabilities inherent in smart contract-based protocols that rely on transaction order processing. Attackers manipulate the sequence of transactions—placing their malicious trade between two legitimate ones—to profit at the expense of unsuspecting users. These tactics can lead to significant financial losses, erode trust in DeFi platforms, and undermine overall ecosystem stability.
Given that many DeFi protocols depend on transparent transaction ordering within blockchain networks like Ethereum, attackers often leverage tools such as front-running bots or gas price manipulation techniques to execute these malicious strategies effectively.
Recognizing Common Types of Sandwich Attacks
Understanding different forms of sandwich attacks helps users identify potential risks:
Front-Running: An attacker spots a pending transaction (e.g., a large trade) and places their own transaction ahead by paying higher gas fees, thus executing first.
Back-Running: The attacker inserts their transaction immediately after a legitimate one to capitalize on price movements or liquidity shifts caused by the initial trade.
Reentrancy Attacks: While slightly different from classic sandwich tactics, reentrancy involves repeatedly calling a contract before previous executions complete—often exploited alongside other attack vectors.
These methods often work together within complex attack sequences aimed at extracting maximum value from targeted transactions.
Practical Strategies for Users to Protect Their Funds
While developers are responsible for implementing security features into smart contracts, individual users also play a crucial role in minimizing risk exposure through best practices:
1. Use Reputable Platforms and Protocols
Choosing well-audited DeFi platforms reduces vulnerability exposure significantly. Established protocols undergo rigorous security assessments that help identify weaknesses susceptible to sandwich or other exploits.
2. Adjust Transaction Timing and Gas Settings
Manipulating your transaction's parameters can make front-running less profitable:
Set Higher Gas Prices Carefully: Paying higher gas fees may prioritize your transactions but also signals attackers about your activity; use this tactic judiciously.
Use Gas Limit Strategies: Some wallets allow setting custom gas limits or using dynamic fee models like EIP-1559 (Ethereum's fee market upgrade), which can help manage transaction priority more predictably.
3. Implement Privacy-Preserving Techniques
Privacy-focused tools obscure user activity from potential attackers:
Use Flashbots or Private RPC Nodes: These services enable submitting transactions directly without broadcasting them publicly first—reducing visibility that front-runners rely upon.
Leverage Layer 2 Solutions: Transactions conducted off-chain via Layer 2 networks often have reduced susceptibility due to less transparent mempool data accessible by attackers.
4. Diversify Investments Across Multiple Protocols
Spreading assets across various platforms minimizes impact if one protocol becomes compromised or targeted by an attack:
Avoid concentrating large sums into single protocols vulnerable to known exploits.
Regularly review protocol security reports before committing significant funds.
5. Stay Informed About Ongoing Threats
Active monitoring enables early detection of suspicious activities:
Subscribe to updates from reputable cybersecurity firms specializing in blockchain security.
Follow community channels such as Twitter accounts dedicated to DeFi safety alerts or Discord groups discussing protocol vulnerabilities.
Leveraging Smart Contract Security Measures as an Individual User
Although most protections are embedded during development phases, some user-centric approaches include:
Using Wallet Features: Many wallets now incorporate features like "transaction speed" controls or "priority fee" settings designed explicitly for mitigating front-running risks.
Engaging with Non-Custodial Services: Non-custodial wallets give you more control over how transactions are broadcasted and processed compared with centralized exchanges' custodial solutions prone to delay-induced vulnerabilities.
The Role of Continuous Education & Vigilance
The rapidly evolving nature of blockchain technology means new attack vectors emerge regularly; hence ongoing education is vital for all participants involved in DeFi activities:
| Action Item | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Regularly review security best practices | Keep up-to-date with latest mitigation techniques |
| Participate in community discussions | Share insights about recent threats |
| Conduct personal research before engaging | Understand specific protocol vulnerabilities |
By staying informed about current trends related to sandwich attacks—and broader smart contract vulnerabilities—users can adapt their strategies proactively rather than reactively reacting after losses occur.
Final Thoughts on User Protection Against Sandwich Attacks
While no method guarantees absolute safety against sophisticated adversaries exploiting complex blockchain mechanics, combining multiple protective measures significantly reduces risk exposure. Prioritizing reputable platforms, customizing transaction parameters thoughtfully, leveraging privacy-enhancing tools, diversifying investments—and maintaining continuous awareness—are key steps toward safeguarding assets within the decentralized finance landscape.
By understanding how sandwich attacks operate and adopting proactive defense strategies tailored for individual use cases, participants can enjoy the benefits offered by DeFi while minimizing vulnerability footprints amid an increasingly competitive threat environment.
Note: Always conduct thorough research before deploying any new protection method or investing substantial funds into unfamiliar protocols; consult trusted sources such as official project documentation and cybersecurity advisories when possible.*


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-09 18:22
How can users protect against sandwich attacks?
How Can Users Protect Against Sandwich Attacks in DeFi?
DeFi (Decentralized Finance) has revolutionized the way individuals interact with financial services, offering greater accessibility and control over assets. However, this innovation comes with its own set of security challenges, notably sandwich attacks. Understanding how these attacks work and implementing effective protective measures is essential for users aiming to safeguard their funds. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of strategies users can adopt to defend against sandwich attacks in the DeFi ecosystem.
What Are Sandwich Attacks and Why Do They Matter?
Sandwich attacks exploit vulnerabilities inherent in smart contract-based protocols that rely on transaction order processing. Attackers manipulate the sequence of transactions—placing their malicious trade between two legitimate ones—to profit at the expense of unsuspecting users. These tactics can lead to significant financial losses, erode trust in DeFi platforms, and undermine overall ecosystem stability.
Given that many DeFi protocols depend on transparent transaction ordering within blockchain networks like Ethereum, attackers often leverage tools such as front-running bots or gas price manipulation techniques to execute these malicious strategies effectively.
Recognizing Common Types of Sandwich Attacks
Understanding different forms of sandwich attacks helps users identify potential risks:
Front-Running: An attacker spots a pending transaction (e.g., a large trade) and places their own transaction ahead by paying higher gas fees, thus executing first.
Back-Running: The attacker inserts their transaction immediately after a legitimate one to capitalize on price movements or liquidity shifts caused by the initial trade.
Reentrancy Attacks: While slightly different from classic sandwich tactics, reentrancy involves repeatedly calling a contract before previous executions complete—often exploited alongside other attack vectors.
These methods often work together within complex attack sequences aimed at extracting maximum value from targeted transactions.
Practical Strategies for Users to Protect Their Funds
While developers are responsible for implementing security features into smart contracts, individual users also play a crucial role in minimizing risk exposure through best practices:
1. Use Reputable Platforms and Protocols
Choosing well-audited DeFi platforms reduces vulnerability exposure significantly. Established protocols undergo rigorous security assessments that help identify weaknesses susceptible to sandwich or other exploits.
2. Adjust Transaction Timing and Gas Settings
Manipulating your transaction's parameters can make front-running less profitable:
Set Higher Gas Prices Carefully: Paying higher gas fees may prioritize your transactions but also signals attackers about your activity; use this tactic judiciously.
Use Gas Limit Strategies: Some wallets allow setting custom gas limits or using dynamic fee models like EIP-1559 (Ethereum's fee market upgrade), which can help manage transaction priority more predictably.
3. Implement Privacy-Preserving Techniques
Privacy-focused tools obscure user activity from potential attackers:
Use Flashbots or Private RPC Nodes: These services enable submitting transactions directly without broadcasting them publicly first—reducing visibility that front-runners rely upon.
Leverage Layer 2 Solutions: Transactions conducted off-chain via Layer 2 networks often have reduced susceptibility due to less transparent mempool data accessible by attackers.
4. Diversify Investments Across Multiple Protocols
Spreading assets across various platforms minimizes impact if one protocol becomes compromised or targeted by an attack:
Avoid concentrating large sums into single protocols vulnerable to known exploits.
Regularly review protocol security reports before committing significant funds.
5. Stay Informed About Ongoing Threats
Active monitoring enables early detection of suspicious activities:
Subscribe to updates from reputable cybersecurity firms specializing in blockchain security.
Follow community channels such as Twitter accounts dedicated to DeFi safety alerts or Discord groups discussing protocol vulnerabilities.
Leveraging Smart Contract Security Measures as an Individual User
Although most protections are embedded during development phases, some user-centric approaches include:
Using Wallet Features: Many wallets now incorporate features like "transaction speed" controls or "priority fee" settings designed explicitly for mitigating front-running risks.
Engaging with Non-Custodial Services: Non-custodial wallets give you more control over how transactions are broadcasted and processed compared with centralized exchanges' custodial solutions prone to delay-induced vulnerabilities.
The Role of Continuous Education & Vigilance
The rapidly evolving nature of blockchain technology means new attack vectors emerge regularly; hence ongoing education is vital for all participants involved in DeFi activities:
| Action Item | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Regularly review security best practices | Keep up-to-date with latest mitigation techniques |
| Participate in community discussions | Share insights about recent threats |
| Conduct personal research before engaging | Understand specific protocol vulnerabilities |
By staying informed about current trends related to sandwich attacks—and broader smart contract vulnerabilities—users can adapt their strategies proactively rather than reactively reacting after losses occur.
Final Thoughts on User Protection Against Sandwich Attacks
While no method guarantees absolute safety against sophisticated adversaries exploiting complex blockchain mechanics, combining multiple protective measures significantly reduces risk exposure. Prioritizing reputable platforms, customizing transaction parameters thoughtfully, leveraging privacy-enhancing tools, diversifying investments—and maintaining continuous awareness—are key steps toward safeguarding assets within the decentralized finance landscape.
By understanding how sandwich attacks operate and adopting proactive defense strategies tailored for individual use cases, participants can enjoy the benefits offered by DeFi while minimizing vulnerability footprints amid an increasingly competitive threat environment.
Note: Always conduct thorough research before deploying any new protection method or investing substantial funds into unfamiliar protocols; consult trusted sources such as official project documentation and cybersecurity advisories when possible.*
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Do Rug Pulls Work in the DeFi Space?
Understanding how rug pulls operate within the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem is crucial for investors, developers, and regulators alike. These scams have become a significant threat, undermining trust and stability in the rapidly growing DeFi sector. This article explores the mechanics behind rug pulls, their common features, and what makes them particularly prevalent in decentralized environments.
What Is a Rug Pull in DeFi?
A rug pull is a type of scam where project creators or developers suddenly withdraw all funds from a liquidity pool or project wallet without warning. This action leaves investors with worthless tokens or assets that have no real value. Unlike traditional scams that might involve direct fraud or deception over time, rug pulls are characterized by their abruptness—developers "pull the rug" out from under investors' feet.
In practical terms, this often involves malicious actors deploying new tokens on blockchain platforms like Ethereum or Binance Smart Chain (BSC), attracting liquidity through promises of high returns or innovative features. Once enough funds are accumulated—either through initial investments or liquidity provision—the scammers execute their exit strategy by draining these funds to disappear with profits.
How Do Rug Pulls Typically Occur?
Rug pulls generally follow a predictable pattern but can vary depending on the sophistication of scammers and complexity of protocols involved:
- Creation of a New Token: Developers launch a new cryptocurrency token with attractive branding and marketing to lure investors.
- Liquidity Pool Setup: They establish liquidity pools on decentralized exchanges (DEXs) such as Uniswap or PancakeSwap by pairing their token with established cryptocurrencies like ETH or BNB.
- Promotion & Hype: The project gains attention via social media hype, influencer endorsements, or community engagement.
- Liquidity Injection & Price Pumping: Investors start buying into the token due to perceived potential for profit; this increases trading volume and price temporarily.
- Withdrawal & Exit: Once sufficient liquidity has been amassed—or when market conditions seem favorable—the developers withdraw all funds from the liquidity pool—often transferring assets to anonymous wallets—and vanish.
This process exploits investor trust built during promotional phases while hiding malicious intent until it’s too late for most participants.
Why Are Rug Pulls So Common in DeFi?
Several factors contribute to why rug pulls are particularly prevalent within decentralized finance:
- Decentralization & Anonymity: The pseudonymous nature of blockchain transactions makes it difficult to trace perpetrators once they move funds offshore.
- Lack of Regulation: Unlike traditional financial markets governed by strict oversight bodies, DeFi operates largely unregulated; this creates an environment where scams can flourish without immediate repercussions.
- Ease of Token Deployment: Creating new tokens requires minimal technical expertise thanks to existing smart contract templates; anyone can launch projects quickly.
- High Liquidity Incentives: Many projects promise high yields through yield farming and staking mechanisms which attract large amounts of capital susceptible to exploitation if not properly secured.
