Popular Posts
What Is a Common Gap in Crypto and Investment Markets?
Understanding the landscape of cryptocurrency and investment markets reveals several recurring challenges, but one of the most prevalent issues is the regulatory gap. This gap refers to the lack of clear, consistent regulations governing crypto activities across different jurisdictions. As digital assets continue to grow in popularity and market capitalization, governments and regulatory bodies worldwide are struggling to establish comprehensive frameworks that protect investors while fostering innovation.
The regulatory gap creates significant uncertainty for market participants. Without well-defined rules, companies face legal ambiguities that can hinder product development, limit market entry, or lead to costly legal disputes. Investors may also be hesitant due to fears of sudden regulatory crackdowns or changes that could impact their holdings negatively. For example, in 2023, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) issued warnings about crypto investments' risks without providing detailed guidelines on compliance or security standards—highlighting this ongoing challenge.
This uncertainty impacts not only individual investors but also institutional players who require clarity before allocating substantial capital into crypto assets. The absence of standardized regulations can result in uneven enforcement across regions, creating a fragmented global market where some jurisdictions are more welcoming than others.
Addressing this common gap involves collaborative efforts among regulators, industry stakeholders, and technology developers to craft balanced policies that promote transparency without stifling innovation. Clearer regulations would help reduce fraud risks, improve investor confidence, and facilitate mainstream adoption by providing a predictable environment for all parties involved.
Why Regulatory Gaps Persist
Several factors contribute to why these gaps remain unfilled:
- Rapid Industry Growth: The fast-paced evolution of blockchain technology outpaces legislative processes.
- Jurisdictional Differences: Countries have varying approaches—some embrace crypto with open policies; others impose strict bans.
- Complexity of Technology: Understanding blockchain's technical aspects makes regulation challenging.
- Balancing Innovation & Security: Regulators aim to foster innovation while protecting consumers from scams or security breaches.
The Impact on Market Stability
Unaddressed regulatory gaps can lead directly to increased volatility within crypto markets. When investors perceive an uncertain legal environment—especially amid high-profile security breaches or scams—they may withdraw funds en masse or avoid participating altogether. This behavior exacerbates price swings and undermines trust in digital assets as reliable investment options.
Furthermore, lack of regulation can enable malicious actors exploiting loopholes for fraudulent schemes like pump-and-dump operations or Ponzi schemes—further damaging industry reputation over time.
Steps Toward Closing the Gap
To bridge this critical divide:
- International Cooperation: Countries need coordinated efforts through organizations such as FATF (Financial Action Task Force) for harmonized standards.
- Transparent Frameworks: Regulators should develop clear guidelines covering key areas like anti-money laundering (AML), know-your-customer (KYC), securities classification, taxation policies.
- Industry Engagement: Stakeholders must participate actively in policy discussions ensuring regulations are practical yet effective.
- Education & Awareness Campaigns: Increasing understanding among users reduces misinformation-driven panic during regulatory shifts.
By focusing on these strategies—and learning from recent developments such as Coinbase’s acquisition efforts aimed at expanding derivatives services—the industry can move toward more stable governance structures that support sustainable growth.
How Addressing Regulatory Gaps Benefits Stakeholders
Closing this common gap benefits everyone involved—from individual traders seeking safer environments for transactions to large institutions looking for predictable operational conditions:
- Enhanced Investor Confidence
- Reduced Fraud & Security Risks
- Increased Market Liquidity
- Greater Adoption Rates
In turn, these improvements foster a healthier ecosystem where technological innovations flourish alongside robust protections against misuse or abuse—a vital step toward mainstream acceptance of cryptocurrencies as legitimate financial instruments.
Semantic Keywords & Related Terms
Throughout discussions about gaps in crypto markets often include terms like "regulatory framework," "compliance standards," "cryptocurrency laws," "market stability," "investor protection," "blockchain regulation," and "crypto legislation." Recognizing these helps clarify how addressing one common issue influences multiple facets within the broader financial ecosystem related to digital currencies.
Summary
A prevalent challenge across cryptocurrency markets is bridging the regulatory gap—a persistent obstacle stemming from inconsistent laws worldwide combined with rapid technological advancements. Tackling this issue requires coordinated international efforts focused on creating transparent rules that balance innovation with security needs while fostering investor confidence and market stability over time.
References
1. SEC Crypto Warnings 2023
2. Crypto Regulation Challenges
3. Industry Efforts Toward Regulation
4. Global Blockchain Adoption


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-20 04:39
What’s a common gap?
What Is a Common Gap in Crypto and Investment Markets?
Understanding the landscape of cryptocurrency and investment markets reveals several recurring challenges, but one of the most prevalent issues is the regulatory gap. This gap refers to the lack of clear, consistent regulations governing crypto activities across different jurisdictions. As digital assets continue to grow in popularity and market capitalization, governments and regulatory bodies worldwide are struggling to establish comprehensive frameworks that protect investors while fostering innovation.
The regulatory gap creates significant uncertainty for market participants. Without well-defined rules, companies face legal ambiguities that can hinder product development, limit market entry, or lead to costly legal disputes. Investors may also be hesitant due to fears of sudden regulatory crackdowns or changes that could impact their holdings negatively. For example, in 2023, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) issued warnings about crypto investments' risks without providing detailed guidelines on compliance or security standards—highlighting this ongoing challenge.
This uncertainty impacts not only individual investors but also institutional players who require clarity before allocating substantial capital into crypto assets. The absence of standardized regulations can result in uneven enforcement across regions, creating a fragmented global market where some jurisdictions are more welcoming than others.
Addressing this common gap involves collaborative efforts among regulators, industry stakeholders, and technology developers to craft balanced policies that promote transparency without stifling innovation. Clearer regulations would help reduce fraud risks, improve investor confidence, and facilitate mainstream adoption by providing a predictable environment for all parties involved.
Why Regulatory Gaps Persist
Several factors contribute to why these gaps remain unfilled:
- Rapid Industry Growth: The fast-paced evolution of blockchain technology outpaces legislative processes.
- Jurisdictional Differences: Countries have varying approaches—some embrace crypto with open policies; others impose strict bans.
- Complexity of Technology: Understanding blockchain's technical aspects makes regulation challenging.
- Balancing Innovation & Security: Regulators aim to foster innovation while protecting consumers from scams or security breaches.
The Impact on Market Stability
Unaddressed regulatory gaps can lead directly to increased volatility within crypto markets. When investors perceive an uncertain legal environment—especially amid high-profile security breaches or scams—they may withdraw funds en masse or avoid participating altogether. This behavior exacerbates price swings and undermines trust in digital assets as reliable investment options.
Furthermore, lack of regulation can enable malicious actors exploiting loopholes for fraudulent schemes like pump-and-dump operations or Ponzi schemes—further damaging industry reputation over time.
Steps Toward Closing the Gap
To bridge this critical divide:
- International Cooperation: Countries need coordinated efforts through organizations such as FATF (Financial Action Task Force) for harmonized standards.
- Transparent Frameworks: Regulators should develop clear guidelines covering key areas like anti-money laundering (AML), know-your-customer (KYC), securities classification, taxation policies.
- Industry Engagement: Stakeholders must participate actively in policy discussions ensuring regulations are practical yet effective.
- Education & Awareness Campaigns: Increasing understanding among users reduces misinformation-driven panic during regulatory shifts.
By focusing on these strategies—and learning from recent developments such as Coinbase’s acquisition efforts aimed at expanding derivatives services—the industry can move toward more stable governance structures that support sustainable growth.
How Addressing Regulatory Gaps Benefits Stakeholders
Closing this common gap benefits everyone involved—from individual traders seeking safer environments for transactions to large institutions looking for predictable operational conditions:
- Enhanced Investor Confidence
- Reduced Fraud & Security Risks
- Increased Market Liquidity
- Greater Adoption Rates
In turn, these improvements foster a healthier ecosystem where technological innovations flourish alongside robust protections against misuse or abuse—a vital step toward mainstream acceptance of cryptocurrencies as legitimate financial instruments.
Semantic Keywords & Related Terms
Throughout discussions about gaps in crypto markets often include terms like "regulatory framework," "compliance standards," "cryptocurrency laws," "market stability," "investor protection," "blockchain regulation," and "crypto legislation." Recognizing these helps clarify how addressing one common issue influences multiple facets within the broader financial ecosystem related to digital currencies.
Summary
A prevalent challenge across cryptocurrency markets is bridging the regulatory gap—a persistent obstacle stemming from inconsistent laws worldwide combined with rapid technological advancements. Tackling this issue requires coordinated international efforts focused on creating transparent rules that balance innovation with security needs while fostering investor confidence and market stability over time.
References
1. SEC Crypto Warnings 2023
2. Crypto Regulation Challenges
3. Industry Efforts Toward Regulation
4. Global Blockchain Adoption
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is Trading Sentiment? A Complete Guide
Understanding Trading Sentiment and Its Role in Financial Markets
Trading sentiment refers to the overall attitude or emotional state of investors and traders toward a particular asset, market, or the economy as a whole. It reflects collective feelings—whether optimistic, pessimistic, or neutral—that influence buying and selling decisions. Unlike fundamental analysis, which examines financial data and economic indicators, sentiment analysis focuses on psychological factors that can drive short-term market movements.
Market participants’ emotions often lead to behaviors such as overbuying during bullish phases or panic selling during downturns. Recognizing these patterns can help traders anticipate potential reversals or continuations in price trends. This makes trading sentiment an essential component for investors aiming to understand not just what is happening but why it is happening in the markets.
How Trading Sentiment Is Measured
There are several methods used to gauge market sentiment accurately:
- Technical Indicators: Tools like Relative Strength Index (RSI), Bollinger Bands, and moving averages help identify overbought or oversold conditions that signal potential shifts in investor mood.
- Fundamental Data with a Sentiment Twist: While traditional fundamental analysis looks at earnings reports and economic data, incorporating qualitative factors such as news headlines and social media trends provides insights into prevailing investor attitudes.
- Sentiment Surveys & Reports: Investor surveys conducted by financial institutions reveal how bullish or bearish market participants feel about specific assets.
- Social Media & News Analysis: Monitoring platforms like Twitter, Reddit forums, and news outlets allows analysts to assess real-time emotional responses from traders worldwide.
The Psychology Behind Market Movements
Market psychology plays a pivotal role in shaping trading sentiment. Emotions such as fear and greed often dominate decision-making processes more than rational evaluation of assets' intrinsic value. For example:
- During bullish periods driven by optimism, investors tend to buy aggressively—sometimes leading to overvaluation.
- Conversely, widespread fear during downturns can trigger mass sell-offs even when fundamentals remain strong.
This collective behavior creates feedback loops where positive sentiment fuels further gains while negative sentiments accelerate declines. Recognizing these psychological patterns helps traders avoid herd mentality pitfalls while capitalizing on emerging opportunities.
Recent Trends Impacting Trading Sentiment
In recent months leading up to 2025's mid-year point, global markets have experienced mixed sentiments influenced by macroeconomic uncertainties. Stock indices across Asia showed caution amid geopolitical tensions; meanwhile U.S.-based stocks faced volatility due to inflation concerns and policy adjustments by central banks.
Specific company performances also reflect shifting investor attitudes:
Webull’s stock experienced a decline following mixed technical signals despite strategic partnerships like Visa integration—highlighting cautious investor behavior amid uncertain prospects.
BioPlus Acquisition Corp.'s delisting fears caused bearish sentiments among shareholders due to regulatory risks impacting its future viability.
Additionally, biotech firms like Spero Therapeutics faced negative market reactions ahead of quarterly earnings releases—a typical scenario where short-term sentiment influences trading volume more than long-term fundamentals.
The Impact of Market Sentiment on Investment Strategies
Understanding current trading sentiment enables investors to make more informed decisions:
- Timing Entry & Exit Points: By analyzing indicators signaling overbought/oversold conditions alongside qualitative data from news sources,traders can better time their trades.
- Risk Management: Recognizing signs of heightened volatility driven by negative sentiment helps mitigate losses through stop-loss ordersor hedging strategies.
- Contrarian Investing: Sometimes extreme negativity presents buying opportunities if underlying fundamentals remain strong,allowing contrarians to capitalize on eventual rebounds.
- Market Volatility Prediction: Sudden shifts in collective mood often precede sharp price swings; monitoring these cues aids in preparing for rapid changes.
Potential Risks Associated With Overreliance on Sentiment Analysis
While valuable tools for understanding market dynamics,
overdependence on trading sentiment alone carries risks:
It may lead traders astray if emotional reactions are mistaken for genuine trend reversals,resulting in premature entries/exits.
Market noise—short-term fluctuations driven purely by emotion rather than fundamentals—can cause false signals,leading investors into costly mistakes without proper confirmation from other analyses.
Therefore,
combining sentiment insights with technical and fundamental research ensures a balanced approach aligned with sound investment principles.
How Traders Can Use Sentiment Data Effectively
To leverage trading sentiment effectively,
investors should adopt best practices:
- Regularly monitor multiple sources including technical indicators,social media trends,and news headlinesto get comprehensive views of current moods.
- Use quantitative models that incorporate both numerical data (like RSI levels) and qualitative inputs (such as analyst opinions).
- Stay aware of broader macroeconomic developments influencing overall investor confidence,such as interest rate changes or geopolitical events.
- Maintain discipline by avoiding impulsive trades based solely on fleeting emotions;instead,
wait for confirmation signals before acting.
Why Understanding Trading Sentiment Matters for Investors Today
In an era characterized by rapid information flow facilitated through digital platforms,
market psychology has become more influential than ever before. The rise of social media has amplified individual voices contributing collectively toward heightened volatility episodes—notably seen during recent crypto booms/busts
or meme-stock rallies where crowd behavior drove prices far beyond intrinsic values temporarily.
For professional investors seeking an edge,
integrating real-time sentiment analysis enhances their ability to navigate complex environments effectively while managing risk appropriately.
Final Thoughts
Trading sentiment offers invaluable insights into the emotional undercurrents shaping financial markets today—from stocks and cryptocurrencies to commodities and forex pairs . By understanding how collective feelings influence price movements—and utilizing various measurement tools—traders gain an advantage that complements traditional analytical methods .
As markets continue evolving amidst technological advancements
staying attuned not only to hard data but also human psychology remains crucial for making informed investment choices — especially when navigating periods marked by uncertainty or high volatility


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-15 03:22
What is trading sentiment?
What Is Trading Sentiment? A Complete Guide
Understanding Trading Sentiment and Its Role in Financial Markets
Trading sentiment refers to the overall attitude or emotional state of investors and traders toward a particular asset, market, or the economy as a whole. It reflects collective feelings—whether optimistic, pessimistic, or neutral—that influence buying and selling decisions. Unlike fundamental analysis, which examines financial data and economic indicators, sentiment analysis focuses on psychological factors that can drive short-term market movements.
Market participants’ emotions often lead to behaviors such as overbuying during bullish phases or panic selling during downturns. Recognizing these patterns can help traders anticipate potential reversals or continuations in price trends. This makes trading sentiment an essential component for investors aiming to understand not just what is happening but why it is happening in the markets.
How Trading Sentiment Is Measured
There are several methods used to gauge market sentiment accurately:
- Technical Indicators: Tools like Relative Strength Index (RSI), Bollinger Bands, and moving averages help identify overbought or oversold conditions that signal potential shifts in investor mood.
- Fundamental Data with a Sentiment Twist: While traditional fundamental analysis looks at earnings reports and economic data, incorporating qualitative factors such as news headlines and social media trends provides insights into prevailing investor attitudes.
- Sentiment Surveys & Reports: Investor surveys conducted by financial institutions reveal how bullish or bearish market participants feel about specific assets.
- Social Media & News Analysis: Monitoring platforms like Twitter, Reddit forums, and news outlets allows analysts to assess real-time emotional responses from traders worldwide.
The Psychology Behind Market Movements
Market psychology plays a pivotal role in shaping trading sentiment. Emotions such as fear and greed often dominate decision-making processes more than rational evaluation of assets' intrinsic value. For example:
- During bullish periods driven by optimism, investors tend to buy aggressively—sometimes leading to overvaluation.
- Conversely, widespread fear during downturns can trigger mass sell-offs even when fundamentals remain strong.
This collective behavior creates feedback loops where positive sentiment fuels further gains while negative sentiments accelerate declines. Recognizing these psychological patterns helps traders avoid herd mentality pitfalls while capitalizing on emerging opportunities.
Recent Trends Impacting Trading Sentiment
In recent months leading up to 2025's mid-year point, global markets have experienced mixed sentiments influenced by macroeconomic uncertainties. Stock indices across Asia showed caution amid geopolitical tensions; meanwhile U.S.-based stocks faced volatility due to inflation concerns and policy adjustments by central banks.
Specific company performances also reflect shifting investor attitudes:
Webull’s stock experienced a decline following mixed technical signals despite strategic partnerships like Visa integration—highlighting cautious investor behavior amid uncertain prospects.
BioPlus Acquisition Corp.'s delisting fears caused bearish sentiments among shareholders due to regulatory risks impacting its future viability.
Additionally, biotech firms like Spero Therapeutics faced negative market reactions ahead of quarterly earnings releases—a typical scenario where short-term sentiment influences trading volume more than long-term fundamentals.
The Impact of Market Sentiment on Investment Strategies
Understanding current trading sentiment enables investors to make more informed decisions:
- Timing Entry & Exit Points: By analyzing indicators signaling overbought/oversold conditions alongside qualitative data from news sources,traders can better time their trades.
- Risk Management: Recognizing signs of heightened volatility driven by negative sentiment helps mitigate losses through stop-loss ordersor hedging strategies.
- Contrarian Investing: Sometimes extreme negativity presents buying opportunities if underlying fundamentals remain strong,allowing contrarians to capitalize on eventual rebounds.
- Market Volatility Prediction: Sudden shifts in collective mood often precede sharp price swings; monitoring these cues aids in preparing for rapid changes.
Potential Risks Associated With Overreliance on Sentiment Analysis
While valuable tools for understanding market dynamics,
overdependence on trading sentiment alone carries risks:
It may lead traders astray if emotional reactions are mistaken for genuine trend reversals,resulting in premature entries/exits.
Market noise—short-term fluctuations driven purely by emotion rather than fundamentals—can cause false signals,leading investors into costly mistakes without proper confirmation from other analyses.
Therefore,
combining sentiment insights with technical and fundamental research ensures a balanced approach aligned with sound investment principles.
How Traders Can Use Sentiment Data Effectively
To leverage trading sentiment effectively,
investors should adopt best practices:
- Regularly monitor multiple sources including technical indicators,social media trends,and news headlinesto get comprehensive views of current moods.
- Use quantitative models that incorporate both numerical data (like RSI levels) and qualitative inputs (such as analyst opinions).
- Stay aware of broader macroeconomic developments influencing overall investor confidence,such as interest rate changes or geopolitical events.
- Maintain discipline by avoiding impulsive trades based solely on fleeting emotions;instead,
wait for confirmation signals before acting.
Why Understanding Trading Sentiment Matters for Investors Today
In an era characterized by rapid information flow facilitated through digital platforms,
market psychology has become more influential than ever before. The rise of social media has amplified individual voices contributing collectively toward heightened volatility episodes—notably seen during recent crypto booms/busts
or meme-stock rallies where crowd behavior drove prices far beyond intrinsic values temporarily.
For professional investors seeking an edge,
integrating real-time sentiment analysis enhances their ability to navigate complex environments effectively while managing risk appropriately.
Final Thoughts
Trading sentiment offers invaluable insights into the emotional undercurrents shaping financial markets today—from stocks and cryptocurrencies to commodities and forex pairs . By understanding how collective feelings influence price movements—and utilizing various measurement tools—traders gain an advantage that complements traditional analytical methods .
As markets continue evolving amidst technological advancements
staying attuned not only to hard data but also human psychology remains crucial for making informed investment choices — especially when navigating periods marked by uncertainty or high volatility
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Quantifying Volume Spikes for Algorithmic Filters in Crypto Markets
Understanding Volume Spikes in Cryptocurrency Trading
In the fast-paced world of cryptocurrency trading, volume spikes are a key indicator of market activity that can signal potential price movements or market anomalies. A volume spike occurs when there is a sudden and significant increase in trading volume over a short period. These surges often reflect heightened trader interest, news events, or large institutional trades. Recognizing and accurately quantifying these spikes is essential for developing effective algorithmic filters that can detect opportunities or warn traders about possible risks.
Volume spikes are particularly important because they often precede major price shifts. For example, an unexpected surge in buying volume might indicate strong bullish sentiment, while a sudden increase in sell orders could signal impending downward movement. Traders and investors rely on precise measurement techniques to distinguish genuine signals from random fluctuations, which helps improve decision-making and reduce false alarms.
Methods to Quantify Volume Spikes
There are several approaches used by traders and quantitative analysts to measure the intensity of volume spikes:
Absolute Volume: This straightforward method measures the total number of trades or total traded value within a specific time frame. When this number exceeds typical levels significantly, it indicates a potential spike.
Relative Volume: Comparing current trading activity against historical averages provides context—if current volume is many times higher than usual, it suggests an abnormal event worth noting.
Rate of Change (ROC): This metric calculates the percentage change between current volume and previous periods’ volumes. Rapid increases reflected by high ROC values point toward active market shifts.
Moving Averages (MA): Applying simple moving averages smooths out short-term fluctuations; when actual trading volumes jump above these averages sharply, it signals unusual activity.
Exponential Moving Averages (EMA): EMAs give more weight to recent data points compared to traditional MAs, making them more responsive to recent changes—ideal for real-time detection of spikes.
Bollinger Bands: By plotting standard deviations around a moving average line for volume data, Bollinger Bands help identify when trading activity moves beyond normal volatility ranges—an indicator of potential spikes.
Machine Learning Models: Advanced algorithms trained on historical data can recognize complex patterns associated with upcoming or ongoing volume surges. These models enhance predictive accuracy but require substantial data processing capabilities.
Recent Advances Enhancing Spike Detection
The evolution of technology has significantly improved how traders quantify and respond to volume spikes:
Advanced Data Analytics Tools — Modern analytics platforms enable rapid processing of vast datasets from multiple sources such as exchanges and blockchain networks. These tools facilitate real-time monitoring with high precision.
AI-Powered Trading Platforms — Artificial intelligence systems now integrate directly into trading environments; they automatically detect unusual activity patterns based on learned models without human intervention.
Blockchain Data Integration — Incorporating transparent blockchain transaction records enhances measurement accuracy since all transactions are publicly recorded and tamper-proof.
Real-Time Market Data Feeds — The availability of instant updates allows traders to react swiftly as soon as significant changes occur—crucial given crypto markets' volatility.
Regulatory Developments Promoting Transparency — Increased oversight ensures better quality data sources which underpin reliable quantification methods while reducing manipulation risks.
Challenges & Risks Associated with Quantifying Volume Spikes
Despite technological progress, accurately measuring these surges remains challenging due to several factors:
False Positives – Overly sensitive filters may trigger alerts during normal fluctuations leading to unnecessary trades or missed opportunities if ignored.
Market Manipulation – Traders employing tactics like wash trading artificially inflate volumes creating misleading signals designed solely for profit extraction at others’ expense.
Data Quality Issues – Incomplete or inaccurate datasets undermine analysis reliability; ensuring clean inputs is critical but not always straightforward across diverse platforms.
Regulatory Scrutiny – As authorities scrutinize crypto markets more closely postulate stricter rules around reporting standards affecting how data should be collected and used ethically.
Ethical Considerations – The deployment of sophisticated algorithms raises questions about fairness especially if certain participants leverage proprietary tools unfairly gaining advantages over less equipped counterparts.
Best Practices for Effective Quantification
To maximize benefits while minimizing pitfalls when analyzing volume spikes:
- Use multiple metrics simultaneously—for example combining relative volumes with ROC—to confirm signals before acting upon them.
- Incorporate machine learning models cautiously—they should complement traditional statistical methods rather than replace human judgment entirely.
- Maintain high-quality datasets by sourcing from reputable exchanges offering transparent transaction records aligned with regulatory standards.
- Regularly backtest algorithms against historical scenarios ensuring robustness across different market conditions.
Impact on Trading Strategies & Market Dynamics
Accurately detecting genuine volume spikes enables algorithmic strategies such as breakout detection systems that capitalize on momentum shifts early enough before prices fully move away from support/resistance levels—a crucial advantage given crypto markets' volatility profile.
Furthermore, understanding these surges helps mitigate risks associated with false signals caused by manipulative practices like spoofing where fake orders create artificial demand/supply impressions temporarily skewing perceived market sentiment.
Future Outlook & Ethical Considerations
Looking ahead, ongoing developments aim at refining spike detection through deeper integration between blockchain transparency tools and AI-driven analytics frameworks—all aimed at fostering fairer markets through better information symmetry.
However, ethical considerations remain paramount; transparency about algorithmic decision-making processes fosters trust among participants while regulators seek balanced oversight that prevents abuse without stifling innovation.
Summary
Quantifying cryptocurrency trade volume spikes involves leveraging various statistical techniques—from simple absolute measures up through sophisticated machine learning models—that help traders identify meaningful shifts amid noisy data streams effectively. Recent technological advancements have enhanced our ability to monitor these phenomena accurately but come bundled with challenges related to manipulation risks and ethical concerns requiring vigilant oversight.
By adopting best practices rooted in transparency—and continuously updating methodologies aligned with evolving regulations—market participants can harness the power of accurate spike detection responsibly within dynamic crypto ecosystems.


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-14 03:19
How can volume spikes be quantified for algorithmic filters?
Quantifying Volume Spikes for Algorithmic Filters in Crypto Markets
Understanding Volume Spikes in Cryptocurrency Trading
In the fast-paced world of cryptocurrency trading, volume spikes are a key indicator of market activity that can signal potential price movements or market anomalies. A volume spike occurs when there is a sudden and significant increase in trading volume over a short period. These surges often reflect heightened trader interest, news events, or large institutional trades. Recognizing and accurately quantifying these spikes is essential for developing effective algorithmic filters that can detect opportunities or warn traders about possible risks.
Volume spikes are particularly important because they often precede major price shifts. For example, an unexpected surge in buying volume might indicate strong bullish sentiment, while a sudden increase in sell orders could signal impending downward movement. Traders and investors rely on precise measurement techniques to distinguish genuine signals from random fluctuations, which helps improve decision-making and reduce false alarms.
Methods to Quantify Volume Spikes
There are several approaches used by traders and quantitative analysts to measure the intensity of volume spikes:
Absolute Volume: This straightforward method measures the total number of trades or total traded value within a specific time frame. When this number exceeds typical levels significantly, it indicates a potential spike.
Relative Volume: Comparing current trading activity against historical averages provides context—if current volume is many times higher than usual, it suggests an abnormal event worth noting.
Rate of Change (ROC): This metric calculates the percentage change between current volume and previous periods’ volumes. Rapid increases reflected by high ROC values point toward active market shifts.
Moving Averages (MA): Applying simple moving averages smooths out short-term fluctuations; when actual trading volumes jump above these averages sharply, it signals unusual activity.
Exponential Moving Averages (EMA): EMAs give more weight to recent data points compared to traditional MAs, making them more responsive to recent changes—ideal for real-time detection of spikes.
Bollinger Bands: By plotting standard deviations around a moving average line for volume data, Bollinger Bands help identify when trading activity moves beyond normal volatility ranges—an indicator of potential spikes.
Machine Learning Models: Advanced algorithms trained on historical data can recognize complex patterns associated with upcoming or ongoing volume surges. These models enhance predictive accuracy but require substantial data processing capabilities.
Recent Advances Enhancing Spike Detection
The evolution of technology has significantly improved how traders quantify and respond to volume spikes:
Advanced Data Analytics Tools — Modern analytics platforms enable rapid processing of vast datasets from multiple sources such as exchanges and blockchain networks. These tools facilitate real-time monitoring with high precision.
AI-Powered Trading Platforms — Artificial intelligence systems now integrate directly into trading environments; they automatically detect unusual activity patterns based on learned models without human intervention.
Blockchain Data Integration — Incorporating transparent blockchain transaction records enhances measurement accuracy since all transactions are publicly recorded and tamper-proof.
Real-Time Market Data Feeds — The availability of instant updates allows traders to react swiftly as soon as significant changes occur—crucial given crypto markets' volatility.
Regulatory Developments Promoting Transparency — Increased oversight ensures better quality data sources which underpin reliable quantification methods while reducing manipulation risks.
Challenges & Risks Associated with Quantifying Volume Spikes
Despite technological progress, accurately measuring these surges remains challenging due to several factors:
False Positives – Overly sensitive filters may trigger alerts during normal fluctuations leading to unnecessary trades or missed opportunities if ignored.
Market Manipulation – Traders employing tactics like wash trading artificially inflate volumes creating misleading signals designed solely for profit extraction at others’ expense.
Data Quality Issues – Incomplete or inaccurate datasets undermine analysis reliability; ensuring clean inputs is critical but not always straightforward across diverse platforms.
Regulatory Scrutiny – As authorities scrutinize crypto markets more closely postulate stricter rules around reporting standards affecting how data should be collected and used ethically.
Ethical Considerations – The deployment of sophisticated algorithms raises questions about fairness especially if certain participants leverage proprietary tools unfairly gaining advantages over less equipped counterparts.
Best Practices for Effective Quantification
To maximize benefits while minimizing pitfalls when analyzing volume spikes:
- Use multiple metrics simultaneously—for example combining relative volumes with ROC—to confirm signals before acting upon them.
- Incorporate machine learning models cautiously—they should complement traditional statistical methods rather than replace human judgment entirely.
- Maintain high-quality datasets by sourcing from reputable exchanges offering transparent transaction records aligned with regulatory standards.
- Regularly backtest algorithms against historical scenarios ensuring robustness across different market conditions.
Impact on Trading Strategies & Market Dynamics
Accurately detecting genuine volume spikes enables algorithmic strategies such as breakout detection systems that capitalize on momentum shifts early enough before prices fully move away from support/resistance levels—a crucial advantage given crypto markets' volatility profile.
Furthermore, understanding these surges helps mitigate risks associated with false signals caused by manipulative practices like spoofing where fake orders create artificial demand/supply impressions temporarily skewing perceived market sentiment.
Future Outlook & Ethical Considerations
Looking ahead, ongoing developments aim at refining spike detection through deeper integration between blockchain transparency tools and AI-driven analytics frameworks—all aimed at fostering fairer markets through better information symmetry.
However, ethical considerations remain paramount; transparency about algorithmic decision-making processes fosters trust among participants while regulators seek balanced oversight that prevents abuse without stifling innovation.
Summary
Quantifying cryptocurrency trade volume spikes involves leveraging various statistical techniques—from simple absolute measures up through sophisticated machine learning models—that help traders identify meaningful shifts amid noisy data streams effectively. Recent technological advancements have enhanced our ability to monitor these phenomena accurately but come bundled with challenges related to manipulation risks and ethical concerns requiring vigilant oversight.
By adopting best practices rooted in transparency—and continuously updating methodologies aligned with evolving regulations—market participants can harness the power of accurate spike detection responsibly within dynamic crypto ecosystems.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How to Set Stop-Loss Levels Around Chart Patterns in Trading
Effective risk management is essential for successful trading, especially in volatile markets like cryptocurrencies. One of the most important tools traders use to limit potential losses is the stop-loss order. When combined with technical analysis—particularly chart patterns—setting appropriate stop-loss levels can significantly improve trading outcomes. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of how to set stop-loss levels around chart patterns, ensuring you make informed decisions that balance risk and reward.
Understanding Stop-Loss Orders and Their Role in Trading
A stop-loss order is an automatic instruction to sell a security once its price reaches a predetermined level. Its primary purpose is to protect traders from significant losses if the market moves against their position. In practice, setting a well-placed stop-loss helps prevent emotional decision-making during volatile market swings and ensures disciplined trading.
In the context of chart patterns, stop-loss levels are strategically placed based on expected price movements associated with specific formations. Proper placement requires understanding both the pattern's characteristics and current market conditions.
Common Chart Patterns Used for Trade Entries
Chart patterns visually represent historical price movements and help predict future trends when interpreted correctly. Recognizing these formations allows traders to identify potential entry points and determine where to place their stops.
Head and Shoulders
This pattern signals a potential trend reversal from bullish to bearish or vice versa. It features three peaks: a higher middle peak (head) flanked by two lower peaks (shoulders). The neckline connects the lows between these peaks; breaking below this line often indicates further downside movement.
Triangles
Triangles are consolidation patterns formed by converging trendlines connecting higher lows and lower highs:
- Symmetrical Triangle: Indicates indecision; breakout direction suggests future trend.
- Ascending Triangle: Bullish continuation pattern.
- Descending Triangle: Bearish continuation pattern.
Wedges
Wedges resemble triangles but have sloped boundaries indicating strong trending behavior before reversal or continuation:
- Rising Wedge: Usually bearish.
- Falling Wedge: Often bullish.
Reversal Patterns: Double Tops & Bottoms
Double tops suggest an impending downtrend after two failed attempts at breaking resistance, while double bottoms indicate potential upward reversals after testing support twice.
Strategies for Setting Stop-Loss Levels Based on Chart Patterns
Choosing where to place your stop-loss depends on your analysis of each pattern’s structure, volatility considerations, and your risk appetite. There are generally two approaches:
Conservative Approach
This method involves placing stops close enough that minor fluctuations won't trigger them unnecessarily but still provide protection against significant adverse moves:
- For head-and-shoulders: Just below the neckline in a bearish setup.