- Limited Due Diligence: Investors often lack comprehensive understanding about smart contract security risks due to technical complexity involved in auditing protocols.
These elements combine into an environment ripe for exploitation by malicious actors seeking quick profits at investor expense.
Recognizing Signs Before Falling Victim
While some rug pulls happen suddenly without warning, there are red flags that alert savvy investors:
- Lack of transparency about team members
- No verifiable audit reports on smart contracts
- Sudden spikes in token price followed by rapid declines
- Promises overly ambitious returns with little backing
- Limited information about project development progress
Due diligence—including reviewing audits from reputable firms—is essential before investing significant capital into any new DeFi project.
Recent Examples Highlighting Rug Pull Mechanics
The past few years have seen notable instances illustrating how these scams unfold:
Poly Network Hack (2021)
Although technically classified as a hack rather than classic rug pull behavior, attackers exploited vulnerabilities across multiple chains resulting in theft estimates around $600 million before returning most stolen assets under community pressure—a reminder that security flaws often facilitate such exploits.
Pancake Bunny Scam (2021)
On Binance Smart Chain (BSC), hackers manipulated prices using flash loans—a technique allowing large trades within one transaction—to artificially inflate prices then sold off holdings at peak values before withdrawing remaining funds totaling over $45 million lost for unsuspecting investors.
These cases underscore how technological tools like flash loans enable sophisticated manipulation tactics used during some rug pulls.
Regulatory Responses & Industry Efforts
Regulators worldwide recognize these threats as serious risks impacting investor confidence and market integrity:
The U.S Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) issued warnings emphasizing caution when participating in unregulated DeFi projects.
- They highlight risks including fraudulence associated with anonymous teams and unverified smart contracts
International bodies like FATF provide guidelines aimed at preventing money laundering linked to crypto scams
- These include KYC/AML measures even within decentralized frameworks
Industry-led initiatives also focus on improving transparency:
- Conducting thorough third-party audits
- Promoting best practices among developers
- Educating users about scam detection
Protecting Yourself Against Rug Pulls
Investors should adopt proactive strategies:
Always verify whether projects have undergone independent security audits
Avoid investing heavily based solely on hype; conduct thorough research
Look for transparent team disclosures
Be cautious if promised returns seem too good to be true
Use reputable platforms known for rigorous vetting processes
Smart contract auditing services play an increasingly vital role here—they help identify vulnerabilities before deployment which could be exploited later during an attack.
Future Outlook: Making Defi Safer
As awareness around rug pulls grows, so does industry innovation aimed at mitigating risks:
Enhanced security standards through formal verification methods
Development of insurance protocols offering coverage against losses
Adoption of multi-signature wallets requiring multiple approvals before fund transfers
Increased use of decentralization principles ensuring no single point-of-failure
While complete elimination remains challenging due to inherent blockchain openness—and human factors—these advancements aim toward creating more resilient ecosystems.
Understanding how rug pulls work provides critical insight into safeguarding your investments within DeFi's dynamic landscape. By recognizing common tactics used by scammers alongside ongoing industry efforts toward transparency and security improvements, participants can better navigate opportunities while minimizing exposure to potential fraud schemes inherent in this innovative yet risky financial frontier.


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-09 15:21
How do rug pulls work in the DeFi space?
How Do Rug Pulls Work in the DeFi Space?
Understanding how rug pulls operate within the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem is crucial for investors, developers, and regulators alike. These scams have become a significant threat, undermining trust and stability in the rapidly growing DeFi sector. This article explores the mechanics behind rug pulls, their common features, and what makes them particularly prevalent in decentralized environments.
What Is a Rug Pull in DeFi?
A rug pull is a type of scam where project creators or developers suddenly withdraw all funds from a liquidity pool or project wallet without warning. This action leaves investors with worthless tokens or assets that have no real value. Unlike traditional scams that might involve direct fraud or deception over time, rug pulls are characterized by their abruptness—developers "pull the rug" out from under investors' feet.
In practical terms, this often involves malicious actors deploying new tokens on blockchain platforms like Ethereum or Binance Smart Chain (BSC), attracting liquidity through promises of high returns or innovative features. Once enough funds are accumulated—either through initial investments or liquidity provision—the scammers execute their exit strategy by draining these funds to disappear with profits.
How Do Rug Pulls Typically Occur?
Rug pulls generally follow a predictable pattern but can vary depending on the sophistication of scammers and complexity of protocols involved:
- Creation of a New Token: Developers launch a new cryptocurrency token with attractive branding and marketing to lure investors.
- Liquidity Pool Setup: They establish liquidity pools on decentralized exchanges (DEXs) such as Uniswap or PancakeSwap by pairing their token with established cryptocurrencies like ETH or BNB.
- Promotion & Hype: The project gains attention via social media hype, influencer endorsements, or community engagement.
- Liquidity Injection & Price Pumping: Investors start buying into the token due to perceived potential for profit; this increases trading volume and price temporarily.
- Withdrawal & Exit: Once sufficient liquidity has been amassed—or when market conditions seem favorable—the developers withdraw all funds from the liquidity pool—often transferring assets to anonymous wallets—and vanish.
This process exploits investor trust built during promotional phases while hiding malicious intent until it’s too late for most participants.
Why Are Rug Pulls So Common in DeFi?
Several factors contribute to why rug pulls are particularly prevalent within decentralized finance:
- Decentralization & Anonymity: The pseudonymous nature of blockchain transactions makes it difficult to trace perpetrators once they move funds offshore.
- Lack of Regulation: Unlike traditional financial markets governed by strict oversight bodies, DeFi operates largely unregulated; this creates an environment where scams can flourish without immediate repercussions.
- Ease of Token Deployment: Creating new tokens requires minimal technical expertise thanks to existing smart contract templates; anyone can launch projects quickly.
- High Liquidity Incentives: Many projects promise high yields through yield farming and staking mechanisms which attract large amounts of capital susceptible to exploitation if not properly secured.
- Limited Due Diligence: Investors often lack comprehensive understanding about smart contract security risks due to technical complexity involved in auditing protocols.
These elements combine into an environment ripe for exploitation by malicious actors seeking quick profits at investor expense.
Recognizing Signs Before Falling Victim
While some rug pulls happen suddenly without warning, there are red flags that alert savvy investors:
- Lack of transparency about team members
- No verifiable audit reports on smart contracts
- Sudden spikes in token price followed by rapid declines
- Promises overly ambitious returns with little backing
- Limited information about project development progress
Due diligence—including reviewing audits from reputable firms—is essential before investing significant capital into any new DeFi project.
Recent Examples Highlighting Rug Pull Mechanics
The past few years have seen notable instances illustrating how these scams unfold:
Poly Network Hack (2021)
Although technically classified as a hack rather than classic rug pull behavior, attackers exploited vulnerabilities across multiple chains resulting in theft estimates around $600 million before returning most stolen assets under community pressure—a reminder that security flaws often facilitate such exploits.
Pancake Bunny Scam (2021)
On Binance Smart Chain (BSC), hackers manipulated prices using flash loans—a technique allowing large trades within one transaction—to artificially inflate prices then sold off holdings at peak values before withdrawing remaining funds totaling over $45 million lost for unsuspecting investors.
These cases underscore how technological tools like flash loans enable sophisticated manipulation tactics used during some rug pulls.
Regulatory Responses & Industry Efforts
Regulators worldwide recognize these threats as serious risks impacting investor confidence and market integrity:
The U.S Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) issued warnings emphasizing caution when participating in unregulated DeFi projects.
- They highlight risks including fraudulence associated with anonymous teams and unverified smart contracts
International bodies like FATF provide guidelines aimed at preventing money laundering linked to crypto scams
- These include KYC/AML measures even within decentralized frameworks
Industry-led initiatives also focus on improving transparency:
- Conducting thorough third-party audits
- Promoting best practices among developers
- Educating users about scam detection
Protecting Yourself Against Rug Pulls
Investors should adopt proactive strategies:
Always verify whether projects have undergone independent security audits
Avoid investing heavily based solely on hype; conduct thorough research
Look for transparent team disclosures
Be cautious if promised returns seem too good to be true
Use reputable platforms known for rigorous vetting processes
Smart contract auditing services play an increasingly vital role here—they help identify vulnerabilities before deployment which could be exploited later during an attack.
Future Outlook: Making Defi Safer
As awareness around rug pulls grows, so does industry innovation aimed at mitigating risks:
Enhanced security standards through formal verification methods
Development of insurance protocols offering coverage against losses
Adoption of multi-signature wallets requiring multiple approvals before fund transfers
Increased use of decentralization principles ensuring no single point-of-failure
While complete elimination remains challenging due to inherent blockchain openness—and human factors—these advancements aim toward creating more resilient ecosystems.
Understanding how rug pulls work provides critical insight into safeguarding your investments within DeFi's dynamic landscape. By recognizing common tactics used by scammers alongside ongoing industry efforts toward transparency and security improvements, participants can better navigate opportunities while minimizing exposure to potential fraud schemes inherent in this innovative yet risky financial frontier.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is a Decentralized Exchange (DEX)?
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) are transforming the landscape of cryptocurrency trading by offering an alternative to traditional, centralized platforms. Unlike conventional exchanges that rely on a central authority to manage transactions and user funds, DEXs operate on blockchain technology, enabling peer-to-peer trading without intermediaries. This shift towards decentralization aims to enhance security, transparency, and user control over assets.
How Do Decentralized Exchanges Work?
At their core, DEXs utilize blockchain networks—most commonly Ethereum—to facilitate trades through smart contracts. These self-executing contracts automatically enforce the terms of a trade once predefined conditions are met. When users initiate a transaction on a DEX, it is recorded directly onto the blockchain ledger, ensuring transparency and immutability.
Instead of depositing funds into an exchange-controlled wallet—as is typical with centralized platforms—users retain custody of their cryptocurrencies throughout the trading process. Trades occur directly between users via peer-to-peer protocols or through liquidity pools that act as shared reservoirs for assets.
Key Features of Decentralized Exchanges
Understanding what sets DEXs apart involves examining their fundamental features:
- Decentralization: Operating without central servers or authorities reduces single points of failure and minimizes risks associated with hacking or censorship.
- Peer-to-Peer Trading: Users can trade directly with each other without intermediaries like brokers or custodians.
- Smart Contracts: Automated agreements execute trades efficiently and securely based on programmed rules.
- Enhanced Security: Cryptographic algorithms protect transactions; since users retain control over private keys, they are less vulnerable to exchange hacks.
- Transparency & Immutability: Every transaction is publicly recorded on the blockchain ledger, providing full visibility into trading activities.
These features collectively contribute to increased trustworthiness and resilience compared to traditional exchanges.
The Rise of DEXs in Response to Centralized Exchange Limitations
Centralized cryptocurrency exchanges have historically dominated digital asset trading but face notable challenges such as security breaches—like Mt. Gox—and regulatory scrutiny worldwide. These issues have fueled demand for decentralized alternatives that offer greater security and privacy protections.
The evolution of blockchain technology has been instrumental in this shift. Innovations like smart contracts enable complex automated processes essential for decentralized operations while maintaining transparency inherent in public ledgers. Additionally, growing interest in decentralized finance (DeFi) applications has propelled DEX adoption by providing more accessible financial services outside traditional banking systems.
Recent Innovations Enhancing DEX Functionality
Several technological advancements have significantly improved how DEXs operate:
Liquidity Pools
Liquidity pools allow users—liquidity providers—to deposit pairs of tokens into shared reserves. In return for providing liquidity, they earn a portion of the trading fees generated within these pools. This model addresses one major challenge faced by early-generation DEXs—the lack of sufficient liquidity—which often resulted in high slippage during large trades.
Automated Market Makers (AMMs)
AMMs are algorithms embedded within liquidity pools that automatically set prices based on supply-demand dynamics using mathematical formulas such as constant product models (e.g., Uniswap). They eliminate reliance on order books used by centralized exchanges and enable continuous market making even when no counterparties are available at specific prices.
Cross-Chain Trading
Recent developments now support cross-chain interoperability allowing assets from different blockchains—such as Bitcoin and Ethereum—to be traded seamlessly across networks via bridges or wrapped tokens. This expansion broadens opportunities for traders seeking diverse asset exposure without needing multiple wallets or accounts across various platforms.
Regulatory Environment Impacting DEX Adoption
As decentralized exchanges grow in popularity, regulators worldwide grapple with how best to oversee them while fostering innovation. Some jurisdictions recognize their potential benefits but express concerns about illicit activities like money laundering due to pseudonymous transactions facilitated by many DEX protocols.
Recent legislative actions—including bills aimed at clarifying DeFi regulations—are shaping future compliance frameworks[1]. For instance, some countries consider imposing KYC/AML requirements even on non-custodial platforms; others advocate for more permissive policies emphasizing innovation-friendly environments.
The evolving regulatory landscape will influence how mainstream adoption unfolds over time—a key consideration for investors and developers alike seeking clarity amidst uncertainty.
Challenges Facing Decentralized Exchanges
Despite their advantages, several hurdles remain before widespread adoption becomes mainstream:
Regulatory Uncertainty
Lack of clear legal guidelines can pose risks for both operators and users who may inadvertently violate local laws related to securities or anti-money laundering statutes when engaging with anonymous or pseudonymous transactions typical in many DEX setups.
Security Risks
While inherently more secure than centralized counterparts due to cryptography and user custody controls, vulnerabilities still exist—in particular smart contract bugs which could be exploited through hacking attacks like reentrancy exploits or front-running strategies where malicious actors manipulate transaction ordering for profit[2].
Scalability Concerns
High network congestion leads to increased transaction fees ("gas costs") especially during peak periods—for example Ethereum's network congestion causes delays impacting usability—and limits throughput necessary for mass-market deployment.
User Experience Barriers
Many current interfaces require technical knowledge about private keys or wallet management; this complexity discourages less experienced traders from engaging fully with decentralized options.
Future Outlook & Opportunities
Despite these challenges, several trends suggest promising growth avenues:
Continued development around layer 2 solutions (e.g., Optimism & Arbitrum) aims at reducing costs while increasing throughput.
Enhanced cross-chain interoperability will unlock new markets beyond single-blockchain ecosystems.
Improved user interfaces focusing on simplicity could lower entry barriers significantly.
Furthermore, institutional interest appears gradually increasing as regulatory clarity improves alongside technological robustness[3].
By addressing scalability issues through innovative solutions such as rollups combined with stronger security protocols—including audits—and better educational resources targeting novice traders—the ecosystem can foster broader acceptance among mainstream audiences.
Understanding Why Decentralized Exchanges Matter
In essence, decentralization aligns closely with core principles valued within crypto communities: sovereignty over one's assets combined with transparent operations free from censorship risks associated with centralized entities.[4] As DeFi continues expanding its scope—from lending platforms to derivatives—the role played by robustly functioning decentralized exchanges becomes increasingly vital.
References
- Crypto Bill Legislation Updates
- Smart Contract Security Risks
- Institutional Adoption Trends
- Principles Behind Crypto Sovereignty
This article aims at providing comprehensive insights into what decentralized exchanges are — covering operational mechanisms — recent innovations — regulatory considerations — challenges — future prospects — all designed around helping readers understand why they matter within the broader crypto ecosystem.


kai
2025-05-09 13:16
What is a decentralized exchange (DEX)?
What Is a Decentralized Exchange (DEX)?
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) are transforming the landscape of cryptocurrency trading by offering an alternative to traditional, centralized platforms. Unlike conventional exchanges that rely on a central authority to manage transactions and user funds, DEXs operate on blockchain technology, enabling peer-to-peer trading without intermediaries. This shift towards decentralization aims to enhance security, transparency, and user control over assets.
How Do Decentralized Exchanges Work?
At their core, DEXs utilize blockchain networks—most commonly Ethereum—to facilitate trades through smart contracts. These self-executing contracts automatically enforce the terms of a trade once predefined conditions are met. When users initiate a transaction on a DEX, it is recorded directly onto the blockchain ledger, ensuring transparency and immutability.
Instead of depositing funds into an exchange-controlled wallet—as is typical with centralized platforms—users retain custody of their cryptocurrencies throughout the trading process. Trades occur directly between users via peer-to-peer protocols or through liquidity pools that act as shared reservoirs for assets.
Key Features of Decentralized Exchanges
Understanding what sets DEXs apart involves examining their fundamental features:
- Decentralization: Operating without central servers or authorities reduces single points of failure and minimizes risks associated with hacking or censorship.
- Peer-to-Peer Trading: Users can trade directly with each other without intermediaries like brokers or custodians.
- Smart Contracts: Automated agreements execute trades efficiently and securely based on programmed rules.
- Enhanced Security: Cryptographic algorithms protect transactions; since users retain control over private keys, they are less vulnerable to exchange hacks.
- Transparency & Immutability: Every transaction is publicly recorded on the blockchain ledger, providing full visibility into trading activities.
These features collectively contribute to increased trustworthiness and resilience compared to traditional exchanges.
The Rise of DEXs in Response to Centralized Exchange Limitations
Centralized cryptocurrency exchanges have historically dominated digital asset trading but face notable challenges such as security breaches—like Mt. Gox—and regulatory scrutiny worldwide. These issues have fueled demand for decentralized alternatives that offer greater security and privacy protections.
The evolution of blockchain technology has been instrumental in this shift. Innovations like smart contracts enable complex automated processes essential for decentralized operations while maintaining transparency inherent in public ledgers. Additionally, growing interest in decentralized finance (DeFi) applications has propelled DEX adoption by providing more accessible financial services outside traditional banking systems.
Recent Innovations Enhancing DEX Functionality
Several technological advancements have significantly improved how DEXs operate:
Liquidity Pools
Liquidity pools allow users—liquidity providers—to deposit pairs of tokens into shared reserves. In return for providing liquidity, they earn a portion of the trading fees generated within these pools. This model addresses one major challenge faced by early-generation DEXs—the lack of sufficient liquidity—which often resulted in high slippage during large trades.
Automated Market Makers (AMMs)
AMMs are algorithms embedded within liquidity pools that automatically set prices based on supply-demand dynamics using mathematical formulas such as constant product models (e.g., Uniswap). They eliminate reliance on order books used by centralized exchanges and enable continuous market making even when no counterparties are available at specific prices.
Cross-Chain Trading
Recent developments now support cross-chain interoperability allowing assets from different blockchains—such as Bitcoin and Ethereum—to be traded seamlessly across networks via bridges or wrapped tokens. This expansion broadens opportunities for traders seeking diverse asset exposure without needing multiple wallets or accounts across various platforms.
Regulatory Environment Impacting DEX Adoption
As decentralized exchanges grow in popularity, regulators worldwide grapple with how best to oversee them while fostering innovation. Some jurisdictions recognize their potential benefits but express concerns about illicit activities like money laundering due to pseudonymous transactions facilitated by many DEX protocols.
Recent legislative actions—including bills aimed at clarifying DeFi regulations—are shaping future compliance frameworks[1]. For instance, some countries consider imposing KYC/AML requirements even on non-custodial platforms; others advocate for more permissive policies emphasizing innovation-friendly environments.
The evolving regulatory landscape will influence how mainstream adoption unfolds over time—a key consideration for investors and developers alike seeking clarity amidst uncertainty.
Challenges Facing Decentralized Exchanges
Despite their advantages, several hurdles remain before widespread adoption becomes mainstream:
Regulatory Uncertainty
Lack of clear legal guidelines can pose risks for both operators and users who may inadvertently violate local laws related to securities or anti-money laundering statutes when engaging with anonymous or pseudonymous transactions typical in many DEX setups.
Security Risks
While inherently more secure than centralized counterparts due to cryptography and user custody controls, vulnerabilities still exist—in particular smart contract bugs which could be exploited through hacking attacks like reentrancy exploits or front-running strategies where malicious actors manipulate transaction ordering for profit[2].
Scalability Concerns
High network congestion leads to increased transaction fees ("gas costs") especially during peak periods—for example Ethereum's network congestion causes delays impacting usability—and limits throughput necessary for mass-market deployment.
User Experience Barriers
Many current interfaces require technical knowledge about private keys or wallet management; this complexity discourages less experienced traders from engaging fully with decentralized options.
Future Outlook & Opportunities
Despite these challenges, several trends suggest promising growth avenues:
Continued development around layer 2 solutions (e.g., Optimism & Arbitrum) aims at reducing costs while increasing throughput.
Enhanced cross-chain interoperability will unlock new markets beyond single-blockchain ecosystems.
Improved user interfaces focusing on simplicity could lower entry barriers significantly.
Furthermore, institutional interest appears gradually increasing as regulatory clarity improves alongside technological robustness[3].
By addressing scalability issues through innovative solutions such as rollups combined with stronger security protocols—including audits—and better educational resources targeting novice traders—the ecosystem can foster broader acceptance among mainstream audiences.
Understanding Why Decentralized Exchanges Matter
In essence, decentralization aligns closely with core principles valued within crypto communities: sovereignty over one's assets combined with transparent operations free from censorship risks associated with centralized entities.[4] As DeFi continues expanding its scope—from lending platforms to derivatives—the role played by robustly functioning decentralized exchanges becomes increasingly vital.
References
- Crypto Bill Legislation Updates
- Smart Contract Security Risks
- Institutional Adoption Trends
- Principles Behind Crypto Sovereignty
This article aims at providing comprehensive insights into what decentralized exchanges are — covering operational mechanisms — recent innovations — regulatory considerations — challenges — future prospects — all designed around helping readers understand why they matter within the broader crypto ecosystem.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Understanding the Theoretical Basis of the Force Index
The Force Index is a widely used technical indicator in financial markets, including cryptocurrencies, designed to measure the strength or momentum behind price movements. Its core purpose is to help traders assess whether a market move is likely to continue or reverse, providing valuable insights into market dynamics. To fully grasp its utility, it’s essential to understand its theoretical foundation rooted in market psychology and volume analysis.
The Concept of Market Momentum and Volume
At its core, the Force Index combines two critical elements: price movement and trading volume. Price movement indicates how much an asset's value has changed over a specific period, reflecting supply and demand dynamics. Volume measures how many units of an asset are traded during that period, serving as an indicator of trader activity and conviction behind price changes.
The underlying theory suggests that significant price moves accompanied by high volume are more likely to be sustainable because they reflect strong trader participation. Conversely, large moves on low volume may lack conviction and could be prone to reversal. This relationship forms the basis for using volume-weighted indicators like the Force Index in technical analysis.
How Alexander Elder Developed the Force Index
The concept was introduced by renowned trader and psychologist Alexander Elder in the 1990s as part of his broader approach to trading psychology and technical analysis. Elder emphasized understanding not just where prices are headed but also how strong those movements are—hence his focus on combining momentum with volume data.
Elder’s insight was that traditional indicators often failed to incorporate trader activity levels effectively. By integrating both price change magnitude and trading volume into a single metric—the Force Index—he provided traders with a tool capable of capturing real-time market energy more accurately than simple trend-following indicators alone.
Mathematical Foundation: How Is It Calculated?
The basic calculation for the Force Index involves multiplying current price data by trading volume:
- Force Index = (Current Price - Previous Price) × Volume
This formula captures both directional movement (price difference) and trade intensity (volume). A positive value indicates buying pressure; a negative one suggests selling pressure.
In practice, traders often smooth this raw data using moving averages or other techniques for clearer signals over different timeframes—such as short-term or long-term analyses—which helps filter out noise inherent in volatile markets like cryptocurrencies.
Why Does Combining Price Movement with Volume Matter?
Integrating these two components aligns with fundamental principles from behavioral finance: markets move because participants act collectively based on their expectations about future prices. When many traders buy aggressively (high volume), it signals confidence; when they sell heavily, it indicates fear or profit-taking.
By quantifying this combined effort through the Force Index:
- Traders can identify whether recent moves have genuine backing.
- It becomes easier to distinguish between false breakouts or temporary corrections versus sustained trends.
- The indicator provides early warning signs when momentum shifts occur before traditional trendlines confirm reversals.
This synergy makes it especially useful for confirming trend strength—a key factor for making informed entry or exit decisions within any trading strategy.
Limitations Rooted in Market Behavior
While theoretically robust, applying the Force Index requires awareness of certain limitations tied directly to market behavior:
- Market Volatility: Cryptocurrency markets exhibit high volatility; sudden spikes can produce misleading force readings.
- Overreliance Risks: Relying solely on this indicator without considering broader context may lead traders astray during unpredictable swings.
- Volume Data Accuracy: In crypto markets especially, discrepancies due to differing exchange reporting standards can impact reliability.
- Regulatory Impact: Changes affecting trade reporting standards could influence how accurately volumes reflect true market activity over time.
Understanding these factors ensures users interpret signals within appropriate contexts rather than viewing them as infallible predictors alone.
Integrating Theory Into Practical Trading Strategies
From a practical standpoint rooted in its theoretical basis:
- The Force Index should be used alongside other tools such as moving averages or RSI for confirmation.
- Divergences between price action and force readings can signal potential reversals—an application grounded directly in behavioral finance principles about collective trader sentiment shifting.