- For bullish reversal patterns: Slightly below key support levels or recent swing lows.
This approach minimizes losses but may result in more frequent triggers due to normal market noise.
Aggressive Approach
Here, stops are set further away from entry points—just above resistance levels in bearish setups or just below support lines in bullish scenarios—to avoid premature exits caused by minor retracements:
- For bearish breakouts: Slightly above resistance zones.
- For bullish breakouts: Slightly below support zones.
While this reduces false triggers, it exposes traders to larger potential losses if the trade goes wrong quickly.
Incorporating Technical Indicators for Better Stop Placement
Using additional technical tools can enhance your ability to set effective stop-loss levels around chart patterns:
- Moving Averages – Placing stops just beyond key moving average lines (e.g., 50-day MA) can provide dynamic support/resistance references.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI) – Overbought or oversold conditions may influence where you place stops relative to overextension zones.
- Bollinger Bands – These volatility bands help identify extreme price deviations; placing stops outside these bands can prevent being stopped out prematurely during normal fluctuations.
Combining these indicators with chart pattern analysis offers more robust risk management strategies aligned with current market dynamics.
Managing Risks Specific To Cryptocurrency Markets
Cryptocurrency markets are known for their high volatility compared to traditional assets like stocks or forex pairs. This characteristic makes precise stop-loss placement even more critical because sudden gaps or sharp moves can trigger orders unexpectedly—a phenomenon known as "market gaps."
To mitigate such risks:
- Use wider buffers when setting stops around volatile crypto assets
- Monitor news events that could cause sudden price jumps
- Consider using trailing stops that adjust as prices move favorably
Additionally, be cautious about overtrading—placing too many tight-stop orders across multiple positions—which can lead not only into increased transaction costs but also emotional fatigue.
Practical Examples of Setting Stop-Losses Around Chart Patterns
Understanding theoretical concepts becomes clearer through real-world examples:
Bitcoin Head & Shoulders Pattern
In January 2021, Bitcoin formed a head-and-shoulders top on its daily chart—a classic reversal signal indicating possible downside movement toward $30,000 area after confirming breakdown below neckline at approximately $35,000–$36,000 . Traders who anticipated this setup placed their stop-loss just above recent swing highs near $37,500 . When Bitcoin broke beneath $35k , those who had positioned their stops accordingly limited losses effectively .
Ethereum Symmetrical Triangle
In March 2023 , Ethereum displayed a symmetrical triangle formation on weekly charts . Traders expecting an upward breakout placed their protective orders slightly above resistance at around $1 ,500 . Once Ethereum surged past this level , triggered buy signals followed by trailing stops helped lock profits while managing downside risks .
These case studies highlight how aligning technical insights with strategic placement enhances overall trade management.
Best Practices for Effective Stop-Loss Placement
To optimize your use of stop-loss orders around chart patterns:
- Always analyze multiple timeframes before entering trades — longer-term charts provide context while shorter-term charts refine entries
- Avoid setting overly tight stops which might be triggered by normal market noise
- Use recent swing lows/highs as logical reference points
- Adjust your position size according to your risk tolerance — risking no more than 1–2% per trade is advisable
- Regularly review open positions — markets evolve rapidly; adapt your exit strategies accordingly
By integrating disciplined planning with continuous learning about technical developments—including new indicator tools—you build resilience against unpredictable crypto market behavior.
In Summary
Setting effective stop-loss levels around chart patterns combines technical analysis expertise with sound risk management principles tailored specifically for highly volatile markets like cryptocurrencies. Recognizing key formations such as head-and shoulders or triangles enables traders not only better entry timing but also strategic exit planning through well-positioned protective orders—all aimed at safeguarding capital while maximizing profit opportunities within defined risk parameters.


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-09 06:17
How do you set stop-loss levels around chart patterns?
How to Set Stop-Loss Levels Around Chart Patterns in Trading
Effective risk management is essential for successful trading, especially in volatile markets like cryptocurrencies. One of the most important tools traders use to limit potential losses is the stop-loss order. When combined with technical analysis—particularly chart patterns—setting appropriate stop-loss levels can significantly improve trading outcomes. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of how to set stop-loss levels around chart patterns, ensuring you make informed decisions that balance risk and reward.
Understanding Stop-Loss Orders and Their Role in Trading
A stop-loss order is an automatic instruction to sell a security once its price reaches a predetermined level. Its primary purpose is to protect traders from significant losses if the market moves against their position. In practice, setting a well-placed stop-loss helps prevent emotional decision-making during volatile market swings and ensures disciplined trading.
In the context of chart patterns, stop-loss levels are strategically placed based on expected price movements associated with specific formations. Proper placement requires understanding both the pattern's characteristics and current market conditions.
Common Chart Patterns Used for Trade Entries
Chart patterns visually represent historical price movements and help predict future trends when interpreted correctly. Recognizing these formations allows traders to identify potential entry points and determine where to place their stops.
Head and Shoulders
This pattern signals a potential trend reversal from bullish to bearish or vice versa. It features three peaks: a higher middle peak (head) flanked by two lower peaks (shoulders). The neckline connects the lows between these peaks; breaking below this line often indicates further downside movement.
Triangles
Triangles are consolidation patterns formed by converging trendlines connecting higher lows and lower highs:
- Symmetrical Triangle: Indicates indecision; breakout direction suggests future trend.
- Ascending Triangle: Bullish continuation pattern.
- Descending Triangle: Bearish continuation pattern.
Wedges
Wedges resemble triangles but have sloped boundaries indicating strong trending behavior before reversal or continuation:
- Rising Wedge: Usually bearish.
- Falling Wedge: Often bullish.
Reversal Patterns: Double Tops & Bottoms
Double tops suggest an impending downtrend after two failed attempts at breaking resistance, while double bottoms indicate potential upward reversals after testing support twice.
Strategies for Setting Stop-Loss Levels Based on Chart Patterns
Choosing where to place your stop-loss depends on your analysis of each pattern’s structure, volatility considerations, and your risk appetite. There are generally two approaches:
Conservative Approach
This method involves placing stops close enough that minor fluctuations won't trigger them unnecessarily but still provide protection against significant adverse moves:
- For head-and-shoulders: Just below the neckline in a bearish setup.
- For bullish reversal patterns: Slightly below key support levels or recent swing lows.
This approach minimizes losses but may result in more frequent triggers due to normal market noise.
Aggressive Approach
Here, stops are set further away from entry points—just above resistance levels in bearish setups or just below support lines in bullish scenarios—to avoid premature exits caused by minor retracements:
- For bearish breakouts: Slightly above resistance zones.
- For bullish breakouts: Slightly below support zones.
While this reduces false triggers, it exposes traders to larger potential losses if the trade goes wrong quickly.
Incorporating Technical Indicators for Better Stop Placement
Using additional technical tools can enhance your ability to set effective stop-loss levels around chart patterns:
- Moving Averages – Placing stops just beyond key moving average lines (e.g., 50-day MA) can provide dynamic support/resistance references.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI) – Overbought or oversold conditions may influence where you place stops relative to overextension zones.
- Bollinger Bands – These volatility bands help identify extreme price deviations; placing stops outside these bands can prevent being stopped out prematurely during normal fluctuations.
Combining these indicators with chart pattern analysis offers more robust risk management strategies aligned with current market dynamics.
Managing Risks Specific To Cryptocurrency Markets
Cryptocurrency markets are known for their high volatility compared to traditional assets like stocks or forex pairs. This characteristic makes precise stop-loss placement even more critical because sudden gaps or sharp moves can trigger orders unexpectedly—a phenomenon known as "market gaps."
To mitigate such risks:
- Use wider buffers when setting stops around volatile crypto assets
- Monitor news events that could cause sudden price jumps
- Consider using trailing stops that adjust as prices move favorably
Additionally, be cautious about overtrading—placing too many tight-stop orders across multiple positions—which can lead not only into increased transaction costs but also emotional fatigue.
Practical Examples of Setting Stop-Losses Around Chart Patterns
Understanding theoretical concepts becomes clearer through real-world examples:
Bitcoin Head & Shoulders Pattern
In January 2021, Bitcoin formed a head-and-shoulders top on its daily chart—a classic reversal signal indicating possible downside movement toward $30,000 area after confirming breakdown below neckline at approximately $35,000–$36,000 . Traders who anticipated this setup placed their stop-loss just above recent swing highs near $37,500 . When Bitcoin broke beneath $35k , those who had positioned their stops accordingly limited losses effectively .
Ethereum Symmetrical Triangle
In March 2023 , Ethereum displayed a symmetrical triangle formation on weekly charts . Traders expecting an upward breakout placed their protective orders slightly above resistance at around $1 ,500 . Once Ethereum surged past this level , triggered buy signals followed by trailing stops helped lock profits while managing downside risks .
These case studies highlight how aligning technical insights with strategic placement enhances overall trade management.
Best Practices for Effective Stop-Loss Placement
To optimize your use of stop-loss orders around chart patterns:
- Always analyze multiple timeframes before entering trades — longer-term charts provide context while shorter-term charts refine entries
- Avoid setting overly tight stops which might be triggered by normal market noise
- Use recent swing lows/highs as logical reference points
- Adjust your position size according to your risk tolerance — risking no more than 1–2% per trade is advisable
- Regularly review open positions — markets evolve rapidly; adapt your exit strategies accordingly
By integrating disciplined planning with continuous learning about technical developments—including new indicator tools—you build resilience against unpredictable crypto market behavior.
In Summary
Setting effective stop-loss levels around chart patterns combines technical analysis expertise with sound risk management principles tailored specifically for highly volatile markets like cryptocurrencies. Recognizing key formations such as head-and shoulders or triangles enables traders not only better entry timing but also strategic exit planning through well-positioned protective orders—all aimed at safeguarding capital while maximizing profit opportunities within defined risk parameters.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is On-Balance Volume (OBV)?
On-Balance Volume (OBV) is a popular technical analysis indicator used by traders to assess the strength of a market trend through volume data. Unlike price alone, OBV considers the cumulative buying and selling pressure, providing insights into whether a trend is likely to continue or reverse. Developed by Joseph Granville in the 1960s, OBV has stood the test of time as an effective tool for confirming price movements and detecting potential reversals.
At its core, OBV adds or subtracts volume based on daily closing prices. When the closing price rises compared to the previous day, that day's volume is added to the total OBV; when it falls, that volume is subtracted. This creates a running total that reflects overall market sentiment—whether buyers or sellers are dominating.
Understanding how OBV functions helps traders interpret whether current price trends are supported by strong trading activity. A rising OBV suggests increasing buying pressure and can signal an upcoming upward move in prices. Conversely, a declining OBV indicates increasing selling pressure and potential downward movement.
How Is On-Balance Volume Calculated?
Calculating OBV involves comparing each day's closing price with that of the previous day:
- If today's close is higher than yesterday's close: Add today's volume to the previous day's OBV.
- If today's close is lower than yesterday's close: Subtract today's volume from the previous day's OBV.
- If there's no change in closing prices: The OBV remains unchanged from its prior value.
The formula can be summarized as:
[ \text{OBV} = \text{Previous OBV} + \begin{cases}\text{Volume}, & \text{if Close today > Close yesterday} \-\text{Volume}, & \text{if Close today < Close yesterday} \0, & \text{if Close today = Close yesterday}\end{cases}]
This straightforward calculation makes it accessible for traders using various charting platforms and trading software.
Interpreting On-Balance Volume
The primary purpose of analyzing OBV lies in understanding market sentiment through its directional movement:
Positive (Rising) OBV: Indicates net buying activity over time; often seen during bullish phases where increased demand supports higher prices.
Negative (Falling) Obv: Reflects net selling pressure; common during bearish periods where supply exceeds demand.
Flat or Diverging Trends: When price moves upward but OBV remains flat or diverges negatively, it may signal weakening momentum or potential reversal points.
Traders often look for divergences between price action and ON-BALANCE VOLUME as early warning signs of trend exhaustion or reversal opportunities. For example:
A new high in stock prices accompanied by an unchanged or declining OB V could suggest underlying weakness despite apparent gains.
Conversely, if both price and ON-BALANCE VOLUME reach new highs together, this confirms strong bullish momentum supporting continued upward movement.
Using these interpretations alongside other indicators like RSI (Relative Strength Index) or moving averages enhances decision-making accuracy.
The Role of Obv in Technical Analysis
OB V serves as a confirmation tool within broader technical analysis strategies. It helps validate whether observed price movements are backed by substantial trading activity—a concept known as "volume confirmation." This makes it particularly valuable when assessing breakouts above resistance levels or breakdowns below support zones.
Additionally, traders utilize chart patterns such as trendlines on ON-BALANCE VOLUME charts to identify shifts in momentum before they become evident on traditional candlestick charts. Combining ON-BALANCE VOLUME with other indicators like MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence), Bollinger Bands®, and Fibonacci retracements creates more robust trade setups rooted in E-A-T principles—Expertise, Authority, Trustworthiness—by relying on multiple data points rather than isolated signals.
In recent years, integrating ON-BALANCE VOLUME into automated trading algorithms has further enhanced its utility by enabling rapid analysis across multiple assets simultaneously while reducing emotional biases inherent to manual trading decisions.
Practical Applications for Traders
Traders employ ON-BALANCE VOLUME across various markets—including stocks and cryptocurrencies—to improve their entry and exit strategies:
- Trend Confirmation: Confirm ongoing trends when both price action and BO volumes align positively.
- Divergence Detection: Spot early signs of reversals through divergence between Price Charts and BO Volumes.
- Breakout Validation: Validate breakouts above resistance levels with rising BO volumes indicating genuine interest behind moves.
- Identifying Hidden Weaknesses/Strengths: Use divergence signals to anticipate potential reversals before they fully materialize on charts.
- Complementing Other Indicators: Combine with RSI for overbought/oversold conditions; use moving averages for trend directionality alongside BO volumes' strength assessment.
Limitations To Keep In Mind
While powerful when used correctly, it's essential not to rely solely on ON BALANCE VOLUME:
It does not account for order flow imbalances caused by institutional trades which can distort signals temporarily.
Sudden spikes due to news events may produce false signals if not corroborated with other analytical tools.
Therefore, integrating multiple forms of analysis ensures more reliable decision-making aligned with sound risk management practices.
Historical Context And Evolution
Since its inception in 1960s financial markets research by Joseph Granville—who aimed at creating tools that reflect true market strength—OB V has evolved significantly:
During stock market booms especially post-WWII era until late 20th century,
Gained popularity among professional traders seeking objective confirmation methods,
Became increasingly relevant during cryptocurrency booms starting around 2017 due to volatile nature requiring precise tools,
Today’s advanced charting platforms incorporate real-time calculations allowing traders instant access without manual computation while also enabling backtesting strategies involving OBSERVATION-based indicators.
Recent Trends
The rise of algorithmic trading systems has integrated OBSERVATION into complex models designed for high-frequency environments where milliseconds matter most—a testament both to its robustness yet also highlighting caution needed against overreliance.
Limitations And Risks Of Using Obv
Despite its strengths within technical analysis frameworks:
Overdependence can lead traders astray if they ignore fundamental factors influencing markets such as economic reports or geopolitical events;
In highly volatile markets like cryptocurrencies experiencing sudden swings driven by news rather than fundamentals,
False signals may occur due to manipulation tactics like spoofing where large orders are placed temporarily without intent-to-trade intentions,
Hence combining OBSERVATION insights with fundamental analysis ensures balanced perspectives aligned with E-A-T standards—trustworthy advice grounded in comprehensive understanding.
Final Thoughts
On-balance volume remains one of the most enduring tools available within technical analysis arsenals because it offers clear insights into underlying market dynamics via trade volumes rather than just raw prices alone. Its ability to confirm trends—and sometimes predict reversals—is invaluable especially when combined thoughtfully with other indicators such as RSI , moving averages ,and pattern recognition techniques . As markets evolve—with crypto assets gaining prominence—the importance of reliable volume-based metrics like OBSERVATION continues growing among professional analysts seeking accurate assessments rooted firmly in data-driven evidence.


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-09 05:07
What is On-Balance Volume (OBV) and how is it interpreted?
What Is On-Balance Volume (OBV)?
On-Balance Volume (OBV) is a popular technical analysis indicator used by traders to assess the strength of a market trend through volume data. Unlike price alone, OBV considers the cumulative buying and selling pressure, providing insights into whether a trend is likely to continue or reverse. Developed by Joseph Granville in the 1960s, OBV has stood the test of time as an effective tool for confirming price movements and detecting potential reversals.
At its core, OBV adds or subtracts volume based on daily closing prices. When the closing price rises compared to the previous day, that day's volume is added to the total OBV; when it falls, that volume is subtracted. This creates a running total that reflects overall market sentiment—whether buyers or sellers are dominating.
Understanding how OBV functions helps traders interpret whether current price trends are supported by strong trading activity. A rising OBV suggests increasing buying pressure and can signal an upcoming upward move in prices. Conversely, a declining OBV indicates increasing selling pressure and potential downward movement.