- Recognizing high-force readings during uptrends confirms strong buying interest; similarly, negative force values reinforce bearish momentum assessments.
By aligning these applications with sound risk management practices—including stop-loss orders—and considering broader macroeconomic factors influencing crypto markets (like regulatory news), traders enhance their ability to make informed decisions based on solid theoretical underpinnings.
How Market Psychology Shapes Indicator Effectiveness
Fundamentally rooted in understanding collective trader behavior—the essence of E-A-T (Expertise-Authoritativeness-Trustrworthiness)—the effectiveness of tools like the Force Index hinges on recognizing psychological patterns driving market movements. High-volume surges often reflect herd behavior where investors act en masse due to fear or greed rather than rational analysis alone—a phenomenon well-documented across financial history including cryptocurrency booms and busts alike.
Final Thoughts
The theoretical foundation behind the Force Index emphasizes its role as an energy gauge derived from combining quantitative measures—price change magnitude coupled with trade volumes—to interpret underlying market sentiment accurately. Its development by Alexander Elder underscores its importance within comprehensive technical analysis frameworks aimed at capturing real-time momentum shifts driven by human psychology—a crucial aspect given modern markets’ complexity today.
By understanding this basis thoroughly—and applying it judiciously alongside other analytical tools—traders gain deeper insights into potential future trends while maintaining awareness of inherent limitations posed by volatile environments like cryptocurrencies—and thus improve their overall decision-making process grounded firmly in proven economic theories about human behavior under uncertainty.


kai
2025-05-09 09:34
What is the theoretical basis of the Force Index?
Understanding the Theoretical Basis of the Force Index
The Force Index is a widely used technical indicator in financial markets, including cryptocurrencies, designed to measure the strength or momentum behind price movements. Its core purpose is to help traders assess whether a market move is likely to continue or reverse, providing valuable insights into market dynamics. To fully grasp its utility, it’s essential to understand its theoretical foundation rooted in market psychology and volume analysis.
The Concept of Market Momentum and Volume
At its core, the Force Index combines two critical elements: price movement and trading volume. Price movement indicates how much an asset's value has changed over a specific period, reflecting supply and demand dynamics. Volume measures how many units of an asset are traded during that period, serving as an indicator of trader activity and conviction behind price changes.
The underlying theory suggests that significant price moves accompanied by high volume are more likely to be sustainable because they reflect strong trader participation. Conversely, large moves on low volume may lack conviction and could be prone to reversal. This relationship forms the basis for using volume-weighted indicators like the Force Index in technical analysis.
How Alexander Elder Developed the Force Index
The concept was introduced by renowned trader and psychologist Alexander Elder in the 1990s as part of his broader approach to trading psychology and technical analysis. Elder emphasized understanding not just where prices are headed but also how strong those movements are—hence his focus on combining momentum with volume data.
Elder’s insight was that traditional indicators often failed to incorporate trader activity levels effectively. By integrating both price change magnitude and trading volume into a single metric—the Force Index—he provided traders with a tool capable of capturing real-time market energy more accurately than simple trend-following indicators alone.
Mathematical Foundation: How Is It Calculated?
The basic calculation for the Force Index involves multiplying current price data by trading volume:
- Force Index = (Current Price - Previous Price) × Volume
This formula captures both directional movement (price difference) and trade intensity (volume). A positive value indicates buying pressure; a negative one suggests selling pressure.
In practice, traders often smooth this raw data using moving averages or other techniques for clearer signals over different timeframes—such as short-term or long-term analyses—which helps filter out noise inherent in volatile markets like cryptocurrencies.
Why Does Combining Price Movement with Volume Matter?
Integrating these two components aligns with fundamental principles from behavioral finance: markets move because participants act collectively based on their expectations about future prices. When many traders buy aggressively (high volume), it signals confidence; when they sell heavily, it indicates fear or profit-taking.
By quantifying this combined effort through the Force Index:
- Traders can identify whether recent moves have genuine backing.
- It becomes easier to distinguish between false breakouts or temporary corrections versus sustained trends.
- The indicator provides early warning signs when momentum shifts occur before traditional trendlines confirm reversals.
This synergy makes it especially useful for confirming trend strength—a key factor for making informed entry or exit decisions within any trading strategy.
Limitations Rooted in Market Behavior
While theoretically robust, applying the Force Index requires awareness of certain limitations tied directly to market behavior:
- Market Volatility: Cryptocurrency markets exhibit high volatility; sudden spikes can produce misleading force readings.
- Overreliance Risks: Relying solely on this indicator without considering broader context may lead traders astray during unpredictable swings.
- Volume Data Accuracy: In crypto markets especially, discrepancies due to differing exchange reporting standards can impact reliability.
- Regulatory Impact: Changes affecting trade reporting standards could influence how accurately volumes reflect true market activity over time.
Understanding these factors ensures users interpret signals within appropriate contexts rather than viewing them as infallible predictors alone.
Integrating Theory Into Practical Trading Strategies
From a practical standpoint rooted in its theoretical basis:
- The Force Index should be used alongside other tools such as moving averages or RSI for confirmation.
- Divergences between price action and force readings can signal potential reversals—an application grounded directly in behavioral finance principles about collective trader sentiment shifting.
- Recognizing high-force readings during uptrends confirms strong buying interest; similarly, negative force values reinforce bearish momentum assessments.
By aligning these applications with sound risk management practices—including stop-loss orders—and considering broader macroeconomic factors influencing crypto markets (like regulatory news), traders enhance their ability to make informed decisions based on solid theoretical underpinnings.
How Market Psychology Shapes Indicator Effectiveness
Fundamentally rooted in understanding collective trader behavior—the essence of E-A-T (Expertise-Authoritativeness-Trustrworthiness)—the effectiveness of tools like the Force Index hinges on recognizing psychological patterns driving market movements. High-volume surges often reflect herd behavior where investors act en masse due to fear or greed rather than rational analysis alone—a phenomenon well-documented across financial history including cryptocurrency booms and busts alike.
Final Thoughts
The theoretical foundation behind the Force Index emphasizes its role as an energy gauge derived from combining quantitative measures—price change magnitude coupled with trade volumes—to interpret underlying market sentiment accurately. Its development by Alexander Elder underscores its importance within comprehensive technical analysis frameworks aimed at capturing real-time momentum shifts driven by human psychology—a crucial aspect given modern markets’ complexity today.
By understanding this basis thoroughly—and applying it judiciously alongside other analytical tools—traders gain deeper insights into potential future trends while maintaining awareness of inherent limitations posed by volatile environments like cryptocurrencies—and thus improve their overall decision-making process grounded firmly in proven economic theories about human behavior under uncertainty.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Potential Use Cases for Decentralized AI
Decentralized AI is transforming how industries leverage artificial intelligence by distributing data and algorithms across a network rather than relying on centralized servers. This shift opens up numerous practical applications across various sectors, enhancing security, privacy, and efficiency. Here’s a detailed look at some of the most promising use cases for decentralized AI.
Enhancing Data Privacy in Healthcare
One of the most significant challenges in healthcare is managing sensitive patient data while ensuring privacy and compliance with regulations like HIPAA or GDPR. Decentralized AI offers a solution by enabling secure, distributed storage and analysis of health records. Instead of consolidating all data into a single database vulnerable to breaches, decentralized systems allow multiple nodes to hold encrypted fragments of information. This setup ensures that only authorized parties can access complete datasets when necessary, facilitating personalized medicine without compromising patient confidentiality.
Moreover, decentralized AI can support collaborative research efforts where multiple institutions share insights without exposing raw data—accelerating medical discoveries while maintaining strict privacy standards.
Securing Financial Transactions with Blockchain-Integrated AI
Financial services are increasingly adopting decentralized AI to improve transaction security and transparency. Decentralized exchanges (DEXs), powered by blockchain technology combined with intelligent algorithms, enable users to trade cryptocurrencies securely without intermediaries. These systems utilize smart contracts—self-executing agreements embedded within blockchain networks—that become more autonomous through integrated AI capabilities.
AI-driven analytics on these platforms can detect fraudulent activities faster by analyzing transaction patterns across the network in real-time. Additionally, decentralization reduces single points of failure or control that could be exploited maliciously or manipulated unfairly.
Improving Environmental Monitoring Systems
Environmental monitoring benefits significantly from decentralized AI's ability to process vast amounts of real-time data collected from distributed sensors worldwide. For example, climate change tracking involves gathering weather patterns, pollution levels, and natural disaster indicators from remote locations where centralized infrastructure might be impractical or vulnerable.
Decentralized networks enable these sensors to analyze their own data locally before sharing summarized insights with other nodes—reducing bandwidth needs and increasing resilience against cyberattacks targeting central servers. This approach results in more accurate environmental models that inform policy decisions promptly.
Powering Autonomous Systems
Autonomous vehicles and smart devices require rapid decision-making capabilities often hindered by reliance on centralized cloud processing due to latency issues or connectivity constraints. Decentralized AI allows these systems to operate independently by executing algorithms directly within local nodes or edge devices.
For instance:
- Self-driving cars can process sensor inputs locally using distributed neural networks.
- Drones performing search-and-rescue missions can analyze surroundings autonomously.
- Smart contracts executing automatically based on real-world conditions benefit from embedded intelligence that adapts dynamically without external intervention.
This autonomy enhances safety features while reducing dependence on potentially slow or unreliable internet connections.
Facilitating Secure Supply Chain Management
Supply chains involve complex logistics requiring transparency at every stage—from manufacturing through delivery—to prevent fraud and ensure product authenticity. Decentralized AI enables companies to create tamper-proof records stored securely via blockchain technology combined with intelligent validation processes.
By deploying decentralized tracking systems:
- Manufacturers can verify product origins.
- Retailers gain confidence in authenticity.
- Consumers receive transparent provenance information about goods they purchase online or offline.
Furthermore, predictive analytics powered by decentralized models help forecast demand fluctuations accurately while safeguarding proprietary business data against competitors’ scrutiny.
Addressing Challenges Through Use Cases
While the potential applications are vast—and growing—the deployment of decentralized AI also faces hurdles such as regulatory uncertainty and technical complexity:
Regulatory Compliance: As decentralization complicates oversight mechanisms for governments worldwide—especially concerning privacy laws—it becomes crucial for organizations adopting this technology to implement transparent governance frameworks aligned with legal standards.
Ethical Considerations: Ensuring fairness in decision-making processes derived from decentralized models requires ongoing auditing for bias mitigation—a challenge given the dispersed nature of training datasets.
Technical Infrastructure: Building robust infrastructure capable of supporting large-scale distributed computing demands skilled developers familiar with both blockchain protocols and advanced machine learning techniques.
The Future Outlook: Expanding Horizons for Decentralized Artificial Intelligence
As innovations continue accelerating within this space—including improved consensus mechanisms for blockchains and more efficient algorithms—the scope for deploying decentralized AI will expand further into everyday life scenarios such as personalized education platforms, resilient IoT ecosystems, autonomous urban infrastructure management—and beyond.
By addressing current limitations through regulatory clarity & technological advancements—and emphasizing ethical deployment practices—decentralized artificial intelligence holds promise not only as an enabler but also as a catalyst toward more secure digital ecosystems rooted firmly in trustworthiness.
Keywords: Decentralized Artificial Intelligence use cases | Blockchain-based AI applications | Secure healthcare data management | Autonomous systems powered by decentralization | Environmental monitoring solutions | Blockchain-enabled financial services | Supply chain transparency using decentralization


Lo
2025-06-09 04:14
What are potential use cases for decentralized AI?
Potential Use Cases for Decentralized AI
Decentralized AI is transforming how industries leverage artificial intelligence by distributing data and algorithms across a network rather than relying on centralized servers. This shift opens up numerous practical applications across various sectors, enhancing security, privacy, and efficiency. Here’s a detailed look at some of the most promising use cases for decentralized AI.
Enhancing Data Privacy in Healthcare
One of the most significant challenges in healthcare is managing sensitive patient data while ensuring privacy and compliance with regulations like HIPAA or GDPR. Decentralized AI offers a solution by enabling secure, distributed storage and analysis of health records. Instead of consolidating all data into a single database vulnerable to breaches, decentralized systems allow multiple nodes to hold encrypted fragments of information. This setup ensures that only authorized parties can access complete datasets when necessary, facilitating personalized medicine without compromising patient confidentiality.
Moreover, decentralized AI can support collaborative research efforts where multiple institutions share insights without exposing raw data—accelerating medical discoveries while maintaining strict privacy standards.
Securing Financial Transactions with Blockchain-Integrated AI
Financial services are increasingly adopting decentralized AI to improve transaction security and transparency. Decentralized exchanges (DEXs), powered by blockchain technology combined with intelligent algorithms, enable users to trade cryptocurrencies securely without intermediaries. These systems utilize smart contracts—self-executing agreements embedded within blockchain networks—that become more autonomous through integrated AI capabilities.
AI-driven analytics on these platforms can detect fraudulent activities faster by analyzing transaction patterns across the network in real-time. Additionally, decentralization reduces single points of failure or control that could be exploited maliciously or manipulated unfairly.
Improving Environmental Monitoring Systems
Environmental monitoring benefits significantly from decentralized AI's ability to process vast amounts of real-time data collected from distributed sensors worldwide. For example, climate change tracking involves gathering weather patterns, pollution levels, and natural disaster indicators from remote locations where centralized infrastructure might be impractical or vulnerable.
Decentralized networks enable these sensors to analyze their own data locally before sharing summarized insights with other nodes—reducing bandwidth needs and increasing resilience against cyberattacks targeting central servers. This approach results in more accurate environmental models that inform policy decisions promptly.
Powering Autonomous Systems
Autonomous vehicles and smart devices require rapid decision-making capabilities often hindered by reliance on centralized cloud processing due to latency issues or connectivity constraints. Decentralized AI allows these systems to operate independently by executing algorithms directly within local nodes or edge devices.
For instance:
- Self-driving cars can process sensor inputs locally using distributed neural networks.
- Drones performing search-and-rescue missions can analyze surroundings autonomously.
- Smart contracts executing automatically based on real-world conditions benefit from embedded intelligence that adapts dynamically without external intervention.
This autonomy enhances safety features while reducing dependence on potentially slow or unreliable internet connections.
Facilitating Secure Supply Chain Management
Supply chains involve complex logistics requiring transparency at every stage—from manufacturing through delivery—to prevent fraud and ensure product authenticity. Decentralized AI enables companies to create tamper-proof records stored securely via blockchain technology combined with intelligent validation processes.
By deploying decentralized tracking systems:
- Manufacturers can verify product origins.
- Retailers gain confidence in authenticity.
- Consumers receive transparent provenance information about goods they purchase online or offline.
Furthermore, predictive analytics powered by decentralized models help forecast demand fluctuations accurately while safeguarding proprietary business data against competitors’ scrutiny.
Addressing Challenges Through Use Cases
While the potential applications are vast—and growing—the deployment of decentralized AI also faces hurdles such as regulatory uncertainty and technical complexity:
Regulatory Compliance: As decentralization complicates oversight mechanisms for governments worldwide—especially concerning privacy laws—it becomes crucial for organizations adopting this technology to implement transparent governance frameworks aligned with legal standards.
Ethical Considerations: Ensuring fairness in decision-making processes derived from decentralized models requires ongoing auditing for bias mitigation—a challenge given the dispersed nature of training datasets.
Technical Infrastructure: Building robust infrastructure capable of supporting large-scale distributed computing demands skilled developers familiar with both blockchain protocols and advanced machine learning techniques.
The Future Outlook: Expanding Horizons for Decentralized Artificial Intelligence
As innovations continue accelerating within this space—including improved consensus mechanisms for blockchains and more efficient algorithms—the scope for deploying decentralized AI will expand further into everyday life scenarios such as personalized education platforms, resilient IoT ecosystems, autonomous urban infrastructure management—and beyond.
By addressing current limitations through regulatory clarity & technological advancements—and emphasizing ethical deployment practices—decentralized artificial intelligence holds promise not only as an enabler but also as a catalyst toward more secure digital ecosystems rooted firmly in trustworthiness.
Keywords: Decentralized Artificial Intelligence use cases | Blockchain-based AI applications | Secure healthcare data management | Autonomous systems powered by decentralization | Environmental monitoring solutions | Blockchain-enabled financial services | Supply chain transparency using decentralization
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Are Student Discounts Available for TradingView?
TradingView has become one of the most popular platforms for financial analysis and online trading, especially among younger traders and students interested in cryptocurrencies, stocks, forex, and other markets. With its user-friendly interface and powerful tools, many wonder whether TradingView offers any discounts specifically tailored for students. This article explores the current status of student discounts on TradingView, the platform’s features relevant to learners, and how students can maximize their experience despite the absence of formal discounts.
Does TradingView Offer Student Discounts?
As of now, TradingView does not provide specific student discount programs or special pricing tailored exclusively for students. The platform operates on a subscription-based model with tiered plans ranging from Basic (free) to Pro, Pro+ and Premium levels. These plans include various features such as real-time data feeds, advanced charting tools, multiple indicators, alerts, and social community access.
While many educational technology companies or software providers offer student discounts to make their services more accessible to learners—such as Adobe Creative Cloud or Microsoft Office—TradingView has yet to implement such initiatives publicly. This means that students looking to access premium features will need to pay regular subscription fees unless they find alternative ways to reduce costs.
How Can Students Access TradingView’s Features?
Although there are no official student discounts available from TradingView itself, students can still benefit from several strategies:
- Utilize Free Plans: The Basic plan is free forever and provides essential charting tools suitable for beginners learning about technical analysis.
- Leverage Educational Resources: TradingView offers webinars, tutorials, articles on trading strategies—and these resources are accessible regardless of subscription level—making it easier for students new to finance.
- Take Advantage of Promotions: Occasionally during sales events or special promotions (e.g., Black Friday), discounted rates may be available across all plans.
- Explore Community Content: The active social community allows users—including students—to learn from shared ideas without needing premium subscriptions initially.
Furthermore, some educational institutions incorporate TradingView into their curricula or partner with the platform through sponsored programs; in these cases—if applicable—students might gain access via institutional licenses or partnerships.
Educational Benefits Without a Discount
While direct savings are appealing when considering paid subscriptions on platforms like TradingView—which can range up to $60/month—the educational value offered by the platform remains significant even at no cost. Students interested in finance can benefit immensely from:
- Real-time market data
- Advanced charting capabilities
- Technical indicators
- Social sharing features that facilitate peer learning
- Webinars led by experienced traders
These resources help build foundational knowledge necessary for careers in trading or investment management while fostering practical skills through hands-on analysis.
Cryptocurrency Markets & Online Trading: What Students Need To Know
The rise of online trading platforms like TradingView coincides with increased interest among young investors in cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum. Many students see crypto markets as opportunities for high returns but must approach them cautiously due to high volatility risks involved.
Tradingview's analytical tools enable users—even beginners—to analyze price trends effectively before making trades. However:
- Cryptocurrency markets are highly volatile; prices can swing dramatically within short periods.
- Proper risk management is crucial; never invest more than you’re willing—or able—to lose.
- Education is key: leverage free resources like tutorials and community insights before committing funds.
By understanding these factors early on—and using available analytical tools—students can develop safer trading habits while expanding their financial literacy.
Recent Developments Impacting Student Traders
Several recent trends influence how young traders engage with platforms like TradingView:
- Market Volatility: Cryptocurrencies have experienced significant fluctuations recently due to regulatory news and macroeconomic factors—all contributing both opportunities and risks.
- Educational Initiatives: Although no direct discount exists yet targeted at learners specifically by Tradingview itself —the company actively promotes financial literacy through partnerships with universities worldwide.
- Community Growth: An expanding user base sharing insights enhances peer-to-peer learning—a valuable resource especially beneficial when formal discounts aren’t available.
Additionally,
- Regulatory changes around online trading could impact accessibility or usage policies,
- Market volatility underscores importance of cautious investing,
- And ongoing efforts toward financial education help demystify complex topics related to investing strategies.
Students should stay informed about these developments so they can adapt their approach accordingly while making responsible investment decisions.
Tips For Students Interested In Using Trading Platforms Like Tradeview
If you're a student eager to explore financial markets using platforms like Tradeview (or similar), consider these tips:
- Start with free resources — Use basic account options until comfortable.
- Educate yourself thoroughly — Use webinars & tutorials provided by the platform.
- Practice risk management — Never invest money you can't afford losing.
- Join communities — Engage with other traders’ insights via social features.
- Keep updated on market trends & regulatory changes affecting your investments.
By following these practices—even without specific student discounts—you’ll maximize your learning potential while minimizing unnecessary risks associated with early-stage investing activities.
Final Thoughts
While currently lacking dedicated student discount programs directly from Tradeview/Tradingview.com—a widely used tool among aspiring traders—the platform remains an invaluable resource thanks largely to its comprehensive suite of analysis tools coupled with extensive educational content accessible at all levels—including free options suited perfectly for learners just starting out in finance or cryptocurrency markets.
Students should focus on leveraging free offerings alongside community support while staying informed about market shifts that could influence their investment journey over time—with patience combined with continuous education being key ingredients toward success in today’s dynamic digital economy landscape


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-27 00:02
Are student discounts available for TradingView?
Are Student Discounts Available for TradingView?
TradingView has become one of the most popular platforms for financial analysis and online trading, especially among younger traders and students interested in cryptocurrencies, stocks, forex, and other markets. With its user-friendly interface and powerful tools, many wonder whether TradingView offers any discounts specifically tailored for students. This article explores the current status of student discounts on TradingView, the platform’s features relevant to learners, and how students can maximize their experience despite the absence of formal discounts.
Does TradingView Offer Student Discounts?
As of now, TradingView does not provide specific student discount programs or special pricing tailored exclusively for students. The platform operates on a subscription-based model with tiered plans ranging from Basic (free) to Pro, Pro+ and Premium levels. These plans include various features such as real-time data feeds, advanced charting tools, multiple indicators, alerts, and social community access.
While many educational technology companies or software providers offer student discounts to make their services more accessible to learners—such as Adobe Creative Cloud or Microsoft Office—TradingView has yet to implement such initiatives publicly. This means that students looking to access premium features will need to pay regular subscription fees unless they find alternative ways to reduce costs.
How Can Students Access TradingView’s Features?
Although there are no official student discounts available from TradingView itself, students can still benefit from several strategies:
- Utilize Free Plans: The Basic plan is free forever and provides essential charting tools suitable for beginners learning about technical analysis.
- Leverage Educational Resources: TradingView offers webinars, tutorials, articles on trading strategies—and these resources are accessible regardless of subscription level—making it easier for students new to finance.
- Take Advantage of Promotions: Occasionally during sales events or special promotions (e.g., Black Friday), discounted rates may be available across all plans.
- Explore Community Content: The active social community allows users—including students—to learn from shared ideas without needing premium subscriptions initially.
Furthermore, some educational institutions incorporate TradingView into their curricula or partner with the platform through sponsored programs; in these cases—if applicable—students might gain access via institutional licenses or partnerships.
Educational Benefits Without a Discount
While direct savings are appealing when considering paid subscriptions on platforms like TradingView—which can range up to $60/month—the educational value offered by the platform remains significant even at no cost. Students interested in finance can benefit immensely from:
- Real-time market data
- Advanced charting capabilities
- Technical indicators
- Social sharing features that facilitate peer learning
- Webinars led by experienced traders
These resources help build foundational knowledge necessary for careers in trading or investment management while fostering practical skills through hands-on analysis.
Cryptocurrency Markets & Online Trading: What Students Need To Know
The rise of online trading platforms like TradingView coincides with increased interest among young investors in cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum. Many students see crypto markets as opportunities for high returns but must approach them cautiously due to high volatility risks involved.
Tradingview's analytical tools enable users—even beginners—to analyze price trends effectively before making trades. However:
- Cryptocurrency markets are highly volatile; prices can swing dramatically within short periods.
- Proper risk management is crucial; never invest more than you’re willing—or able—to lose.
- Education is key: leverage free resources like tutorials and community insights before committing funds.
By understanding these factors early on—and using available analytical tools—students can develop safer trading habits while expanding their financial literacy.
Recent Developments Impacting Student Traders
Several recent trends influence how young traders engage with platforms like TradingView:
- Market Volatility: Cryptocurrencies have experienced significant fluctuations recently due to regulatory news and macroeconomic factors—all contributing both opportunities and risks.
- Educational Initiatives: Although no direct discount exists yet targeted at learners specifically by Tradingview itself —the company actively promotes financial literacy through partnerships with universities worldwide.
- Community Growth: An expanding user base sharing insights enhances peer-to-peer learning—a valuable resource especially beneficial when formal discounts aren’t available.
Additionally,
- Regulatory changes around online trading could impact accessibility or usage policies,
- Market volatility underscores importance of cautious investing,
- And ongoing efforts toward financial education help demystify complex topics related to investing strategies.
Students should stay informed about these developments so they can adapt their approach accordingly while making responsible investment decisions.
Tips For Students Interested In Using Trading Platforms Like Tradeview
If you're a student eager to explore financial markets using platforms like Tradeview (or similar), consider these tips:
- Start with free resources — Use basic account options until comfortable.