How Is On-Balance Volume Calculated?
Calculating OBV involves comparing each day's closing price with that of the previous day:
- If today's close is higher than yesterday's close: Add today's volume to the previous day's OBV.
- If today's close is lower than yesterday's close: Subtract today's volume from the previous day's OBV.
- If there's no change in closing prices: The OBV remains unchanged from its prior value.
The formula can be summarized as:
[ \text{OBV} = \text{Previous OBV} + \begin{cases}\text{Volume}, & \text{if Close today > Close yesterday} \-\text{Volume}, & \text{if Close today < Close yesterday} \0, & \text{if Close today = Close yesterday}\end{cases}]
This straightforward calculation makes it accessible for traders using various charting platforms and trading software.
Interpreting On-Balance Volume
The primary purpose of analyzing OBV lies in understanding market sentiment through its directional movement:
Positive (Rising) OBV: Indicates net buying activity over time; often seen during bullish phases where increased demand supports higher prices.
Negative (Falling) Obv: Reflects net selling pressure; common during bearish periods where supply exceeds demand.
Flat or Diverging Trends: When price moves upward but OBV remains flat or diverges negatively, it may signal weakening momentum or potential reversal points.
Traders often look for divergences between price action and ON-BALANCE VOLUME as early warning signs of trend exhaustion or reversal opportunities. For example:
A new high in stock prices accompanied by an unchanged or declining OB V could suggest underlying weakness despite apparent gains.
Conversely, if both price and ON-BALANCE VOLUME reach new highs together, this confirms strong bullish momentum supporting continued upward movement.
Using these interpretations alongside other indicators like RSI (Relative Strength Index) or moving averages enhances decision-making accuracy.
The Role of Obv in Technical Analysis
OB V serves as a confirmation tool within broader technical analysis strategies. It helps validate whether observed price movements are backed by substantial trading activity—a concept known as "volume confirmation." This makes it particularly valuable when assessing breakouts above resistance levels or breakdowns below support zones.
Additionally, traders utilize chart patterns such as trendlines on ON-BALANCE VOLUME charts to identify shifts in momentum before they become evident on traditional candlestick charts. Combining ON-BALANCE VOLUME with other indicators like MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence), Bollinger Bands®, and Fibonacci retracements creates more robust trade setups rooted in E-A-T principles—Expertise, Authority, Trustworthiness—by relying on multiple data points rather than isolated signals.
In recent years, integrating ON-BALANCE VOLUME into automated trading algorithms has further enhanced its utility by enabling rapid analysis across multiple assets simultaneously while reducing emotional biases inherent to manual trading decisions.
Practical Applications for Traders
Traders employ ON-BALANCE VOLUME across various markets—including stocks and cryptocurrencies—to improve their entry and exit strategies:
- Trend Confirmation: Confirm ongoing trends when both price action and BO volumes align positively.
- Divergence Detection: Spot early signs of reversals through divergence between Price Charts and BO Volumes.
- Breakout Validation: Validate breakouts above resistance levels with rising BO volumes indicating genuine interest behind moves.
- Identifying Hidden Weaknesses/Strengths: Use divergence signals to anticipate potential reversals before they fully materialize on charts.
- Complementing Other Indicators: Combine with RSI for overbought/oversold conditions; use moving averages for trend directionality alongside BO volumes' strength assessment.
Limitations To Keep In Mind
While powerful when used correctly, it's essential not to rely solely on ON BALANCE VOLUME:
It does not account for order flow imbalances caused by institutional trades which can distort signals temporarily.
Sudden spikes due to news events may produce false signals if not corroborated with other analytical tools.
Therefore, integrating multiple forms of analysis ensures more reliable decision-making aligned with sound risk management practices.
Historical Context And Evolution
Since its inception in 1960s financial markets research by Joseph Granville—who aimed at creating tools that reflect true market strength—OB V has evolved significantly:
During stock market booms especially post-WWII era until late 20th century,
Gained popularity among professional traders seeking objective confirmation methods,
Became increasingly relevant during cryptocurrency booms starting around 2017 due to volatile nature requiring precise tools,
Today’s advanced charting platforms incorporate real-time calculations allowing traders instant access without manual computation while also enabling backtesting strategies involving OBSERVATION-based indicators.
Recent Trends
The rise of algorithmic trading systems has integrated OBSERVATION into complex models designed for high-frequency environments where milliseconds matter most—a testament both to its robustness yet also highlighting caution needed against overreliance.
Limitations And Risks Of Using Obv
Despite its strengths within technical analysis frameworks:
Overdependence can lead traders astray if they ignore fundamental factors influencing markets such as economic reports or geopolitical events;
In highly volatile markets like cryptocurrencies experiencing sudden swings driven by news rather than fundamentals,
False signals may occur due to manipulation tactics like spoofing where large orders are placed temporarily without intent-to-trade intentions,
Hence combining OBSERVATION insights with fundamental analysis ensures balanced perspectives aligned with E-A-T standards—trustworthy advice grounded in comprehensive understanding.
Final Thoughts
On-balance volume remains one of the most enduring tools available within technical analysis arsenals because it offers clear insights into underlying market dynamics via trade volumes rather than just raw prices alone. Its ability to confirm trends—and sometimes predict reversals—is invaluable especially when combined thoughtfully with other indicators such as RSI , moving averages ,and pattern recognition techniques . As markets evolve—with crypto assets gaining prominence—the importance of reliable volume-based metrics like OBSERVATION continues growing among professional analysts seeking accurate assessments rooted firmly in data-driven evidence.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Risks and Challenges of Using Bitcoin: A Comprehensive Overview
Bitcoin has revolutionized the financial landscape since its creation in 2009, offering a decentralized alternative to traditional currencies. Its appeal lies in its potential for high returns, privacy features, and the promise of a borderless financial system. However, alongside these advantages come significant risks and challenges that investors and users must understand to navigate the crypto space effectively.
Financial Risks Associated with Bitcoin
One of the most prominent concerns surrounding Bitcoin is its extreme price volatility. Unlike fiat currencies backed by governments or commodities like gold, Bitcoin's value can fluctuate dramatically within short periods. For example, in recent years, it has experienced rapid surges followed by sharp declines—making it difficult for traders to predict future prices accurately. This volatility can lead to substantial financial losses for investors who buy at peak prices or sell during downturns.
Market manipulation is another risk stemming from the largely unregulated nature of cryptocurrency markets. Without comprehensive oversight from regulatory bodies like those governing traditional finance sectors, malicious actors can influence prices through tactics such as pump-and-dump schemes or coordinated trading activities. Such practices distort market signals and pose risks for retail investors unfamiliar with these manipulative strategies.
Regulatory uncertainty remains a critical challenge impacting Bitcoin’s stability and adoption rates. Governments worldwide are still formulating policies regarding cryptocurrencies; sudden regulatory changes—such as bans or stricter compliance requirements—can cause abrupt price drops or restrict access altogether. For instance, recent developments like the repeal of certain IRS rules on decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms have created both opportunities and uncertainties within this evolving legal landscape.
Investment Challenges When Using Bitcoin
Unlike traditional assets supported by institutions like banks or governments, Bitcoin lacks centralized backing that guarantees its value stability. This absence means that investor confidence heavily depends on market sentiment rather than intrinsic backing—a factor contributing to its high volatility.
Security concerns also pose significant hurdles for users engaging with Bitcoin transactions. While blockchain technology offers a secure ledger system resistant to tampering under ideal conditions, vulnerabilities exist elsewhere in the ecosystem—for example, through hacking exchanges or phishing scams targeting individual wallets. Recent incidents involving cyber espionage groups exploiting weaknesses highlight ongoing security threats faced by crypto users globally.
Furthermore, scams remain prevalent due to the decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies which makes regulation enforcement challenging. Fraudulent schemes such as fake investment platforms or Ponzi schemes lure unsuspecting investors into losing their funds without recourse—a stark reminder that due diligence is essential when dealing with digital assets.
Blockchain Technology Challenges Impacting Adoption
Bitcoin’s underlying blockchain technology faces several technical limitations affecting scalability and usability:
- Scalability Issues: The current infrastructure struggles under increasing transaction volumes; network congestion leads to slower processing times and higher fees during peak periods.
- Energy Consumption: Mining operations require substantial computational power—often consuming energy comparable to small countries—which raises environmental concerns amid global efforts toward sustainability.
- Interoperability Gaps: Limited compatibility between different blockchain networks hampers seamless asset transfers across platforms—a barrier for broader mainstream adoption where interoperability is key.
Addressing these technological challenges requires ongoing innovation within blockchain development communities but remains an obstacle until solutions are widely implemented.
Recent Developments Shaping the Crypto Landscape
The year 2025 has been pivotal in shaping perceptions around Bitcoin’s risks:
In April 2025, Bitcoin's price surged past $94,000 driven partly by increased inflows into exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and easing geopolitical tensions such as cooling-off periods related to trade conflicts.
Regulatory reforms marked a turning point when authorities repealed restrictive IRS rules concerning DeFi platforms; this move aimed at fostering innovation while balancing compliance demands.
Security threats persistently evolve: North Korean cyber spies reportedly established U.S.-based firms targeting cryptocurrency exchanges through sophisticated hacking campaigns—highlighting persistent cybersecurity vulnerabilities within crypto ecosystems.
These developments underscore how rapidly market dynamics shift based on technological advances and policy changes—and why staying informed is crucial for participants at all levels.
Potential Fallout from Current Risks
Given these intertwined risks—from market volatility to security breaches—the potential fallout could be severe:
Market Crashes: Sudden downturns triggered by regulatory crackdowns or large-scale sell-offs could wipe out significant portions of investor wealth.
Regulatory Clampdowns: Governments may impose stricter controls if they perceive cryptocurrencies threaten monetary systems’ stability—potentially leading to bans or restrictions that diminish usability.
Security Breaches Eroding Trust: Continued hacking incidents undermine confidence among users; diminished trust can slow adoption rates further impacting liquidity and valuation over time.
Understanding these possible outcomes helps stakeholders prepare contingency plans while advocating responsible regulation aligned with technological progress.
Navigating Risks: Best Practices for Users & Investors
To mitigate exposure:
- Conduct thorough research before investing—in particular understanding project fundamentals,
- Use reputable wallets & exchanges with robust security measures,3.. Stay updated on regulatory developments relevant in your jurisdiction,4.. Diversify holdings across different assets beyond just cryptocurrencies,5.. Be cautious about speculative investments driven solely by hype rather than fundamentals,
By adopting prudent strategies rooted in awareness of inherent risks—and leveraging trusted sources—you can better position yourself amidst an evolving crypto environment filled with both opportunity and peril.
Final Thoughts: Balancing Innovation With Caution
Bitcoin continues transforming how we think about money—but it does so amid complex challenges requiring careful consideration from all participants involved—from individual traders up to policymakers worldwide . Recognizing associated risks—including volatility fluctuations , security vulnerabilities , scalability hurdles ,and uncertain regulations—is essential not only for safeguarding investments but also fostering sustainable growth within this innovative sector .
Staying informed about recent developments ensures you’re prepared against potential fallout while contributing positively toward shaping responsible frameworks that support innovation without compromising safety standards.
Keywords: bitcoin risks , cryptocurrency challenges , blockchain scalability issues , crypto security threats , bitcoin regulation updates


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-06 08:13
What are the risks and challenges associated with using Bitcoin?
Risks and Challenges of Using Bitcoin: A Comprehensive Overview
Bitcoin has revolutionized the financial landscape since its creation in 2009, offering a decentralized alternative to traditional currencies. Its appeal lies in its potential for high returns, privacy features, and the promise of a borderless financial system. However, alongside these advantages come significant risks and challenges that investors and users must understand to navigate the crypto space effectively.
Financial Risks Associated with Bitcoin
One of the most prominent concerns surrounding Bitcoin is its extreme price volatility. Unlike fiat currencies backed by governments or commodities like gold, Bitcoin's value can fluctuate dramatically within short periods. For example, in recent years, it has experienced rapid surges followed by sharp declines—making it difficult for traders to predict future prices accurately. This volatility can lead to substantial financial losses for investors who buy at peak prices or sell during downturns.
Market manipulation is another risk stemming from the largely unregulated nature of cryptocurrency markets. Without comprehensive oversight from regulatory bodies like those governing traditional finance sectors, malicious actors can influence prices through tactics such as pump-and-dump schemes or coordinated trading activities. Such practices distort market signals and pose risks for retail investors unfamiliar with these manipulative strategies.
Regulatory uncertainty remains a critical challenge impacting Bitcoin’s stability and adoption rates. Governments worldwide are still formulating policies regarding cryptocurrencies; sudden regulatory changes—such as bans or stricter compliance requirements—can cause abrupt price drops or restrict access altogether. For instance, recent developments like the repeal of certain IRS rules on decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms have created both opportunities and uncertainties within this evolving legal landscape.
Investment Challenges When Using Bitcoin
Unlike traditional assets supported by institutions like banks or governments, Bitcoin lacks centralized backing that guarantees its value stability. This absence means that investor confidence heavily depends on market sentiment rather than intrinsic backing—a factor contributing to its high volatility.
Security concerns also pose significant hurdles for users engaging with Bitcoin transactions. While blockchain technology offers a secure ledger system resistant to tampering under ideal conditions, vulnerabilities exist elsewhere in the ecosystem—for example, through hacking exchanges or phishing scams targeting individual wallets. Recent incidents involving cyber espionage groups exploiting weaknesses highlight ongoing security threats faced by crypto users globally.
Furthermore, scams remain prevalent due to the decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies which makes regulation enforcement challenging. Fraudulent schemes such as fake investment platforms or Ponzi schemes lure unsuspecting investors into losing their funds without recourse—a stark reminder that due diligence is essential when dealing with digital assets.
Blockchain Technology Challenges Impacting Adoption
Bitcoin’s underlying blockchain technology faces several technical limitations affecting scalability and usability:
- Scalability Issues: The current infrastructure struggles under increasing transaction volumes; network congestion leads to slower processing times and higher fees during peak periods.
- Energy Consumption: Mining operations require substantial computational power—often consuming energy comparable to small countries—which raises environmental concerns amid global efforts toward sustainability.
- Interoperability Gaps: Limited compatibility between different blockchain networks hampers seamless asset transfers across platforms—a barrier for broader mainstream adoption where interoperability is key.
Addressing these technological challenges requires ongoing innovation within blockchain development communities but remains an obstacle until solutions are widely implemented.
Recent Developments Shaping the Crypto Landscape
The year 2025 has been pivotal in shaping perceptions around Bitcoin’s risks:
In April 2025, Bitcoin's price surged past $94,000 driven partly by increased inflows into exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and easing geopolitical tensions such as cooling-off periods related to trade conflicts.
Regulatory reforms marked a turning point when authorities repealed restrictive IRS rules concerning DeFi platforms; this move aimed at fostering innovation while balancing compliance demands.
Security threats persistently evolve: North Korean cyber spies reportedly established U.S.-based firms targeting cryptocurrency exchanges through sophisticated hacking campaigns—highlighting persistent cybersecurity vulnerabilities within crypto ecosystems.
These developments underscore how rapidly market dynamics shift based on technological advances and policy changes—and why staying informed is crucial for participants at all levels.
Potential Fallout from Current Risks
Given these intertwined risks—from market volatility to security breaches—the potential fallout could be severe:
Market Crashes: Sudden downturns triggered by regulatory crackdowns or large-scale sell-offs could wipe out significant portions of investor wealth.
Regulatory Clampdowns: Governments may impose stricter controls if they perceive cryptocurrencies threaten monetary systems’ stability—potentially leading to bans or restrictions that diminish usability.
Security Breaches Eroding Trust: Continued hacking incidents undermine confidence among users; diminished trust can slow adoption rates further impacting liquidity and valuation over time.
Understanding these possible outcomes helps stakeholders prepare contingency plans while advocating responsible regulation aligned with technological progress.
Navigating Risks: Best Practices for Users & Investors
To mitigate exposure:
- Conduct thorough research before investing—in particular understanding project fundamentals,
- Use reputable wallets & exchanges with robust security measures,3.. Stay updated on regulatory developments relevant in your jurisdiction,4.. Diversify holdings across different assets beyond just cryptocurrencies,5.. Be cautious about speculative investments driven solely by hype rather than fundamentals,
By adopting prudent strategies rooted in awareness of inherent risks—and leveraging trusted sources—you can better position yourself amidst an evolving crypto environment filled with both opportunity and peril.
Final Thoughts: Balancing Innovation With Caution
Bitcoin continues transforming how we think about money—but it does so amid complex challenges requiring careful consideration from all participants involved—from individual traders up to policymakers worldwide . Recognizing associated risks—including volatility fluctuations , security vulnerabilities , scalability hurdles ,and uncertain regulations—is essential not only for safeguarding investments but also fostering sustainable growth within this innovative sector .
Staying informed about recent developments ensures you’re prepared against potential fallout while contributing positively toward shaping responsible frameworks that support innovation without compromising safety standards.
Keywords: bitcoin risks , cryptocurrency challenges , blockchain scalability issues , crypto security threats , bitcoin regulation updates
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Does the SOC 2 Type 1 Certification Impact User Experience in Coinbase Staking?
Understanding SOC 2 Type 1 Certification and Its Relevance
SOC 2 (Service Organization Control 2) certification is a widely recognized standard that evaluates how companies manage and protect customer data. Specifically, the Type 1 version assesses whether a company's controls are suitably designed and implemented as of a specific date. For platforms like Coinbase Staking, this certification signals to users that their assets and personal information are handled with high standards of security, privacy, and operational integrity.
In the context of cryptocurrency staking—where users lock up digital assets to earn rewards—the importance of trustworthiness cannot be overstated. Users want assurance that their investments are safe from breaches or mismanagement. Achieving SOC 2 Type 1 certification demonstrates Coinbase’s commitment to these principles by adhering to rigorous industry standards.
Why Is This Certification Important for Coinbase Staking?
Coinbase Staking involves complex financial transactions that require robust security measures. The process includes validating transactions, managing private keys, and ensuring seamless reward distribution—all critical components where vulnerabilities could lead to loss or theft.
The SOC 2 Type 1 certification provides several key assurances:
- Security Controls: It confirms that Coinbase has implemented appropriate safeguards against unauthorized access.
- Trust Building: It reassures users about the platform’s reliability.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many jurisdictions require such certifications for financial service providers, helping Coinbase meet legal obligations.
- Operational Transparency: Sharing details about control measures enhances user confidence in platform integrity.
By obtaining this certification, Coinbase not only aligns itself with industry best practices but also differentiates its staking services in a competitive market increasingly focused on security.
Recent Developments Highlighting Commitment
Coinbase's journey toward SOC 2 compliance reflects its proactive approach toward safeguarding user assets. Starting efforts around early 2023, the company dedicated resources toward establishing comprehensive controls tailored for staking operations. In April 2024, Coinbase announced it had successfully achieved SOC 2 Type 1 certification specifically for its staking services—a milestone celebrated within the industry as an indicator of maturity in security practices.
This achievement aligns with broader trends where crypto exchanges prioritize compliance amid rising regulatory scrutiny and increasing user demand for secure platforms. Other firms are following suit by pursuing similar certifications; however, Coinbase's early adoption positions it as an industry leader committed to transparency.
Failure to attain or maintain such certifications can have serious repercussions—including loss of user trust or regulatory penalties—making ongoing compliance essential for long-term success.
How Does SOC 2 Certification Improve User Experience?
The impact on end-users is tangible across several dimensions:
Enhanced Security Measures
With SOC 2 validation confirming robust controls are in place, users can feel more confident about their staked assets' safety. This includes protections against hacking attempts or internal mishandling—crucial factors given the irreversible nature of blockchain transactions if compromised.
Increased Trust and Confidence
Trust is fundamental when dealing with digital assets; knowing that a reputable third-party auditor has verified platform controls significantly boosts user confidence. This reassurance encourages more active participation in staking activities without fear of losing funds due to preventable security lapses.
Regulatory Assurance
Compliance signals adherence to legal standards governing data privacy and asset management—reducing concerns over potential legal issues affecting account access or asset recovery processes should disputes arise.
Competitive Edge Over Other Platforms
Many competitors may not yet have achieved similar levels of certification; thus, displaying this credential helps differentiate Coinbase Staking as a secure choice among numerous options available today.
The Broader Industry Context
As cryptocurrency markets grow more mature—and regulators pay closer attention—the emphasis on formal certifications like SOC audits increases across all service providers offering staking solutions. Companies investing in such standards demonstrate responsibility towards their users’ interests while positioning themselves favorably within evolving regulatory landscapes.
Future Outlook: Maintaining Trust Through Continuous Improvement
While achieving SOC 2 Type I is significant—it verifies control design at one point—it also sets the stage for ongoing improvements through subsequent assessments like type II audits which evaluate operational effectiveness over time. For users engaging with platforms like Coinbase Staking,
this means continuous enhancements in security protocols,greater transparency,and sustained commitment from providers dedicated to safeguarding digital assets.
Key Takeaways for Users Considering Crypto Staking Services
- Look for platforms with recognized certifications such as SOC reports—they indicate higher levels of trustworthiness.
- Understand that certified controls cover areas including data protection, system availability, confidentiality policies,and processing integrity.
- Recognize that ongoing compliance efforts reflect a company's dedication beyond just meeting minimum requirements.
By prioritizing these factors when choosing where to stake cryptocurrencies—and understanding what certifications imply—you can make informed decisions aligned with your risk appetite and confidence needs.
Final Thoughts
The attainment of SOC 2 Type I certification by Coinbase Staking marks an important step forward in enhancing user experience through strengthened security posture and increased transparency. As cybersecurity threats evolve alongside growing market demands for trustworthy services, such credentials serve both as reassurance tools for current users and benchmarks encouraging broader industry adoption — ultimately fostering safer environments where individuals can confidently participate in crypto earning opportunities without undue concern over risks related to data breaches or asset mismanagement.


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-06-05 06:34
How does the SOC 2 Type 1 certification impact user experience in Coinbase Staking?
How Does the SOC 2 Type 1 Certification Impact User Experience in Coinbase Staking?
Understanding SOC 2 Type 1 Certification and Its Relevance
SOC 2 (Service Organization Control 2) certification is a widely recognized standard that evaluates how companies manage and protect customer data. Specifically, the Type 1 version assesses whether a company's controls are suitably designed and implemented as of a specific date. For platforms like Coinbase Staking, this certification signals to users that their assets and personal information are handled with high standards of security, privacy, and operational integrity.
In the context of cryptocurrency staking—where users lock up digital assets to earn rewards—the importance of trustworthiness cannot be overstated. Users want assurance that their investments are safe from breaches or mismanagement. Achieving SOC 2 Type 1 certification demonstrates Coinbase’s commitment to these principles by adhering to rigorous industry standards.
Why Is This Certification Important for Coinbase Staking?
Coinbase Staking involves complex financial transactions that require robust security measures. The process includes validating transactions, managing private keys, and ensuring seamless reward distribution—all critical components where vulnerabilities could lead to loss or theft.
The SOC 2 Type 1 certification provides several key assurances:
- Security Controls: It confirms that Coinbase has implemented appropriate safeguards against unauthorized access.
- Trust Building: It reassures users about the platform’s reliability.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many jurisdictions require such certifications for financial service providers, helping Coinbase meet legal obligations.
- Operational Transparency: Sharing details about control measures enhances user confidence in platform integrity.
By obtaining this certification, Coinbase not only aligns itself with industry best practices but also differentiates its staking services in a competitive market increasingly focused on security.
Recent Developments Highlighting Commitment
Coinbase's journey toward SOC 2 compliance reflects its proactive approach toward safeguarding user assets. Starting efforts around early 2023, the company dedicated resources toward establishing comprehensive controls tailored for staking operations. In April 2024, Coinbase announced it had successfully achieved SOC 2 Type 1 certification specifically for its staking services—a milestone celebrated within the industry as an indicator of maturity in security practices.
This achievement aligns with broader trends where crypto exchanges prioritize compliance amid rising regulatory scrutiny and increasing user demand for secure platforms. Other firms are following suit by pursuing similar certifications; however, Coinbase's early adoption positions it as an industry leader committed to transparency.
Failure to attain or maintain such certifications can have serious repercussions—including loss of user trust or regulatory penalties—making ongoing compliance essential for long-term success.
How Does SOC 2 Certification Improve User Experience?
The impact on end-users is tangible across several dimensions:
Enhanced Security Measures
With SOC 2 validation confirming robust controls are in place, users can feel more confident about their staked assets' safety. This includes protections against hacking attempts or internal mishandling—crucial factors given the irreversible nature of blockchain transactions if compromised.
Increased Trust and Confidence
Trust is fundamental when dealing with digital assets; knowing that a reputable third-party auditor has verified platform controls significantly boosts user confidence. This reassurance encourages more active participation in staking activities without fear of losing funds due to preventable security lapses.
Regulatory Assurance
Compliance signals adherence to legal standards governing data privacy and asset management—reducing concerns over potential legal issues affecting account access or asset recovery processes should disputes arise.
Competitive Edge Over Other Platforms
Many competitors may not yet have achieved similar levels of certification; thus, displaying this credential helps differentiate Coinbase Staking as a secure choice among numerous options available today.
The Broader Industry Context
As cryptocurrency markets grow more mature—and regulators pay closer attention—the emphasis on formal certifications like SOC audits increases across all service providers offering staking solutions. Companies investing in such standards demonstrate responsibility towards their users’ interests while positioning themselves favorably within evolving regulatory landscapes.
Future Outlook: Maintaining Trust Through Continuous Improvement
While achieving SOC 2 Type I is significant—it verifies control design at one point—it also sets the stage for ongoing improvements through subsequent assessments like type II audits which evaluate operational effectiveness over time. For users engaging with platforms like Coinbase Staking,
this means continuous enhancements in security protocols,greater transparency,and sustained commitment from providers dedicated to safeguarding digital assets.
Key Takeaways for Users Considering Crypto Staking Services
- Look for platforms with recognized certifications such as SOC reports—they indicate higher levels of trustworthiness.
- Understand that certified controls cover areas including data protection, system availability, confidentiality policies,and processing integrity.
- Recognize that ongoing compliance efforts reflect a company's dedication beyond just meeting minimum requirements.
By prioritizing these factors when choosing where to stake cryptocurrencies—and understanding what certifications imply—you can make informed decisions aligned with your risk appetite and confidence needs.
Final Thoughts
The attainment of SOC 2 Type I certification by Coinbase Staking marks an important step forward in enhancing user experience through strengthened security posture and increased transparency. As cybersecurity threats evolve alongside growing market demands for trustworthy services, such credentials serve both as reassurance tools for current users and benchmarks encouraging broader industry adoption — ultimately fostering safer environments where individuals can confidently participate in crypto earning opportunities without undue concern over risks related to data breaches or asset mismanagement.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is the Execution Speed of a Market Order?
Understanding the execution speed of a market order is essential for traders and investors aiming to optimize their trading strategies. In fast-moving markets like cryptocurrencies, stocks, or forex, milliseconds can make the difference between profit and loss. This article explores what determines how quickly a market order gets filled, why it matters, and recent trends influencing this critical aspect of trading.
How Does Market Order Execution Work?
A market order is one of the simplest types of trading orders. When you place a market order, you're instructing your broker to buy or sell a security immediately at the best available current price. Unlike limit orders that specify a maximum or minimum price point, market orders prioritize speed over price control.
Once submitted, these orders are routed through various systems—brokerage platforms, exchanges, and sometimes high-frequency trading (HFT) algorithms—to be matched with existing buy or sell offers in the marketplace. The time it takes from clicking "buy" or "sell" to seeing your trade executed is known as execution speed.
Factors Influencing How Quickly Market Orders Are Filled
Several elements influence how fast your market order gets executed:
Market Liquidity: Markets with high liquidity—meaning many buyers and sellers actively trading—allow for faster fills because matching orders are readily available.
Order Size: Larger trades may take longer to execute because they can impact current prices or require multiple smaller transactions across different liquidity pools.
Trading Infrastructure: Advanced technological infrastructure—including low-latency servers and optimized routing systems—enables quicker processing times for executing trades.
Market Conditions: During periods of high volatility or sudden news events (like earnings reports), execution speeds can fluctuate due to increased demand on exchange systems.
Understanding these factors helps traders anticipate potential delays during certain conditions and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Types of Execution Related to Market Orders
While standard market orders aim for immediate execution at prevailing prices, there are variations that influence how quickly they are filled:
Immediate or Cancel (IOC): Executes immediately; any unfilled portion is canceled.
Fill or Kill (FOK): Must be filled entirely at once; otherwise canceled.
Good Till Cancelled (GTC): Remains active until explicitly canceled but may not execute instantly if conditions aren’t met.
These variations affect not only whether an order executes quickly but also how much control traders have over fill prices during volatile periods.
Recent Trends Impacting Execution Speed
The landscape of trade execution has evolved rapidly over recent years due to technological innovations and regulatory shifts:
High-Frequency Trading (HFT)
HFT firms utilize algorithms capable executing thousands of trades within fractions of a second. Their focus on ultra-fast execution speeds has driven exchanges and brokers to invest heavily in infrastructure upgrades. While HFT enhances overall liquidity and reduces spreads—which benefits all traders—it also raises concerns about fairness and stability in markets due to potential flash crashes caused by rapid-fire trades gone awry.
Blockchain Technology & Cryptocurrency Markets
Blockchain advancements have significantly improved transaction transparency while reducing settlement times in crypto markets. Decentralized exchanges leveraging blockchain technology enable near-instantaneous trade executions without traditional intermediaries—a development that continues pushing down latency issues associated with digital asset trading.
Regulatory Environment
Regulators worldwide scrutinize HFT practices because extremely rapid executions can contribute to increased volatility. Some jurisdictions have introduced rules limiting certain high-speed activities which could slow down some aspects of trade processing but aim ultimately at maintaining fairer markets with stable prices.
Why Does Execution Speed Matter?
Fast execution speeds directly impact trader profitability especially in volatile environments where prices change rapidly within seconds. For retail investors using online platforms without sophisticated infrastructure, delays might mean missing out on favorable entry points—or worse—increasing slippage where actual transaction prices differ from expected ones due to lag time.
Moreover, institutional players employing algorithmic strategies depend heavily on minimal latency; even microseconds matter when executing large volumes across multiple assets simultaneously. As such, understanding what influences speed helps both individual traders optimize their setups—and regulators monitor systemic risks associated with ultra-fast trading practices.
Potential Risks Associated With Rapid Trade Executions
While faster executions generally benefit traders by providing more precise entry/exit points—and potentially better pricing—they also carry risks:
Market Instability: Rapid-fire trades can amplify volatility leading sometimes into flash crashes if algorithms react unpredictably during turbulent moments.
Increased Costs: Achieving higher speeds often involves investing in expensive technology infrastructure which might not be feasible for retail investors.
Regulatory Scrutiny: Growing concern about unfair advantages held by HFT firms could lead regulators worldwide to impose restrictions affecting overall execution times.
Final Thoughts: Navigating Modern Trading Speeds
The evolution toward faster market order executions reflects ongoing technological progress aimed at enhancing efficiency—but it’s accompanied by new challenges related to stability and fairness. Traders should stay informed about factors influencing speed such as platform capabilities, current market conditions, regulatory changes—and consider these when designing their strategies.
By understanding what impacts how quickly your orders get filled—from liquidity levels through technological infrastructure—you’re better equipped for making timely decisions that align with your investment goals while managing inherent risks associated with rapid-market dynamics.
This overview aims to provide clarity around what determines the execution speed of a market order today. Whether you're an individual investor seeking quick entries/exits or an institutional trader relying on cutting-edge technology—knowing these fundamentals helps you navigate increasingly complex financial markets effectively while adhering to best practices rooted in transparency and risk management.


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-29 02:22
What is the execution speed of a market order?
What Is the Execution Speed of a Market Order?
Understanding the execution speed of a market order is essential for traders and investors aiming to optimize their trading strategies. In fast-moving markets like cryptocurrencies, stocks, or forex, milliseconds can make the difference between profit and loss. This article explores what determines how quickly a market order gets filled, why it matters, and recent trends influencing this critical aspect of trading.
How Does Market Order Execution Work?
A market order is one of the simplest types of trading orders. When you place a market order, you're instructing your broker to buy or sell a security immediately at the best available current price. Unlike limit orders that specify a maximum or minimum price point, market orders prioritize speed over price control.
Once submitted, these orders are routed through various systems—brokerage platforms, exchanges, and sometimes high-frequency trading (HFT) algorithms—to be matched with existing buy or sell offers in the marketplace. The time it takes from clicking "buy" or "sell" to seeing your trade executed is known as execution speed.
Factors Influencing How Quickly Market Orders Are Filled
Several elements influence how fast your market order gets executed:
Market Liquidity: Markets with high liquidity—meaning many buyers and sellers actively trading—allow for faster fills because matching orders are readily available.
Order Size: Larger trades may take longer to execute because they can impact current prices or require multiple smaller transactions across different liquidity pools.
Trading Infrastructure: Advanced technological infrastructure—including low-latency servers and optimized routing systems—enables quicker processing times for executing trades.
Market Conditions: During periods of high volatility or sudden news events (like earnings reports), execution speeds can fluctuate due to increased demand on exchange systems.