- Educate yourself thoroughly — Use webinars & tutorials provided by the platform.
- Practice risk management — Never invest money you can't afford losing.
- Join communities — Engage with other traders’ insights via social features.
- Keep updated on market trends & regulatory changes affecting your investments.
By following these practices—even without specific student discounts—you’ll maximize your learning potential while minimizing unnecessary risks associated with early-stage investing activities.
Final Thoughts
While currently lacking dedicated student discount programs directly from Tradeview/Tradingview.com—a widely used tool among aspiring traders—the platform remains an invaluable resource thanks largely to its comprehensive suite of analysis tools coupled with extensive educational content accessible at all levels—including free options suited perfectly for learners just starting out in finance or cryptocurrency markets.
Students should focus on leveraging free offerings alongside community support while staying informed about market shifts that could influence their investment journey over time—with patience combined with continuous education being key ingredients toward success in today’s dynamic digital economy landscape
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Are NFTs Minted and Traded on Blockchain Marketplaces?
Understanding the process of minting and trading Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) is essential for creators, collectors, and investors navigating the rapidly evolving digital asset landscape. This guide provides a clear overview of how NFTs are created, bought, and sold on blockchain platforms, emphasizing key steps, recent trends, and important considerations.
What Are NFTs and Why Do They Matter?
NFTs are unique digital assets stored on blockchain networks that represent ownership of a specific item—be it art, music, videos, or other digital collectibles. Unlike cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum—which are interchangeable—NFTs are non-fungible; each token has distinct properties that make it one-of-a-kind. This uniqueness has transformed how creators monetize their work online by providing verifiable proof of ownership and authenticity.
The significance of NFTs lies in their ability to empower artists and content creators to directly connect with audiences without intermediaries. For collectors, NFTs offer new avenues for investment in digital assets with potential appreciation value. As the market matures alongside advancements in blockchain technology and regulatory frameworks, understanding how these tokens are minted and traded becomes increasingly vital.
The Process of Minting an NFT
Minting refers to creating a new NFT by recording its details onto a blockchain network. This process involves several critical steps designed to ensure authenticity while leveraging decentralized ledger technology:
Creating Digital Content: The first step involves producing the digital item—such as artwork, music files, videos—and preparing it for tokenization.
Choosing a Blockchain Platform: Creators select an appropriate blockchain platform like Ethereum (most popular), Binance Smart Chain (BSC), or Flow based on factors like transaction fees (“gas”), speed, community support, and environmental impact.
Deploying Smart Contracts: A smart contract—a self-executing code—is deployed onto the chosen blockchain to define rules governing the NFT’s creation & management.
Using Minting Platforms: Tools such as OpenSea’s minting feature or Rarible enable users to generate NFTs easily by linking their content with smart contracts without requiring extensive coding knowledge.
Tokenization & Storage: Once minted successfully via these platforms or custom contracts—the digital asset is linked as metadata within the token structure stored securely on-chain.
This entire process ensures that each NFT is uniquely identifiable while maintaining transparency regarding ownership history through immutable records.
How Are NFTs Traded? Step-by-Step Overview
Trading NFTs involves listing them for sale on specialized marketplaces where buyers can browse collections or place bids:
Marketplace Selection: Sellers choose from popular platforms like OpenSea—which boasts over 10 million registered users—or Rarible that offers additional features such as governance tokens.
Listing Items for Sale: Sellers create listings specifying price points—fixed prices or auction formats—and include detailed descriptions along with relevant tags for discoverability.
Bidding & Offers: Potential buyers can either purchase immediately at listed prices or participate in bidding wars during timed auctions—driving up value based on demand.
Executing Transactions: When a bid matches seller criteria—or when fixed-price sales occur—the transaction is processed via smart contracts executing securely over the blockchain network.
Ownership Transfer & Confirmation: Post-payment confirmation triggers automatic transfer of ownership rights from seller to buyer; this update is recorded permanently within the blockchain ledger.
This transparent process ensures trust among participants while enabling global access regardless of geographical boundaries.
Recent Trends Shaping NFT Markets
The past few years have seen significant developments influencing how NFTs are minted and traded:
Growth in Art & Collectibles
NFTs have gained mainstream attention through high-profile sales like Beeple’s “Everydays” which fetched $69 million at Christie's auction house—a milestone demonstrating mainstream acceptance beyond niche communities.
Expansion Across Blockchain Platforms
While Ethereum remains dominant due to its mature ecosystem—including standards like ERC-721—it faces challenges related to high gas fees during peak demand periods. Alternatives such as Binance Smart Chain (BSC) offer lower costs but may lack some ecosystem maturity; meanwhile platforms like Flow focus specifically on sports collectibles with partnerships involving NBA Top Shot.
Regulatory Environment Evolution
Governments worldwide recognize both opportunities and risks associated with digital assets:
- In 2022 alone, U.S regulators issued guidelines clarifying classification issues around certain types of tokens,
- The European Union explores comprehensive regulations affecting marketplace operations,which could influence future compliance requirements across jurisdictions.
Environmental Concerns & Sustainability Efforts
Ethereum's energy-intensive proof-of-work model prompted criticism about environmental impact; consequently:
- Many marketplaces now adopt layer-two solutions reducing energy consumption,
- Alternative blockchains offering eco-friendly options gain popularity among environmentally conscious users.
Challenges Facing NFT Marketplaces
Despite rapid growth opportunities — including increased liquidity — several hurdles remain:
Regulatory Uncertainty
Lack of clear legal frameworks creates volatility risks; creators must stay informed about evolving policies affecting intellectual property rights versus securities classifications which could impact trading practices significantly.
Scalability Limitations
High demand often results in slow transactions ("gas wars") especially during market surges:
- Solutions involve adopting layer-two scaling techniques,
- Transitioning toward more scalable blockchains helps reduce congestion but requires technical adaptation from platform operators.
Security Risks
Smart contract vulnerabilities pose hacking threats:
- Marketplace operators need robust security audits,
- Users should employ secure wallets combined with multi-factor authentication measures.
Navigating Market Volatility & Investment Risks
The NFT space remains highly speculative—with prices driven largely by hype rather than intrinsic value:
- Investors should conduct thorough research before purchasing,
- Diversification strategies help mitigate potential losses amid sudden price swings,
- Staying updated through reputable sources enhances decision-making capabilities.
Final Thoughts
NFTs continue reshaping our understanding of ownership within digital realms—from art collections to gaming assets—and present exciting opportunities alongside notable challenges. As technological innovations advance alongside clearer regulations aimed at protecting consumers while fostering innovation—they will likely become more integrated into mainstream financial ecosystems over time. Whether you're an artist looking to monetize your work or an investor seeking new avenues for growth—as well-informed participants—you'll benefit from staying current about processes involved in minting and trading these unique tokens across diverse marketplaces.


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-22 23:21
How are NFTs minted and traded on blockchain marketplaces?
How Are NFTs Minted and Traded on Blockchain Marketplaces?
Understanding the process of minting and trading Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) is essential for creators, collectors, and investors navigating the rapidly evolving digital asset landscape. This guide provides a clear overview of how NFTs are created, bought, and sold on blockchain platforms, emphasizing key steps, recent trends, and important considerations.
What Are NFTs and Why Do They Matter?
NFTs are unique digital assets stored on blockchain networks that represent ownership of a specific item—be it art, music, videos, or other digital collectibles. Unlike cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum—which are interchangeable—NFTs are non-fungible; each token has distinct properties that make it one-of-a-kind. This uniqueness has transformed how creators monetize their work online by providing verifiable proof of ownership and authenticity.
The significance of NFTs lies in their ability to empower artists and content creators to directly connect with audiences without intermediaries. For collectors, NFTs offer new avenues for investment in digital assets with potential appreciation value. As the market matures alongside advancements in blockchain technology and regulatory frameworks, understanding how these tokens are minted and traded becomes increasingly vital.
The Process of Minting an NFT
Minting refers to creating a new NFT by recording its details onto a blockchain network. This process involves several critical steps designed to ensure authenticity while leveraging decentralized ledger technology:
Creating Digital Content: The first step involves producing the digital item—such as artwork, music files, videos—and preparing it for tokenization.
Choosing a Blockchain Platform: Creators select an appropriate blockchain platform like Ethereum (most popular), Binance Smart Chain (BSC), or Flow based on factors like transaction fees (“gas”), speed, community support, and environmental impact.
Deploying Smart Contracts: A smart contract—a self-executing code—is deployed onto the chosen blockchain to define rules governing the NFT’s creation & management.
Using Minting Platforms: Tools such as OpenSea’s minting feature or Rarible enable users to generate NFTs easily by linking their content with smart contracts without requiring extensive coding knowledge.
Tokenization & Storage: Once minted successfully via these platforms or custom contracts—the digital asset is linked as metadata within the token structure stored securely on-chain.
This entire process ensures that each NFT is uniquely identifiable while maintaining transparency regarding ownership history through immutable records.
How Are NFTs Traded? Step-by-Step Overview
Trading NFTs involves listing them for sale on specialized marketplaces where buyers can browse collections or place bids:
Marketplace Selection: Sellers choose from popular platforms like OpenSea—which boasts over 10 million registered users—or Rarible that offers additional features such as governance tokens.
Listing Items for Sale: Sellers create listings specifying price points—fixed prices or auction formats—and include detailed descriptions along with relevant tags for discoverability.
Bidding & Offers: Potential buyers can either purchase immediately at listed prices or participate in bidding wars during timed auctions—driving up value based on demand.
Executing Transactions: When a bid matches seller criteria—or when fixed-price sales occur—the transaction is processed via smart contracts executing securely over the blockchain network.
Ownership Transfer & Confirmation: Post-payment confirmation triggers automatic transfer of ownership rights from seller to buyer; this update is recorded permanently within the blockchain ledger.
This transparent process ensures trust among participants while enabling global access regardless of geographical boundaries.
Recent Trends Shaping NFT Markets
The past few years have seen significant developments influencing how NFTs are minted and traded:
Growth in Art & Collectibles
NFTs have gained mainstream attention through high-profile sales like Beeple’s “Everydays” which fetched $69 million at Christie's auction house—a milestone demonstrating mainstream acceptance beyond niche communities.
Expansion Across Blockchain Platforms
While Ethereum remains dominant due to its mature ecosystem—including standards like ERC-721—it faces challenges related to high gas fees during peak demand periods. Alternatives such as Binance Smart Chain (BSC) offer lower costs but may lack some ecosystem maturity; meanwhile platforms like Flow focus specifically on sports collectibles with partnerships involving NBA Top Shot.
Regulatory Environment Evolution
Governments worldwide recognize both opportunities and risks associated with digital assets:
- In 2022 alone, U.S regulators issued guidelines clarifying classification issues around certain types of tokens,
- The European Union explores comprehensive regulations affecting marketplace operations,which could influence future compliance requirements across jurisdictions.
Environmental Concerns & Sustainability Efforts
Ethereum's energy-intensive proof-of-work model prompted criticism about environmental impact; consequently:
- Many marketplaces now adopt layer-two solutions reducing energy consumption,
- Alternative blockchains offering eco-friendly options gain popularity among environmentally conscious users.
Challenges Facing NFT Marketplaces
Despite rapid growth opportunities — including increased liquidity — several hurdles remain:
Regulatory Uncertainty
Lack of clear legal frameworks creates volatility risks; creators must stay informed about evolving policies affecting intellectual property rights versus securities classifications which could impact trading practices significantly.
Scalability Limitations
High demand often results in slow transactions ("gas wars") especially during market surges:
- Solutions involve adopting layer-two scaling techniques,
- Transitioning toward more scalable blockchains helps reduce congestion but requires technical adaptation from platform operators.
Security Risks
Smart contract vulnerabilities pose hacking threats:
- Marketplace operators need robust security audits,
- Users should employ secure wallets combined with multi-factor authentication measures.
Navigating Market Volatility & Investment Risks
The NFT space remains highly speculative—with prices driven largely by hype rather than intrinsic value:
- Investors should conduct thorough research before purchasing,
- Diversification strategies help mitigate potential losses amid sudden price swings,
- Staying updated through reputable sources enhances decision-making capabilities.
Final Thoughts
NFTs continue reshaping our understanding of ownership within digital realms—from art collections to gaming assets—and present exciting opportunities alongside notable challenges. As technological innovations advance alongside clearer regulations aimed at protecting consumers while fostering innovation—they will likely become more integrated into mainstream financial ecosystems over time. Whether you're an artist looking to monetize your work or an investor seeking new avenues for growth—as well-informed participants—you'll benefit from staying current about processes involved in minting and trading these unique tokens across diverse marketplaces.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is Slippage in Trading and How Can You Minimize Its Effects?