Understanding these factors helps traders anticipate potential delays during certain conditions and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Types of Execution Related to Market Orders
While standard market orders aim for immediate execution at prevailing prices, there are variations that influence how quickly they are filled:
Immediate or Cancel (IOC): Executes immediately; any unfilled portion is canceled.
Fill or Kill (FOK): Must be filled entirely at once; otherwise canceled.
Good Till Cancelled (GTC): Remains active until explicitly canceled but may not execute instantly if conditions aren’t met.
These variations affect not only whether an order executes quickly but also how much control traders have over fill prices during volatile periods.
Recent Trends Impacting Execution Speed
The landscape of trade execution has evolved rapidly over recent years due to technological innovations and regulatory shifts:
High-Frequency Trading (HFT)
HFT firms utilize algorithms capable executing thousands of trades within fractions of a second. Their focus on ultra-fast execution speeds has driven exchanges and brokers to invest heavily in infrastructure upgrades. While HFT enhances overall liquidity and reduces spreads—which benefits all traders—it also raises concerns about fairness and stability in markets due to potential flash crashes caused by rapid-fire trades gone awry.
Blockchain Technology & Cryptocurrency Markets
Blockchain advancements have significantly improved transaction transparency while reducing settlement times in crypto markets. Decentralized exchanges leveraging blockchain technology enable near-instantaneous trade executions without traditional intermediaries—a development that continues pushing down latency issues associated with digital asset trading.
Regulatory Environment
Regulators worldwide scrutinize HFT practices because extremely rapid executions can contribute to increased volatility. Some jurisdictions have introduced rules limiting certain high-speed activities which could slow down some aspects of trade processing but aim ultimately at maintaining fairer markets with stable prices.
Why Does Execution Speed Matter?
Fast execution speeds directly impact trader profitability especially in volatile environments where prices change rapidly within seconds. For retail investors using online platforms without sophisticated infrastructure, delays might mean missing out on favorable entry points—or worse—increasing slippage where actual transaction prices differ from expected ones due to lag time.
Moreover, institutional players employing algorithmic strategies depend heavily on minimal latency; even microseconds matter when executing large volumes across multiple assets simultaneously. As such, understanding what influences speed helps both individual traders optimize their setups—and regulators monitor systemic risks associated with ultra-fast trading practices.
Potential Risks Associated With Rapid Trade Executions
While faster executions generally benefit traders by providing more precise entry/exit points—and potentially better pricing—they also carry risks:
Market Instability: Rapid-fire trades can amplify volatility leading sometimes into flash crashes if algorithms react unpredictably during turbulent moments.
Increased Costs: Achieving higher speeds often involves investing in expensive technology infrastructure which might not be feasible for retail investors.
Regulatory Scrutiny: Growing concern about unfair advantages held by HFT firms could lead regulators worldwide to impose restrictions affecting overall execution times.
Final Thoughts: Navigating Modern Trading Speeds
The evolution toward faster market order executions reflects ongoing technological progress aimed at enhancing efficiency—but it’s accompanied by new challenges related to stability and fairness. Traders should stay informed about factors influencing speed such as platform capabilities, current market conditions, regulatory changes—and consider these when designing their strategies.
By understanding what impacts how quickly your orders get filled—from liquidity levels through technological infrastructure—you’re better equipped for making timely decisions that align with your investment goals while managing inherent risks associated with rapid-market dynamics.
This overview aims to provide clarity around what determines the execution speed of a market order today. Whether you're an individual investor seeking quick entries/exits or an institutional trader relying on cutting-edge technology—knowing these fundamentals helps you navigate increasingly complex financial markets effectively while adhering to best practices rooted in transparency and risk management.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What’s the McClellan Oscillator?
The McClellan Oscillator is a widely used technical analysis tool that helps traders and investors assess the overall health of the stock market by measuring market breadth. Developed in the 1960s by Sherman and Marian McClellan, this indicator provides valuable insights into whether market movements are supported by broad participation across stocks or driven by a few large-cap stocks. Understanding how to interpret this oscillator can enhance your ability to identify potential trend reversals and confirm ongoing market trends.
How Does the McClellan Oscillator Work?
At its core, the McClellan Oscillator calculates the difference between two key components: advancing stocks and declining stocks. It uses data from daily stock exchanges to determine how many stocks are moving higher versus those moving lower. This difference is then smoothed using exponential moving averages (EMAs) to produce a line chart that oscillates above and below zero.
When more stocks are advancing than declining, the oscillator shows positive values, indicating bullish sentiment across broader segments of the market. Conversely, negative readings suggest bearish conditions with more declining stocks than advancing ones. Traders often look for divergences—situations where price action moves contrary to what breadth indicators suggest—as signals of potential trend reversals.
Why Is Market Breadth Important?
Market breadth measures how widespread buying or selling activity is within an index or entire market. A rising index accompanied by strong breadth suggests healthy participation from many stocks, reinforcing bullish momentum. On the other hand, if an index advances while only a handful of large-cap stocks lead it higher—indicated by weak breadth—the rally may lack sustainability.
The McClellan Oscillator serves as an effective gauge of this participation level because it distills complex data about individual stock movements into a single, easy-to-interpret line. This makes it particularly useful for identifying when underlying strength supports or contradicts price trends.
Interpreting Signals from the McClellan Oscillator
Traders primarily use two types of signals from this indicator:
Positive/Negative Readings: When values cross above zero into positive territory, it suggests increasing bullishness; crossing below zero indicates bearish sentiment.
Divergences: If prices reach new highs but the oscillator fails to confirm with similar highs (a divergence), it could signal weakening momentum and potential reversal points.
Additionally, extreme overbought or oversold levels—often identified through specific threshold lines—can alert traders to possible upcoming corrections or rallies before they unfold in price charts.
Recent Trends in Using The McClellan Oscillator
In modern trading environments characterized by rapid information flow and algorithmic strategies, tools like the McClellan Oscillator remain relevant due to their simplicity and effectiveness in capturing broad-market shifts quickly. Many traders incorporate it alongside other technical indicators such as moving averages or RSI (Relative Strength Index) for confirmation purposes.
Furthermore, there’s growing interest in adapting these traditional tools beyond equities—for example, applying similar breadth analysis techniques within cryptocurrency markets despite their high volatility levels. While still experimental due to differing asset dynamics compared with traditional markets, these efforts highlight ongoing innovation driven by trader demand for comprehensive analysis methods.
Limitations & Cautions When Using The Indicator
Despite its usefulness, relying solely on any single technical indicator—including the McClellan Oscillator—can be risky:
Short-term signals: The oscillator tends to generate frequent fluctuations that may not always translate into meaningful long-term trend changes.
Market context: Breadth indicators should be interpreted within broader frameworks including fundamental analysis and macroeconomic factors.
False signals: Divergences can sometimes produce false alarms; therefore combining multiple indicators enhances reliability.
It’s essential for traders—and especially those managing significant portfolios—to understand these limitations before making decisions based solely on oscillators like this one.
Practical Tips for Traders
To maximize effectiveness when using the McClellan Oscillator:
- Watch for crossings above/below zero as initial signs of changing momentum.
- Confirm divergence signals with other technical tools such as volume analysis or trendlines.
- Be cautious during highly volatile periods where false signals are more common.
- Use historical thresholds (e.g., +50/-50) cautiously—they’re helpful but not definitive on their own.
Historical Significance & Notable Usage
Throughout history—including during major events like 2008 financial crisis—the McClellan Oscillator has proven valuable in anticipating shifts before they fully materialize in prices thanks to its focus on underlying market participation rather than just price action alone.
Many experienced traders consider it part of their core toolkit because it offers insight into whether current moves have broad support—a crucial factor when assessing sustainability.
How To Incorporate The MacLeallan Into Your Trading Strategy
Integrating this tool effectively involves understanding both its strengths and limitations:
- Use alongside trend-following systems such as moving averages
- Look for confirmation through volume patterns
- Monitor divergence signs carefully
- Combine with fundamental insights about economic conditions
Final Thoughts: Is The MacLeallan Still Relevant Today?
Yes — despite being over half a century old —the MacLeallan remains relevant because of its straightforward approach toward measuring market health via breadth analysis . Its ability to provide early warnings about potential reversals makes it invaluable especially when combined with modern analytical techniques like algorithmic trading platforms which can process vast amounts of data efficiently .
While adaptations might be necessary when applying similar concepts within emerging markets like cryptocurrencies due to different asset behaviors , understanding traditional tools such as this one forms a solid foundation upon which innovative strategies can be built.
Keywords: MacLeallanOscillator , MarketBreadth , TechnicalAnalysis , StockMarketIndicators , MarketReversals , TradingStrategies , CryptocurrencyAnalysis


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-20 03:29
What’s the McClellan Oscillator?
What’s the McClellan Oscillator?
The McClellan Oscillator is a widely used technical analysis tool that helps traders and investors assess the overall health of the stock market by measuring market breadth. Developed in the 1960s by Sherman and Marian McClellan, this indicator provides valuable insights into whether market movements are supported by broad participation across stocks or driven by a few large-cap stocks. Understanding how to interpret this oscillator can enhance your ability to identify potential trend reversals and confirm ongoing market trends.
How Does the McClellan Oscillator Work?
At its core, the McClellan Oscillator calculates the difference between two key components: advancing stocks and declining stocks. It uses data from daily stock exchanges to determine how many stocks are moving higher versus those moving lower. This difference is then smoothed using exponential moving averages (EMAs) to produce a line chart that oscillates above and below zero.
When more stocks are advancing than declining, the oscillator shows positive values, indicating bullish sentiment across broader segments of the market. Conversely, negative readings suggest bearish conditions with more declining stocks than advancing ones. Traders often look for divergences—situations where price action moves contrary to what breadth indicators suggest—as signals of potential trend reversals.
Why Is Market Breadth Important?
Market breadth measures how widespread buying or selling activity is within an index or entire market. A rising index accompanied by strong breadth suggests healthy participation from many stocks, reinforcing bullish momentum. On the other hand, if an index advances while only a handful of large-cap stocks lead it higher—indicated by weak breadth—the rally may lack sustainability.
The McClellan Oscillator serves as an effective gauge of this participation level because it distills complex data about individual stock movements into a single, easy-to-interpret line. This makes it particularly useful for identifying when underlying strength supports or contradicts price trends.
Interpreting Signals from the McClellan Oscillator
Traders primarily use two types of signals from this indicator:
Positive/Negative Readings: When values cross above zero into positive territory, it suggests increasing bullishness; crossing below zero indicates bearish sentiment.
Divergences: If prices reach new highs but the oscillator fails to confirm with similar highs (a divergence), it could signal weakening momentum and potential reversal points.
Additionally, extreme overbought or oversold levels—often identified through specific threshold lines—can alert traders to possible upcoming corrections or rallies before they unfold in price charts.
Recent Trends in Using The McClellan Oscillator
In modern trading environments characterized by rapid information flow and algorithmic strategies, tools like the McClellan Oscillator remain relevant due to their simplicity and effectiveness in capturing broad-market shifts quickly. Many traders incorporate it alongside other technical indicators such as moving averages or RSI (Relative Strength Index) for confirmation purposes.
Furthermore, there’s growing interest in adapting these traditional tools beyond equities—for example, applying similar breadth analysis techniques within cryptocurrency markets despite their high volatility levels. While still experimental due to differing asset dynamics compared with traditional markets, these efforts highlight ongoing innovation driven by trader demand for comprehensive analysis methods.
Limitations & Cautions When Using The Indicator
Despite its usefulness, relying solely on any single technical indicator—including the McClellan Oscillator—can be risky:
Short-term signals: The oscillator tends to generate frequent fluctuations that may not always translate into meaningful long-term trend changes.
Market context: Breadth indicators should be interpreted within broader frameworks including fundamental analysis and macroeconomic factors.
False signals: Divergences can sometimes produce false alarms; therefore combining multiple indicators enhances reliability.
It’s essential for traders—and especially those managing significant portfolios—to understand these limitations before making decisions based solely on oscillators like this one.
Practical Tips for Traders
To maximize effectiveness when using the McClellan Oscillator:
- Watch for crossings above/below zero as initial signs of changing momentum.
- Confirm divergence signals with other technical tools such as volume analysis or trendlines.
- Be cautious during highly volatile periods where false signals are more common.
- Use historical thresholds (e.g., +50/-50) cautiously—they’re helpful but not definitive on their own.
Historical Significance & Notable Usage
Throughout history—including during major events like 2008 financial crisis—the McClellan Oscillator has proven valuable in anticipating shifts before they fully materialize in prices thanks to its focus on underlying market participation rather than just price action alone.
Many experienced traders consider it part of their core toolkit because it offers insight into whether current moves have broad support—a crucial factor when assessing sustainability.
How To Incorporate The MacLeallan Into Your Trading Strategy
Integrating this tool effectively involves understanding both its strengths and limitations:
- Use alongside trend-following systems such as moving averages
- Look for confirmation through volume patterns
- Monitor divergence signs carefully
- Combine with fundamental insights about economic conditions
Final Thoughts: Is The MacLeallan Still Relevant Today?
Yes — despite being over half a century old —the MacLeallan remains relevant because of its straightforward approach toward measuring market health via breadth analysis . Its ability to provide early warnings about potential reversals makes it invaluable especially when combined with modern analytical techniques like algorithmic trading platforms which can process vast amounts of data efficiently .
While adaptations might be necessary when applying similar concepts within emerging markets like cryptocurrencies due to different asset behaviors , understanding traditional tools such as this one forms a solid foundation upon which innovative strategies can be built.
Keywords: MacLeallanOscillator , MarketBreadth , TechnicalAnalysis , StockMarketIndicators , MarketReversals , TradingStrategies , CryptocurrencyAnalysis
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How to Optimize Gap Strategies for Earnings Gaps in Financial Markets
Understanding Gap Strategies and Earnings Gaps
Gap strategies are investment techniques designed to capitalize on temporary price discrepancies between financial instruments. These discrepancies often occur due to market inefficiencies, news releases, or earnings reports. In particular, earnings gaps refer to the difference between a company's actual reported earnings and what analysts or investors expected. When a company reports earnings that significantly differ from forecasts—either positively or negatively—it can create a gap in the stock price, presenting opportunities for traders who can anticipate and react swiftly.
In the context of financial markets, especially with volatile assets like cryptocurrencies, identifying and exploiting these gaps requires a combination of analytical tools and strategic planning. Investors aim to predict when an earnings gap will occur or identify its impact early enough to profit before the market adjusts.
Key Steps in Optimizing Gap Strategies for Earnings Gaps
- Conduct Thorough Market Analysis
The foundation of effective gap trading lies in comprehensive market analysis. This involves monitoring financial news outlets, earning reports scheduled by companies, macroeconomic indicators, and overall market sentiment. By staying informed about upcoming earnings releases and potential catalysts—such as regulatory changes or geopolitical events—investors can better anticipate where gaps might form.
Additionally, analyzing historical data on past earnings surprises helps identify patterns that could repeat under similar circumstances. For example, some sectors tend to experience more frequent positive surprises than others; recognizing these trends enhances predictive accuracy.
- Gather Historical Data on Earnings Gaps
Building a database of previous earnings gaps allows traders to understand their frequency, size distribution, and typical impact on asset prices. Statistical analysis of this data reveals probabilities associated with different types of gaps (upward vs downward) under various conditions.
This historical perspective aids in setting realistic expectations regarding potential gains and risks associated with specific trades based on prior occurrences.
- Implement Robust Risk Management Techniques
Given the inherent unpredictability of markets—and especially high-volatility assets like cryptocurrencies—risk management is crucial when deploying gap strategies. Setting stop-loss orders ensures losses are contained if an anticipated move does not materialize as expected.
Diversification across multiple assets reduces exposure risk related to any single event triggering an adverse movement. Position sizing should also be carefully calibrated based on volatility levels; larger positions may be justified during periods of high confidence but should always include safeguards against sudden reversals.
- Utilize Technical Indicators Effectively
Technical analysis complements fundamental insights by providing real-time signals about potential price movements around earning dates or identified gaps:
- Moving Averages: Help determine trend direction.
- Bollinger Bands: Indicate volatility levels that may precede significant moves.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): Highlights overbought or oversold conditions which could signal impending reversals post-gap closure.
Combining these indicators improves timing precision when entering or exiting trades related to earning surprises.
- Leverage Algorithmic Trading Tools
Automation through algorithmic trading platforms enables rapid identification of price discrepancies aligned with predefined criteria such as volume spikes around earning reports or technical indicator thresholds linked with historical gap patterns.
Algorithms can process vast datasets faster than manual methods — crucial for capturing fleeting opportunities before they close as markets adjust post-announcement.
Recent Developments Enhancing Gap Strategy Optimization
Advances in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) have revolutionized how traders approach gap strategies today:
AI-Powered Prediction Models: These models analyze massive datasets—including social media sentiment, news feeds, macroeconomic variables—to forecast potential earning surprises more accurately.