Understanding Slippage in Financial Markets
Slippage is a common phenomenon experienced by traders across various financial markets, including stocks, forex, commodities, and especially cryptocurrencies. It refers to the difference between the expected price of a trade—often based on current market quotes—and the actual price at which the trade is executed. This discrepancy can occur for multiple reasons but primarily stems from rapid market movements and liquidity constraints.
For traders, slippage can be both a minor inconvenience or a significant risk that impacts profitability. When placing large orders or trading during volatile periods, understanding how slippage works becomes essential for effective risk management. It’s important to recognize that some degree of slippage is inevitable due to the dynamic nature of markets; however, employing strategic measures can help reduce its adverse effects.
Causes of Slippage in Financial Trading
Several factors contribute to slippage:
- Market Volatility: Sudden price swings caused by economic news releases or geopolitical events can lead to rapid changes in asset prices.
- Liquidity Levels: Low liquidity assets have fewer buy and sell orders available at any given time. During such periods, even small trades can cause significant price shifts.
- Order Execution Speed: The time it takes for an order to be processed influences whether it fills at the desired price or not. Faster execution reduces exposure to unfavorable movements.
- Order Type Used: Market orders are more susceptible to slippage because they execute immediately at current prices; limit orders offer more control but may not fill if conditions aren’t met.
Types of Slippage
Understanding different types helps traders choose appropriate strategies:
- Market Order Slippage: When executing a market order (buy/sell immediately), traders often encounter execution at prices worse than expected due to rapid market changes.
- Limit Order Slippage: Limit orders specify maximum purchase or minimum sale prices; however, during fast-moving markets, these may fill at less favorable prices than intended if conditions change quickly.
Impact on Traders
Slippage can significantly affect trading outcomes—particularly for day traders and those using leverage—by reducing profits or increasing losses unexpectedly. For example, attempting to buy an asset at $100 might result in execution at $101 due to upward price movement during order processing. Conversely, selling might occur below your target if downward volatility occurs suddenly.
Recent Trends Affecting Slippage
The cryptocurrency landscape has seen increased volatility over recent years driven by regulatory developments and macroeconomic factors like inflation concerns and geopolitical tensions. These elements intensify unpredictable price swings that exacerbate slippage risks.
Additionally, technological advancements aim to mitigate these issues through improved trading platforms featuring faster execution speeds and sophisticated algorithms designed for optimal order placement under varying market conditions.
Strategies To Reduce Slippages Effectively
Minimizing slippage involves combining technical tools with sound trading practices:
Use Limit Orders: By setting specific entry or exit points rather than relying solely on market orders, you gain control over your trade prices—even if it means waiting longer for your order fill.
Implement Stop-Loss Orders: Protect yourself from unexpected adverse moves by predefining exit points that limit potential losses when markets move against you swiftly.
Conduct Thorough Market Analysis: Employ technical indicators like moving averages or RSI alongside fundamental analysis insights before executing trades—anticipating possible volatile moves helps avoid unfavorable fills.
Manage Position Sizes Carefully: Larger positions tend to cause more noticeable impact on liquidity pools; keeping sizes manageable reduces this effect's magnitude.
Diversify Portfolio Holdings: Spreading investments across different assets minimizes exposure concentrated within highly volatile markets prone to severe slippages.
Advanced Execution Techniques
For professional traders seeking further mitigation strategies:
- High-Frequency Trading (HFT): Utilizing algorithms capable of executing trades within milliseconds allows quick responses during volatile periods—reducing potential slip points.
- Dark Pools & Alternative Venues: Some institutional investors use dark pools where large blocks are traded anonymously without impacting public order books significantly—a method that may lower visible slippages but requires access privileges.
- Algorithmic Trading Systems: Customized algorithms adapt dynamically based on real-time data inputs ensuring optimal timing and pricing during high-volatility phases.
Risks Associated With High Levels of Slippage
Persistent high-slipping environments not only erode individual trader profits but also undermine overall confidence in financial markets — especially when frequent unexpected losses occur without clear explanations or controls in place.
Regulators monitor such phenomena closely because excessive slip-related issues could indicate underlying systemic problems like insufficient transparency or unfair trading practices leading toward stricter oversight measures aimed at protecting investors’ interests.
Practical Tips For Traders
To navigate around high-slipping scenarios effectively:
– Always set realistic expectations about potential costs associated with each trade based on current market conditions– Use demo accounts extensively before deploying real capital into volatile assets– Keep abreast with news updates affecting your traded instruments– Regularly review past trades’ performance concerning slip occurrences—to refine future strategies accordingly
By integrating these best practices into daily routines—and leveraging technological innovations—you enhance your ability not only to minimize loss from slips but also improve overall trading discipline amid unpredictable environments.
How Technological Advances Are Changing The Game
Emerging technologies continue transforming how traders approach slip management:
• Real-Time Data Analytics – Advanced analytics provide insights into likely volatility spikes ahead of time• Improved API Integrations – Faster connectivity between platforms ensures quicker executions• Machine Learning Algorithms – Adaptive models learn from past patterns improving decision-making accuracy
These innovations empower both retail investors and institutional players alike with tools designed specifically for better control over their trades amidst turbulent conditions.
Final Thoughts
While complete elimination of slippage remains impossible due to inherent market dynamics — understanding its causes enables smarter decision-making processes tailored toward risk reduction strategies like limit ordering techniques combined with robust analysis methods will serve you well as you navigate modern financial landscapes—including cryptocurrencies characterized by heightened volatility levels today.
By staying informed about recent trends—including regulatory shifts—and adopting advanced technological solutions—you position yourself better against adverse effects caused by unforeseen price movements during your trades.


kai
2025-05-22 22:25
What is slippage and what strategies minimize its impact?
What Is Slippage in Trading and How Can You Minimize Its Effects?
Understanding Slippage in Financial Markets
Slippage is a common phenomenon experienced by traders across various financial markets, including stocks, forex, commodities, and especially cryptocurrencies. It refers to the difference between the expected price of a trade—often based on current market quotes—and the actual price at which the trade is executed. This discrepancy can occur for multiple reasons but primarily stems from rapid market movements and liquidity constraints.
For traders, slippage can be both a minor inconvenience or a significant risk that impacts profitability. When placing large orders or trading during volatile periods, understanding how slippage works becomes essential for effective risk management. It’s important to recognize that some degree of slippage is inevitable due to the dynamic nature of markets; however, employing strategic measures can help reduce its adverse effects.
Causes of Slippage in Financial Trading
Several factors contribute to slippage:
- Market Volatility: Sudden price swings caused by economic news releases or geopolitical events can lead to rapid changes in asset prices.
- Liquidity Levels: Low liquidity assets have fewer buy and sell orders available at any given time. During such periods, even small trades can cause significant price shifts.
- Order Execution Speed: The time it takes for an order to be processed influences whether it fills at the desired price or not. Faster execution reduces exposure to unfavorable movements.
- Order Type Used: Market orders are more susceptible to slippage because they execute immediately at current prices; limit orders offer more control but may not fill if conditions aren’t met.
Types of Slippage
Understanding different types helps traders choose appropriate strategies:
- Market Order Slippage: When executing a market order (buy/sell immediately), traders often encounter execution at prices worse than expected due to rapid market changes.
- Limit Order Slippage: Limit orders specify maximum purchase or minimum sale prices; however, during fast-moving markets, these may fill at less favorable prices than intended if conditions change quickly.
Impact on Traders
Slippage can significantly affect trading outcomes—particularly for day traders and those using leverage—by reducing profits or increasing losses unexpectedly. For example, attempting to buy an asset at $100 might result in execution at $101 due to upward price movement during order processing. Conversely, selling might occur below your target if downward volatility occurs suddenly.
Recent Trends Affecting Slippage
The cryptocurrency landscape has seen increased volatility over recent years driven by regulatory developments and macroeconomic factors like inflation concerns and geopolitical tensions. These elements intensify unpredictable price swings that exacerbate slippage risks.
Additionally, technological advancements aim to mitigate these issues through improved trading platforms featuring faster execution speeds and sophisticated algorithms designed for optimal order placement under varying market conditions.
Strategies To Reduce Slippages Effectively
Minimizing slippage involves combining technical tools with sound trading practices:
Use Limit Orders: By setting specific entry or exit points rather than relying solely on market orders, you gain control over your trade prices—even if it means waiting longer for your order fill.
Implement Stop-Loss Orders: Protect yourself from unexpected adverse moves by predefining exit points that limit potential losses when markets move against you swiftly.
Conduct Thorough Market Analysis: Employ technical indicators like moving averages or RSI alongside fundamental analysis insights before executing trades—anticipating possible volatile moves helps avoid unfavorable fills.
Manage Position Sizes Carefully: Larger positions tend to cause more noticeable impact on liquidity pools; keeping sizes manageable reduces this effect's magnitude.
Diversify Portfolio Holdings: Spreading investments across different assets minimizes exposure concentrated within highly volatile markets prone to severe slippages.
Advanced Execution Techniques
For professional traders seeking further mitigation strategies:
- High-Frequency Trading (HFT): Utilizing algorithms capable of executing trades within milliseconds allows quick responses during volatile periods—reducing potential slip points.
- Dark Pools & Alternative Venues: Some institutional investors use dark pools where large blocks are traded anonymously without impacting public order books significantly—a method that may lower visible slippages but requires access privileges.
- Algorithmic Trading Systems: Customized algorithms adapt dynamically based on real-time data inputs ensuring optimal timing and pricing during high-volatility phases.
Risks Associated With High Levels of Slippage
Persistent high-slipping environments not only erode individual trader profits but also undermine overall confidence in financial markets — especially when frequent unexpected losses occur without clear explanations or controls in place.
Regulators monitor such phenomena closely because excessive slip-related issues could indicate underlying systemic problems like insufficient transparency or unfair trading practices leading toward stricter oversight measures aimed at protecting investors’ interests.
Practical Tips For Traders
To navigate around high-slipping scenarios effectively:
– Always set realistic expectations about potential costs associated with each trade based on current market conditions– Use demo accounts extensively before deploying real capital into volatile assets– Keep abreast with news updates affecting your traded instruments– Regularly review past trades’ performance concerning slip occurrences—to refine future strategies accordingly
By integrating these best practices into daily routines—and leveraging technological innovations—you enhance your ability not only to minimize loss from slips but also improve overall trading discipline amid unpredictable environments.
How Technological Advances Are Changing The Game
Emerging technologies continue transforming how traders approach slip management:
• Real-Time Data Analytics – Advanced analytics provide insights into likely volatility spikes ahead of time• Improved API Integrations – Faster connectivity between platforms ensures quicker executions• Machine Learning Algorithms – Adaptive models learn from past patterns improving decision-making accuracy
These innovations empower both retail investors and institutional players alike with tools designed specifically for better control over their trades amidst turbulent conditions.
Final Thoughts
While complete elimination of slippage remains impossible due to inherent market dynamics — understanding its causes enables smarter decision-making processes tailored toward risk reduction strategies like limit ordering techniques combined with robust analysis methods will serve you well as you navigate modern financial landscapes—including cryptocurrencies characterized by heightened volatility levels today.
By staying informed about recent trends—including regulatory shifts—and adopting advanced technological solutions—you position yourself better against adverse effects caused by unforeseen price movements during your trades.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Best Practices for Backing Up Your Cryptocurrency Wallet Securely
Cryptocurrency ownership has surged in recent years, making the security of digital assets more critical than ever. One of the most fundamental aspects of safeguarding your investments is implementing effective backup strategies for your cryptocurrency wallets. Proper backups ensure that you can recover your funds if your wallet is lost, stolen, or compromised. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of best practices to back up cryptocurrency wallets securely, incorporating recent trends and potential risks.
Understanding Cryptocurrency Wallets and Their Importance
A cryptocurrency wallet is a digital tool that allows users to store, send, and receive cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum. These wallets can be software applications on computers or smartphones, hardware devices designed for offline storage, or even third-party online services. Despite their differences in form factor and connectivity, all wallets contain sensitive information—private keys—that grant access to your funds.
Because transactions are irreversible once confirmed on the blockchain—meaning there’s no way to reverse an accidental transfer or theft—the importance of backing up these wallets cannot be overstated. Losing access due to hardware failure or cyberattacks could result in permanent loss of assets unless proper backup measures are in place.
Why Backing Up Cryptocurrency Wallets Is Critical
Backing up ensures continuity in accessing your crypto holdings regardless of unforeseen events like device damage or hacking incidents. Without a reliable backup plan:
- You risk losing access permanently if the device storing private keys becomes unusable.