Real-Time Data Processing: ML algorithms continuously monitor live market data streams for anomalies indicative of upcoming gaps — enabling quicker decision-making.
The rise of cryptocurrency markets has further expanded opportunities for applying optimized gap strategies due to their high liquidity combined with extreme volatility levels that often produce sizable pricing discrepancies following major events like protocol upgrades or regulatory announcements.
Impacting Factors: Regulatory Changes & Market Volatility
Regulatory developments significantly influence how effectively traders can implement gap strategies:
New tax laws might alter investor behavior by increasing transaction costs.
Securities regulation adjustments could restrict certain trading practices temporarily affecting strategy deployment.
Market volatility also plays a dual role: while it amplifies profit potentials from large gaps during turbulent periods — it simultaneously raises risks due to unpredictable swings that may negate initial assumptions.
Risks Associated With Gap Trading During Earnings Events
Despite their profitability prospects, employing gap strategies involves notable risks:
Market Volatility: Sudden shifts driven by unforeseen news can lead prices far beyond anticipated ranges.
Information Overload: The sheer volume of available data might overwhelm traders leading them astray without proper filtering mechanisms.
Psychological Biases: Emotional reactions such as fear-of-missing-out (FOMO) may cause impulsive decisions contrary to strategic plans.
Best Practices for Effective Implementation
To maximize success while mitigating risks when optimizing gap strategies around earnings:
- Maintain disciplined adherence to predefined entry/exit points based on technical signals rather than emotions.
- Continuously update models using recent data inputs reflecting current market conditions.
- Use diversification across sectors/assets where possible so adverse moves do not wipe out entire portfolios.4.. Regularly review risk management protocols including stop-loss placements aligned with changing volatility landscapes.
Staying Informed About Market Trends
Successful application depends heavily on staying updated about evolving trends influencing both traditional stocks and cryptocurrencies alike:
- Follow credible financial news sources.*
- Monitor scheduled corporate disclosures.*
- Keep abreast of regulatory updates impacting trading environments.*
By integrating fundamental insights with technical tools enhanced through AI/ML innovations—and maintaining disciplined risk controls—investors can better position themselves within dynamic markets prone to frequent earning-related price movements.
Enhancing Your Strategy Through Continuous Learning
Finally—and perhaps most importantly—the landscape surrounding gap trading is constantly evolving thanks largely due to technological advancements and shifting regulations.* Engaging regularly in educational resources such as webinars*, industry reports*, forums*, helps refine your approach over time.* Staying adaptable ensures you remain competitive regardless of changing market dynamics.*
Optimizing your approach toward exploiting earnings gaps via well-informed strategy development offers significant advantages—but only if executed thoughtfully within a framework emphasizing risk management alongside technological innovation.* Combining fundamental research with cutting-edge tools empowers investors seeking consistent gains amid volatile environments like cryptocurrency markets.*


Lo
2025-05-14 04:37
How can gap strategies be optimized for earnings gaps?
How to Optimize Gap Strategies for Earnings Gaps in Financial Markets
Understanding Gap Strategies and Earnings Gaps
Gap strategies are investment techniques designed to capitalize on temporary price discrepancies between financial instruments. These discrepancies often occur due to market inefficiencies, news releases, or earnings reports. In particular, earnings gaps refer to the difference between a company's actual reported earnings and what analysts or investors expected. When a company reports earnings that significantly differ from forecasts—either positively or negatively—it can create a gap in the stock price, presenting opportunities for traders who can anticipate and react swiftly.
In the context of financial markets, especially with volatile assets like cryptocurrencies, identifying and exploiting these gaps requires a combination of analytical tools and strategic planning. Investors aim to predict when an earnings gap will occur or identify its impact early enough to profit before the market adjusts.
Key Steps in Optimizing Gap Strategies for Earnings Gaps
- Conduct Thorough Market Analysis
The foundation of effective gap trading lies in comprehensive market analysis. This involves monitoring financial news outlets, earning reports scheduled by companies, macroeconomic indicators, and overall market sentiment. By staying informed about upcoming earnings releases and potential catalysts—such as regulatory changes or geopolitical events—investors can better anticipate where gaps might form.
Additionally, analyzing historical data on past earnings surprises helps identify patterns that could repeat under similar circumstances. For example, some sectors tend to experience more frequent positive surprises than others; recognizing these trends enhances predictive accuracy.
- Gather Historical Data on Earnings Gaps
Building a database of previous earnings gaps allows traders to understand their frequency, size distribution, and typical impact on asset prices. Statistical analysis of this data reveals probabilities associated with different types of gaps (upward vs downward) under various conditions.
This historical perspective aids in setting realistic expectations regarding potential gains and risks associated with specific trades based on prior occurrences.
- Implement Robust Risk Management Techniques
Given the inherent unpredictability of markets—and especially high-volatility assets like cryptocurrencies—risk management is crucial when deploying gap strategies. Setting stop-loss orders ensures losses are contained if an anticipated move does not materialize as expected.
Diversification across multiple assets reduces exposure risk related to any single event triggering an adverse movement. Position sizing should also be carefully calibrated based on volatility levels; larger positions may be justified during periods of high confidence but should always include safeguards against sudden reversals.
- Utilize Technical Indicators Effectively
Technical analysis complements fundamental insights by providing real-time signals about potential price movements around earning dates or identified gaps:
- Moving Averages: Help determine trend direction.
- Bollinger Bands: Indicate volatility levels that may precede significant moves.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): Highlights overbought or oversold conditions which could signal impending reversals post-gap closure.
Combining these indicators improves timing precision when entering or exiting trades related to earning surprises.
- Leverage Algorithmic Trading Tools
Automation through algorithmic trading platforms enables rapid identification of price discrepancies aligned with predefined criteria such as volume spikes around earning reports or technical indicator thresholds linked with historical gap patterns.
Algorithms can process vast datasets faster than manual methods — crucial for capturing fleeting opportunities before they close as markets adjust post-announcement.
Recent Developments Enhancing Gap Strategy Optimization
Advances in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) have revolutionized how traders approach gap strategies today:
AI-Powered Prediction Models: These models analyze massive datasets—including social media sentiment, news feeds, macroeconomic variables—to forecast potential earning surprises more accurately.
Real-Time Data Processing: ML algorithms continuously monitor live market data streams for anomalies indicative of upcoming gaps — enabling quicker decision-making.
The rise of cryptocurrency markets has further expanded opportunities for applying optimized gap strategies due to their high liquidity combined with extreme volatility levels that often produce sizable pricing discrepancies following major events like protocol upgrades or regulatory announcements.
Impacting Factors: Regulatory Changes & Market Volatility
Regulatory developments significantly influence how effectively traders can implement gap strategies:
New tax laws might alter investor behavior by increasing transaction costs.
Securities regulation adjustments could restrict certain trading practices temporarily affecting strategy deployment.
Market volatility also plays a dual role: while it amplifies profit potentials from large gaps during turbulent periods — it simultaneously raises risks due to unpredictable swings that may negate initial assumptions.
Risks Associated With Gap Trading During Earnings Events
Despite their profitability prospects, employing gap strategies involves notable risks:
Market Volatility: Sudden shifts driven by unforeseen news can lead prices far beyond anticipated ranges.
Information Overload: The sheer volume of available data might overwhelm traders leading them astray without proper filtering mechanisms.
Psychological Biases: Emotional reactions such as fear-of-missing-out (FOMO) may cause impulsive decisions contrary to strategic plans.
Best Practices for Effective Implementation
To maximize success while mitigating risks when optimizing gap strategies around earnings:
- Maintain disciplined adherence to predefined entry/exit points based on technical signals rather than emotions.
- Continuously update models using recent data inputs reflecting current market conditions.
- Use diversification across sectors/assets where possible so adverse moves do not wipe out entire portfolios.4.. Regularly review risk management protocols including stop-loss placements aligned with changing volatility landscapes.
Staying Informed About Market Trends
Successful application depends heavily on staying updated about evolving trends influencing both traditional stocks and cryptocurrencies alike:
- Follow credible financial news sources.*
- Monitor scheduled corporate disclosures.*
- Keep abreast of regulatory updates impacting trading environments.*
By integrating fundamental insights with technical tools enhanced through AI/ML innovations—and maintaining disciplined risk controls—investors can better position themselves within dynamic markets prone to frequent earning-related price movements.
Enhancing Your Strategy Through Continuous Learning
Finally—and perhaps most importantly—the landscape surrounding gap trading is constantly evolving thanks largely due to technological advancements and shifting regulations.* Engaging regularly in educational resources such as webinars*, industry reports*, forums*, helps refine your approach over time.* Staying adaptable ensures you remain competitive regardless of changing market dynamics.*
Optimizing your approach toward exploiting earnings gaps via well-informed strategy development offers significant advantages—but only if executed thoughtfully within a framework emphasizing risk management alongside technological innovation.* Combining fundamental research with cutting-edge tools empowers investors seeking consistent gains amid volatile environments like cryptocurrency markets.*
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Are Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)?
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) are transforming the landscape of global finance. As digital innovations reshape how we conduct transactions, understanding what CBDCs are and their implications becomes essential for consumers, businesses, and policymakers alike. This article provides a comprehensive overview of CBDCs, exploring their definition, development status worldwide, benefits, challenges, and future prospects.
Understanding CBDCs: Definition and Core Features
CBDCs are digital versions of fiat currencies issued directly by a country's central bank. Unlike cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum—which operate on decentralized networks—CBDCs are centralized digital currencies backed by the government’s credit. They aim to replicate physical cash in a digital format while leveraging modern technology to enhance security and efficiency.
Key characteristics include:
- Issuer: Central banks issue CBDCs.
- Backing: Fully backed by government authority.
- Control: Managed centrally without decentralization.
- Security Measures: Employ advanced cryptography to prevent counterfeiting.
- Regulatory Compliance: Designed to adhere strictly to AML (Anti-Money Laundering) and KYC (Know Your Customer) regulations.
This structure ensures that CBDCs maintain trustworthiness comparable to traditional fiat currency but with the advantages of digital technology.
Why Are Central Banks Developing Digital Currencies?
The push toward CBDC adoption stems from multiple factors influencing modern economies:
- Digital Payment Growth: The surge in online transactions demands faster and more efficient payment systems.
- Cryptocurrency Trends: The rise of private cryptocurrencies has prompted governments to develop official digital alternatives that can be regulated effectively.
- Financial Inclusion: Many unbanked populations lack access to traditional banking services; CBDCs could bridge this gap by providing accessible digital financial tools via smartphones or other devices.
- Monetary Policy Tools: Digital currencies offer new avenues for central banks to implement monetary policy more precisely.
By embracing these innovations, central banks aim not only at modernization but also at safeguarding monetary sovereignty amid evolving financial ecosystems.
Global Progress on CBDC Implementation
Several countries have made significant strides in developing or piloting their own versions of CBDC:
China’s Digital Yuan
China is arguably leading the world with its pilot program launched in 2020. Known as the e-CNY or digital yuan, it is designed for everyday use alongside physical cash within China’s existing financial infrastructure[1]. The project aims at enhancing transaction speed while maintaining strict regulatory oversight.
European Central Bank's Digital Euro Initiative
The ECB has been exploring a potential euro-based digital currency since 2022[2]. Its focus lies in ensuring compatibility with current banking systems while addressing privacy concerns and regulatory frameworks necessary for widespread adoption across Europe.
United States Federal Reserve Studies
While still in research phases as of 2023[3], the U.S. Federal Reserve is examining how a potential dollar-backed CBDC could influence monetary policy stability without disrupting existing financial markets.
International Collaboration & Guidance
Organizations like the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) facilitate cooperation among central banks worldwide[4]. Their guidance helps harmonize standards around security protocols, interoperability between different national currencies’ blockchain platforms, and regulatory approaches—paving way for smoother cross-border transactions involving multiple jurisdictions' CBDCs.
Benefits Offered by Central Bank Digital Currencies
Implementing a well-designed CBDC can bring numerous advantages:
Enhanced Transaction Efficiency: Faster settlement times reduce delays associated with traditional banking processes.
Reduced Costs: Eliminating intermediaries lowers transaction fees both domestically and internationally.
Improved Financial Inclusion: Providing accessible access points via mobile devices allows underserved populations entry into formal financial systems.
Strengthened Monetary Policy Tools: Real-time data collection enables more precise adjustments based on economic indicators derived from transaction patterns.
Counteracting Private Cryptocurrencies’ Volatility
Furthermore, because they are regulated entities backed by governments rather than decentralized networks prone to volatility like Bitcoin or Ethereum—they provide stability crucial during economic uncertainties.
Challenges & Risks Associated With CBDC Adoption
Despite promising benefits, several hurdles must be addressed before widespread implementation:
Privacy Concerns
As all transactions conducted through a central bank-issued wallet would generate data stored securely under government oversight—raising fears about surveillance capabilities infringing on individual privacy rights[5].
Regulatory Complexities
Adapting existing legal frameworks such as AML/KYC laws requires significant updates; ensuring compliance across borders adds further complexity especially when considering cross-currency operations involving multiple jurisdictions’ regulations[6].
Cybersecurity Threats
Digital assets inherently face risks related to hacking attempts targeting critical infrastructure—necessitating robust cybersecurity measures that evolve alongside technological advancements[7].
Potential Disruption To Banking Sector
If consumers prefer holding funds directly with central banks via wallets rather than commercial banks—a scenario known as disintermediation—it could impact traditional banking models adversely including job losses within retail banking sectors.
Future Outlook & Strategic Considerations
As interest grows globally—with countries like China already piloting programs—the landscape suggests an increasing likelihood that many nations will adopt some form of retail or wholesale CBDC over coming years. Key considerations include:
Ensuring interoperability between different countries' digital currencies facilitates seamless cross-border payments—a vital aspect given globalization trends.[8]
Balancing privacy protections against anti-fraud measures remains critical; transparent yet secure data management policies will shape public trust.[9]
Collaboration among regulators worldwide can help establish common standards reducing fragmentation risks.[10]
Ultimately, successful integration depends on aligning technological innovation with sound regulation while maintaining public confidence through transparency.
Understanding what constitutes a Central Bank Digital Currency reveals its potential transformative impact on global finance—from improving payment efficiency and promoting inclusion to reshaping monetary policy tools—all underpinned by rigorous regulation aimed at safeguarding stability amidst rapid technological change.[11] As developments continue apace across major economies—and international cooperation deepens—the future role of CBDCs promises both opportunities and challenges worth watching closely.
References
- People's Bank of China Official Reports
- European Central Bank Publications
- Federal Reserve Research Papers
- BIS Reports on Cross-Border Payments5–11 Various academic articles discussing privacy issues, cybersecurity threats, regulatory frameworks etc., up-to-date until October 2023


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-11 13:50
What are central bank digital currencies (CBDCs)?
What Are Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)?
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) are transforming the landscape of global finance. As digital innovations reshape how we conduct transactions, understanding what CBDCs are and their implications becomes essential for consumers, businesses, and policymakers alike. This article provides a comprehensive overview of CBDCs, exploring their definition, development status worldwide, benefits, challenges, and future prospects.
Understanding CBDCs: Definition and Core Features
CBDCs are digital versions of fiat currencies issued directly by a country's central bank. Unlike cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum—which operate on decentralized networks—CBDCs are centralized digital currencies backed by the government’s credit. They aim to replicate physical cash in a digital format while leveraging modern technology to enhance security and efficiency.
Key characteristics include:
- Issuer: Central banks issue CBDCs.
- Backing: Fully backed by government authority.
- Control: Managed centrally without decentralization.
- Security Measures: Employ advanced cryptography to prevent counterfeiting.
- Regulatory Compliance: Designed to adhere strictly to AML (Anti-Money Laundering) and KYC (Know Your Customer) regulations.
This structure ensures that CBDCs maintain trustworthiness comparable to traditional fiat currency but with the advantages of digital technology.
Why Are Central Banks Developing Digital Currencies?
The push toward CBDC adoption stems from multiple factors influencing modern economies:
- Digital Payment Growth: The surge in online transactions demands faster and more efficient payment systems.
- Cryptocurrency Trends: The rise of private cryptocurrencies has prompted governments to develop official digital alternatives that can be regulated effectively.
- Financial Inclusion: Many unbanked populations lack access to traditional banking services; CBDCs could bridge this gap by providing accessible digital financial tools via smartphones or other devices.
- Monetary Policy Tools: Digital currencies offer new avenues for central banks to implement monetary policy more precisely.
By embracing these innovations, central banks aim not only at modernization but also at safeguarding monetary sovereignty amid evolving financial ecosystems.
Global Progress on CBDC Implementation
Several countries have made significant strides in developing or piloting their own versions of CBDC:
China’s Digital Yuan
China is arguably leading the world with its pilot program launched in 2020. Known as the e-CNY or digital yuan, it is designed for everyday use alongside physical cash within China’s existing financial infrastructure[1]. The project aims at enhancing transaction speed while maintaining strict regulatory oversight.