- You may become vulnerable to theft if backups fall into malicious hands.
- Recovery options become limited when seed phrases or private keys are not stored securely.
Given that cryptocurrency transactions are final and irreversible, having multiple secure backups acts as an insurance policy against accidental loss while maintaining control over your assets.
Best Practices for Securely Backing Up Cryptocurrency Wallets
Use Multiple Types of Wallets: Hot vs Cold Storage
A balanced approach involves utilizing both hot (online) and cold (offline) storage solutions:
- Hot wallets facilitate quick transactions but pose higher security risks due to internet exposure.
- Cold wallets, such as hardware devices kept offline in safes or vaults, provide enhanced security suitable for long-term holdings.
Diversifying storage methods minimizes risk by ensuring that even if one method is compromised, others remain secure.
Select Reliable Backup Methods: Hardware & Software Solutions
Choosing reputable tools enhances security:
- Hardware wallets like Ledger Nano S/X or Trezor offer robust offline protection against hacking attempts.
- Software wallets should incorporate encrypted seed phrases stored securely; avoid cloud-based software unless they support strong encryption features.
Always verify the integrity of backup devices before storing sensitive information on them.
Generate and Safeguard Seed Phrases Carefully
Most modern crypto wallets generate a seed phrase—a sequence typically comprising 12–24 words—that serves as a master key for restoring access. Handling this phrase with care involves:
- Generating it within trusted environments
- Writing it down manually rather than saving digitally
- Storing it physically in secure locations such as safes
- Avoiding sharing it with anyone else
Remember: anyone with access to this seed phrase can control your funds entirely.
Encrypt Your Backups With Strong Security Measures
Encrypting backups adds an extra layer of protection against unauthorized access:
- Use complex passwords combined with encryption tools like VeraCrypt
- Store encrypted files separately from unencrypted copies
- Consider biometric authentication where available
This approach ensures that even if someone gains physical possession of the backup media, they cannot easily extract sensitive data without decryption credentials.
Keep Software Updated Regularly
Wallet providers frequently release updates addressing vulnerabilities discovered since previous versions. Regularly updating wallet software reduces exposure to known exploits—an essential step aligned with maintaining E-A-T (Expertise, Authority & Trustworthiness).
Set automatic updates where possible; otherwise check periodically for new releases from trusted sources only.
Implement Multi-Signature Security Protocols
Multi-signature (multi-sig) addresses require multiple private keys before executing transactions—adding layers beyond single-key controls:
- Distribute different signatures across geographically separated locations.
- Require consensus among several authorized parties before moving funds.
- Reduce risks associated with lost private keys by requiring multiple approvals instead of relying solely on one key holder’s safety measures.
This method significantly enhances overall wallet security by preventing unauthorized transfers—even if one key becomes compromised.
Store Physical Backups Securely
Physical storage remains vital because digital copies can be vulnerable during transmission or online storage breaches:
- Use fireproof safes located in secure areas
- Employ tamper-evident seals on safe containers
- Keep backups away from common hazards like water damage or theft
Physical safeguards protect critical recovery data over long periods without reliance on electronic systems vulnerable to cyber threats.
Leverage Cloud Storage Wisely
While cloud services offer convenience—they also pose risks related to hacking incidents—they can still be part of a comprehensive strategy when used cautiously:
- Choose reputable providers offering end-to-end encryption
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA)
- Limit permissions strictly regarding who can access stored data
Cloud backups should complement physical ones rather than replace them entirely.
Schedule Regular Backup Updates
Automation helps maintain current copies reflecting any changes made over time:
- Set reminders for periodic manual updates
- Utilize automated backup solutions compatible with your wallet type
- Review stored data periodically ensuring accuracy
Regular updates prevent discrepancies between actual wallet states and backed-up versions.
Recent Trends Enhancing Wallet Backup Security
The landscape continues evolving rapidly:
2023: The rise of decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms has led many users toward advanced multi-signature setups and decentralized custody solutions designed explicitly around enhanced security protocols tailored for high-value assets.
2024: Hardware wallet adoption has increased significantly amid growing awareness about offline cold storage benefits; companies have introduced features like biometric authentication integrated directly into devices.
2025: Artificial intelligence (AI) integration into crypto-wallet ecosystems now offers threat detection capabilities—monitoring unusual activity patterns—and automates responses such as alert notifications when suspicious behavior occurs.
These developments reflect ongoing efforts toward making crypto asset management safer through technological innovation aligned with user needs.
Risks Associated With Poor Backup Practices
Neglecting proper backing-up procedures exposes users to various dangers:
• Loss Of Funds: Failure to back up seeds properly means losing entire holdings after device failure or mishandling.• Security Breaches: Inadequate encryption increases vulnerability during storage/transmission phases leading potentially catastrophic breaches involving theft via phishing scams or malware attacks.• Regulatory Changes Impact: As governments update policies around crypto custody standards—including KYC/AML requirements—users must adapt their practices accordingly; ignorance could lead not only financial but legal consequences.
Understanding these pitfalls underscores why diligent adherence to best practices is essential—not just technically but also legally.
Final Thoughts: Prioritize Security When Managing Crypto Assets
Securing cryptocurrency investments requires proactive planning rooted in best practices tailored specifically toward safeguarding sensitive information like seed phrases and private keys effectively across physical and digital mediums alike.. Staying informed about emerging trends—including AI-driven threat detection—and regularly reviewing backup procedures help maintain resilience amidst evolving cybersecurity challenges within the crypto space.
By adopting these comprehensive strategies—from diversified storage options through encrypted backups—you significantly reduce vulnerability points while enhancing confidence that assets remain protected under various scenarios.. Remember: investing time upfront today saves potential losses tomorrow!


Lo
2025-05-22 17:29
What are the best practices for backing up my cryptocurrency wallet securely?
Best Practices for Backing Up Your Cryptocurrency Wallet Securely
Cryptocurrency ownership has surged in recent years, making the security of digital assets more critical than ever. One of the most fundamental aspects of safeguarding your investments is implementing effective backup strategies for your cryptocurrency wallets. Proper backups ensure that you can recover your funds if your wallet is lost, stolen, or compromised. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of best practices to back up cryptocurrency wallets securely, incorporating recent trends and potential risks.
Understanding Cryptocurrency Wallets and Their Importance
A cryptocurrency wallet is a digital tool that allows users to store, send, and receive cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum. These wallets can be software applications on computers or smartphones, hardware devices designed for offline storage, or even third-party online services. Despite their differences in form factor and connectivity, all wallets contain sensitive information—private keys—that grant access to your funds.
Because transactions are irreversible once confirmed on the blockchain—meaning there’s no way to reverse an accidental transfer or theft—the importance of backing up these wallets cannot be overstated. Losing access due to hardware failure or cyberattacks could result in permanent loss of assets unless proper backup measures are in place.
Why Backing Up Cryptocurrency Wallets Is Critical
Backing up ensures continuity in accessing your crypto holdings regardless of unforeseen events like device damage or hacking incidents. Without a reliable backup plan:
- You risk losing access permanently if the device storing private keys becomes unusable.
- You may become vulnerable to theft if backups fall into malicious hands.
- Recovery options become limited when seed phrases or private keys are not stored securely.
Given that cryptocurrency transactions are final and irreversible, having multiple secure backups acts as an insurance policy against accidental loss while maintaining control over your assets.
Best Practices for Securely Backing Up Cryptocurrency Wallets
Use Multiple Types of Wallets: Hot vs Cold Storage
A balanced approach involves utilizing both hot (online) and cold (offline) storage solutions:
- Hot wallets facilitate quick transactions but pose higher security risks due to internet exposure.
- Cold wallets, such as hardware devices kept offline in safes or vaults, provide enhanced security suitable for long-term holdings.
Diversifying storage methods minimizes risk by ensuring that even if one method is compromised, others remain secure.
Select Reliable Backup Methods: Hardware & Software Solutions
Choosing reputable tools enhances security:
- Hardware wallets like Ledger Nano S/X or Trezor offer robust offline protection against hacking attempts.
- Software wallets should incorporate encrypted seed phrases stored securely; avoid cloud-based software unless they support strong encryption features.
Always verify the integrity of backup devices before storing sensitive information on them.
Generate and Safeguard Seed Phrases Carefully
Most modern crypto wallets generate a seed phrase—a sequence typically comprising 12–24 words—that serves as a master key for restoring access. Handling this phrase with care involves:
- Generating it within trusted environments
- Writing it down manually rather than saving digitally
- Storing it physically in secure locations such as safes
- Avoiding sharing it with anyone else
Remember: anyone with access to this seed phrase can control your funds entirely.
Encrypt Your Backups With Strong Security Measures
Encrypting backups adds an extra layer of protection against unauthorized access:
- Use complex passwords combined with encryption tools like VeraCrypt
- Store encrypted files separately from unencrypted copies
- Consider biometric authentication where available
This approach ensures that even if someone gains physical possession of the backup media, they cannot easily extract sensitive data without decryption credentials.
Keep Software Updated Regularly
Wallet providers frequently release updates addressing vulnerabilities discovered since previous versions. Regularly updating wallet software reduces exposure to known exploits—an essential step aligned with maintaining E-A-T (Expertise, Authority & Trustworthiness).
Set automatic updates where possible; otherwise check periodically for new releases from trusted sources only.
Implement Multi-Signature Security Protocols
Multi-signature (multi-sig) addresses require multiple private keys before executing transactions—adding layers beyond single-key controls:
- Distribute different signatures across geographically separated locations.
- Require consensus among several authorized parties before moving funds.
- Reduce risks associated with lost private keys by requiring multiple approvals instead of relying solely on one key holder’s safety measures.
This method significantly enhances overall wallet security by preventing unauthorized transfers—even if one key becomes compromised.
Store Physical Backups Securely
Physical storage remains vital because digital copies can be vulnerable during transmission or online storage breaches:
- Use fireproof safes located in secure areas
- Employ tamper-evident seals on safe containers
- Keep backups away from common hazards like water damage or theft
Physical safeguards protect critical recovery data over long periods without reliance on electronic systems vulnerable to cyber threats.
Leverage Cloud Storage Wisely
While cloud services offer convenience—they also pose risks related to hacking incidents—they can still be part of a comprehensive strategy when used cautiously:
- Choose reputable providers offering end-to-end encryption
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA)
- Limit permissions strictly regarding who can access stored data
Cloud backups should complement physical ones rather than replace them entirely.
Schedule Regular Backup Updates
Automation helps maintain current copies reflecting any changes made over time:
- Set reminders for periodic manual updates
- Utilize automated backup solutions compatible with your wallet type
- Review stored data periodically ensuring accuracy
Regular updates prevent discrepancies between actual wallet states and backed-up versions.
Recent Trends Enhancing Wallet Backup Security
The landscape continues evolving rapidly:
2023: The rise of decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms has led many users toward advanced multi-signature setups and decentralized custody solutions designed explicitly around enhanced security protocols tailored for high-value assets.
2024: Hardware wallet adoption has increased significantly amid growing awareness about offline cold storage benefits; companies have introduced features like biometric authentication integrated directly into devices.
2025: Artificial intelligence (AI) integration into crypto-wallet ecosystems now offers threat detection capabilities—monitoring unusual activity patterns—and automates responses such as alert notifications when suspicious behavior occurs.
These developments reflect ongoing efforts toward making crypto asset management safer through technological innovation aligned with user needs.
Risks Associated With Poor Backup Practices
Neglecting proper backing-up procedures exposes users to various dangers:
• Loss Of Funds: Failure to back up seeds properly means losing entire holdings after device failure or mishandling.• Security Breaches: Inadequate encryption increases vulnerability during storage/transmission phases leading potentially catastrophic breaches involving theft via phishing scams or malware attacks.• Regulatory Changes Impact: As governments update policies around crypto custody standards—including KYC/AML requirements—users must adapt their practices accordingly; ignorance could lead not only financial but legal consequences.
Understanding these pitfalls underscores why diligent adherence to best practices is essential—not just technically but also legally.
Final Thoughts: Prioritize Security When Managing Crypto Assets
Securing cryptocurrency investments requires proactive planning rooted in best practices tailored specifically toward safeguarding sensitive information like seed phrases and private keys effectively across physical and digital mediums alike.. Staying informed about emerging trends—including AI-driven threat detection—and regularly reviewing backup procedures help maintain resilience amidst evolving cybersecurity challenges within the crypto space.
By adopting these comprehensive strategies—from diversified storage options through encrypted backups—you significantly reduce vulnerability points while enhancing confidence that assets remain protected under various scenarios.. Remember: investing time upfront today saves potential losses tomorrow!
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