European Central Bank's Digital Euro Initiative
The ECB has been exploring a potential euro-based digital currency since 2022[2]. Its focus lies in ensuring compatibility with current banking systems while addressing privacy concerns and regulatory frameworks necessary for widespread adoption across Europe.
United States Federal Reserve Studies
While still in research phases as of 2023[3], the U.S. Federal Reserve is examining how a potential dollar-backed CBDC could influence monetary policy stability without disrupting existing financial markets.
International Collaboration & Guidance
Organizations like the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) facilitate cooperation among central banks worldwide[4]. Their guidance helps harmonize standards around security protocols, interoperability between different national currencies’ blockchain platforms, and regulatory approaches—paving way for smoother cross-border transactions involving multiple jurisdictions' CBDCs.
Benefits Offered by Central Bank Digital Currencies
Implementing a well-designed CBDC can bring numerous advantages:
Enhanced Transaction Efficiency: Faster settlement times reduce delays associated with traditional banking processes.
Reduced Costs: Eliminating intermediaries lowers transaction fees both domestically and internationally.
Improved Financial Inclusion: Providing accessible access points via mobile devices allows underserved populations entry into formal financial systems.
Strengthened Monetary Policy Tools: Real-time data collection enables more precise adjustments based on economic indicators derived from transaction patterns.
Counteracting Private Cryptocurrencies’ Volatility
Furthermore, because they are regulated entities backed by governments rather than decentralized networks prone to volatility like Bitcoin or Ethereum—they provide stability crucial during economic uncertainties.
Challenges & Risks Associated With CBDC Adoption
Despite promising benefits, several hurdles must be addressed before widespread implementation:
Privacy Concerns
As all transactions conducted through a central bank-issued wallet would generate data stored securely under government oversight—raising fears about surveillance capabilities infringing on individual privacy rights[5].
Regulatory Complexities
Adapting existing legal frameworks such as AML/KYC laws requires significant updates; ensuring compliance across borders adds further complexity especially when considering cross-currency operations involving multiple jurisdictions’ regulations[6].
Cybersecurity Threats
Digital assets inherently face risks related to hacking attempts targeting critical infrastructure—necessitating robust cybersecurity measures that evolve alongside technological advancements[7].
Potential Disruption To Banking Sector
If consumers prefer holding funds directly with central banks via wallets rather than commercial banks—a scenario known as disintermediation—it could impact traditional banking models adversely including job losses within retail banking sectors.
Future Outlook & Strategic Considerations
As interest grows globally—with countries like China already piloting programs—the landscape suggests an increasing likelihood that many nations will adopt some form of retail or wholesale CBDC over coming years. Key considerations include:
Ensuring interoperability between different countries' digital currencies facilitates seamless cross-border payments—a vital aspect given globalization trends.[8]
Balancing privacy protections against anti-fraud measures remains critical; transparent yet secure data management policies will shape public trust.[9]
Collaboration among regulators worldwide can help establish common standards reducing fragmentation risks.[10]
Ultimately, successful integration depends on aligning technological innovation with sound regulation while maintaining public confidence through transparency.
Understanding what constitutes a Central Bank Digital Currency reveals its potential transformative impact on global finance—from improving payment efficiency and promoting inclusion to reshaping monetary policy tools—all underpinned by rigorous regulation aimed at safeguarding stability amidst rapid technological change.[11] As developments continue apace across major economies—and international cooperation deepens—the future role of CBDCs promises both opportunities and challenges worth watching closely.
References
- People's Bank of China Official Reports
- European Central Bank Publications
- Federal Reserve Research Papers
- BIS Reports on Cross-Border Payments5–11 Various academic articles discussing privacy issues, cybersecurity threats, regulatory frameworks etc., up-to-date until October 2023
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Can DMI Be Used to Define Trend Strength Thresholds?
Understanding trend strength is essential for traders and investors aiming to make informed decisions in financial markets, including cryptocurrencies. The Directional Movement Index (DMI), developed by J. Wells Wilder, offers a reliable way to quantify the strength and direction of market trends. By effectively interpreting DMI signals—particularly the ADX line—traders can set meaningful thresholds that help identify when a trend is strong enough to warrant action.
What Is the Directional Movement Index (DMI)?
The DMI comprises three key components: the +DI (Positive Directional Indicator), -DI (Negative Directional Indicator), and ADX (Average Directional Index). The +DI and -DI lines indicate whether an upward or downward movement dominates, providing insight into trend direction. Meanwhile, the ADX measures overall trend strength regardless of direction.
Developed by Wilder in the 1970s, this indicator has stood the test of time due to its simplicity and effectiveness. It helps traders distinguish between trending markets and sideways consolidations—a critical factor for timing entries and exits.
Interpreting ADX Values for Trend Strength
The core utility of DMI lies in its ability to quantify how strong a current trend is through specific threshold levels on the ADX line:
- 0-25: Indicates weak or no clear trend; markets may be ranging.
- 26-50: Signifies developing or moderate trends.
- 51-75: Represents strong trending conditions.
- 76+: Suggests extremely powerful trends with high momentum.
These thresholds serve as practical benchmarks for traders seeking confirmation before executing trades. For example, an ADX crossing above 50 could signal that a significant move is underway, prompting traders to consider entering positions aligned with prevailing momentum.
Setting Effective Trend Strength Thresholds
To leverage DMI effectively, traders often establish specific rules based on these threshold levels:
- When ADX crosses above 25, it may indicate that a new or ongoing trend has gained enough momentum.
- An ADX rising above 50 can be viewed as confirmation of an extremely strong market move—ideal for aggressive trading strategies.
- Conversely, if ADX remains below 25, it suggests low volatility or sideways movement; trading strategies should be cautious during such periods.
Combining these thresholds with other technical indicators enhances decision-making accuracy—for instance:
- Confirming an uptrend when +DI > -DI alongside high ADX values.
- Recognizing potential reversals if +DI crosses below -DI during declining ADX readings.
This layered approach reduces false signals often encountered when relying solely on one indicator.
Enhancing Trend Analysis Through Multi-indicator Strategies
While DMI provides valuable insights into trend strength and direction, integrating it with other tools improves reliability:
- Moving averages can confirm whether price action aligns with identified trends.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI) helps assess overbought or oversold conditions within trending phases indicated by DMI.
For example:
An asset shows an ADX rising above 50 while RSI indicates overbought conditions. This combination might suggest a very strong uptrend nearing exhaustion—prompting caution rather than immediate entry.
Using multiple indicators together ensures more robust analysis aligned with user intent—to confirm genuine breakouts versus false signals caused by market noise.
Recent Trends: AI Integration & Cryptocurrency Markets
In recent years, technological advancements have expanded how traders utilize DMI in practice. Artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms now analyze large datasets—including historical price movements combined with real-time DMI signals—to automate detection of significant trend shifts based on predefined thresholds like those discussed earlier.
This automation allows for quicker responses amid volatile environments such as cryptocurrency markets where rapid changes are common. Cryptocurrencies' inherent volatility makes traditional analysis challenging; however, combining AI-driven models with tools like DMI enhances predictive accuracy regarding emerging trends' strength levels.
Furthermore, community adoption has grown significantly within crypto circles—online forums frequently discuss setting custom threshold levels tailored to specific assets’ behavior patterns rather than rigid standards alone.
Potential Pitfalls When Using DMI Thresholds
Despite its strengths, overreliance on any single indicator—including DMI—can lead to pitfalls such as false signals during sudden market swings or whipsaws in choppy conditions. Market volatility especially impacts cryptocurrencies where abrupt price moves are frequent; thus,
Traders should always corroborate findings from DMI-based thresholds with fundamental analysis, news events,and other technical tools like volume indicators or candlestick patterns.
Additionally,
Regulatory developments can influence how these technical tools are applied across different jurisdictions—for instance,new laws affecting crypto trading might alter typical market behaviors,making previously reliable thresholds less effective temporarily.
Best Practices for Using Trend Thresholds Effectively
To maximize benefits from using DMI-based thresholds:
- Combine multiple indicators rather than relying solely on one metric.
- Adjust threshold levels according to asset-specific behavior; some assets may require higher/lower cutoffs due to their unique volatility profiles.
- Use alerts triggered at key threshold crossings—for example,notifying when ADX surpasses 50—to facilitate timely decision-making without constant monitoring.
By adhering to these practices rooted in sound technical analysis principles—and understanding both their strengths and limitations—you improve your chances of accurately capturing profitable trends while minimizing risks associated with false signals.
Final Thoughts: Applying Knowledge Strategically
Using the Directional Movement Index's threshold levels offers valuable insights into current market dynamics across various asset classes—including cryptocurrencies—and supports strategic trade planning based on quantifiable data points about trend strength and directionality.
By integrating modern technologies like AI-driven analytics alongside traditional methods—and maintaining awareness about potential pitfalls—you position yourself better within competitive markets where timing matters most.
Ultimately,
a disciplined approach combining well-understood indicator thresholds like those provided by the DMI will enhance your ability not only to identify promising opportunities but also manage risk more effectively amidst ever-changing financial landscapes.


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-09 11:43
How can DMI be used to define trend strength thresholds?
How Can DMI Be Used to Define Trend Strength Thresholds?
Understanding trend strength is essential for traders and investors aiming to make informed decisions in financial markets, including cryptocurrencies. The Directional Movement Index (DMI), developed by J. Wells Wilder, offers a reliable way to quantify the strength and direction of market trends. By effectively interpreting DMI signals—particularly the ADX line—traders can set meaningful thresholds that help identify when a trend is strong enough to warrant action.
What Is the Directional Movement Index (DMI)?
The DMI comprises three key components: the +DI (Positive Directional Indicator), -DI (Negative Directional Indicator), and ADX (Average Directional Index). The +DI and -DI lines indicate whether an upward or downward movement dominates, providing insight into trend direction. Meanwhile, the ADX measures overall trend strength regardless of direction.
Developed by Wilder in the 1970s, this indicator has stood the test of time due to its simplicity and effectiveness. It helps traders distinguish between trending markets and sideways consolidations—a critical factor for timing entries and exits.
Interpreting ADX Values for Trend Strength
The core utility of DMI lies in its ability to quantify how strong a current trend is through specific threshold levels on the ADX line:
- 0-25: Indicates weak or no clear trend; markets may be ranging.
- 26-50: Signifies developing or moderate trends.
- 51-75: Represents strong trending conditions.
- 76+: Suggests extremely powerful trends with high momentum.
These thresholds serve as practical benchmarks for traders seeking confirmation before executing trades. For example, an ADX crossing above 50 could signal that a significant move is underway, prompting traders to consider entering positions aligned with prevailing momentum.
Setting Effective Trend Strength Thresholds
To leverage DMI effectively, traders often establish specific rules based on these threshold levels:
- When ADX crosses above 25, it may indicate that a new or ongoing trend has gained enough momentum.
- An ADX rising above 50 can be viewed as confirmation of an extremely strong market move—ideal for aggressive trading strategies.
- Conversely, if ADX remains below 25, it suggests low volatility or sideways movement; trading strategies should be cautious during such periods.
Combining these thresholds with other technical indicators enhances decision-making accuracy—for instance:
- Confirming an uptrend when +DI > -DI alongside high ADX values.
- Recognizing potential reversals if +DI crosses below -DI during declining ADX readings.
This layered approach reduces false signals often encountered when relying solely on one indicator.
Enhancing Trend Analysis Through Multi-indicator Strategies
While DMI provides valuable insights into trend strength and direction, integrating it with other tools improves reliability:
- Moving averages can confirm whether price action aligns with identified trends.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI) helps assess overbought or oversold conditions within trending phases indicated by DMI.
For example:
An asset shows an ADX rising above 50 while RSI indicates overbought conditions. This combination might suggest a very strong uptrend nearing exhaustion—prompting caution rather than immediate entry.
Using multiple indicators together ensures more robust analysis aligned with user intent—to confirm genuine breakouts versus false signals caused by market noise.
Recent Trends: AI Integration & Cryptocurrency Markets
In recent years, technological advancements have expanded how traders utilize DMI in practice. Artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms now analyze large datasets—including historical price movements combined with real-time DMI signals—to automate detection of significant trend shifts based on predefined thresholds like those discussed earlier.
This automation allows for quicker responses amid volatile environments such as cryptocurrency markets where rapid changes are common. Cryptocurrencies' inherent volatility makes traditional analysis challenging; however, combining AI-driven models with tools like DMI enhances predictive accuracy regarding emerging trends' strength levels.
Furthermore, community adoption has grown significantly within crypto circles—online forums frequently discuss setting custom threshold levels tailored to specific assets’ behavior patterns rather than rigid standards alone.
Potential Pitfalls When Using DMI Thresholds
Despite its strengths, overreliance on any single indicator—including DMI—can lead to pitfalls such as false signals during sudden market swings or whipsaws in choppy conditions. Market volatility especially impacts cryptocurrencies where abrupt price moves are frequent; thus,
Traders should always corroborate findings from DMI-based thresholds with fundamental analysis, news events,and other technical tools like volume indicators or candlestick patterns.
Additionally,
Regulatory developments can influence how these technical tools are applied across different jurisdictions—for instance,new laws affecting crypto trading might alter typical market behaviors,making previously reliable thresholds less effective temporarily.
Best Practices for Using Trend Thresholds Effectively
To maximize benefits from using DMI-based thresholds:
- Combine multiple indicators rather than relying solely on one metric.
- Adjust threshold levels according to asset-specific behavior; some assets may require higher/lower cutoffs due to their unique volatility profiles.
- Use alerts triggered at key threshold crossings—for example,notifying when ADX surpasses 50—to facilitate timely decision-making without constant monitoring.
By adhering to these practices rooted in sound technical analysis principles—and understanding both their strengths and limitations—you improve your chances of accurately capturing profitable trends while minimizing risks associated with false signals.
Final Thoughts: Applying Knowledge Strategically
Using the Directional Movement Index's threshold levels offers valuable insights into current market dynamics across various asset classes—including cryptocurrencies—and supports strategic trade planning based on quantifiable data points about trend strength and directionality.
By integrating modern technologies like AI-driven analytics alongside traditional methods—and maintaining awareness about potential pitfalls—you position yourself better within competitive markets where timing matters most.
Ultimately,
a disciplined approach combining well-understood indicator thresholds like those provided by the DMI will enhance your ability not only to identify promising opportunities but also manage risk more effectively amidst ever-changing financial landscapes.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is the Effect of Smoothing Periods on Moving Average Responsiveness?
Understanding how moving averages respond to market changes is essential for traders and investors, especially in volatile markets like cryptocurrencies. One of the key factors influencing this responsiveness is the smoothing period — a parameter that determines how sensitive the moving average is to recent price fluctuations. In this article, we will explore what smoothing periods are, how they affect moving average responsiveness, and why choosing the right period matters for effective technical analysis.
What Are Moving Averages and How Do They Work?
Moving averages (MAs) are popular technical indicators used to smooth out price data over a specified time frame. They help traders identify trends by filtering out short-term volatility and highlighting longer-term movements. The most common types include Simple Moving Average (SMA) and Exponential Moving Average (EMA).
The calculation involves averaging closing prices over a set number of periods — for example, 20 days or 50 days — which results in a line that moves along with price action but with varying degrees of smoothness depending on the period selected.
The Role of Smoothing Periods in Moving Averages
The smoothing period refers to the number of data points used when calculating the moving average. It directly influences how quickly or slowly this indicator reacts to recent market changes:
Shorter Smoothing Periods (e.g., 5-day or 10-day MA): These produce more responsive lines that closely follow current prices. They react swiftly to sudden shifts but can also generate false signals due to noise.
Longer Smoothing Periods (e.g., 100-day or 200-day MA): These create smoother lines that lag behind rapid market movements but provide clearer signals about long-term trends.
Choosing an appropriate smoothing period depends on your trading style—whether you prefer quick signals suitable for short-term trading or more stable indicators aligned with long-term investing.
How Does Smoothing Period Affect Market Responsiveness?
Responsiveness refers to how quickly a moving average adjusts when prices change. Shorter periods make MAs highly sensitive; they will shift direction rapidly as new data comes in, making them useful for catching early trend reversals or entry points in fast-moving markets like cryptocurrencies.
Conversely, longer periods tend to filter out minor fluctuations—often considered noise—and focus on overarching trends. While this reduces false alarms caused by random price swings, it also means delayed responses which could cause missed opportunities during rapid market shifts.
For example:
- A 20-day EMA might signal an upward trend sooner than a 200-day SMA, but it may also be prone to whipsaws during volatile phases.
- Traders seeking quick entries might favor shorter SMAs/EMAs despite increased risk of false signals.
- Investors aiming for stability often rely on longer-period MAs as confirmation tools rather than primary triggers.
Impact on Trading Strategies
The choice of smoothing period influences various aspects of trading strategies:
Support and Resistance Levels
Moving averages often act as dynamic support/resistance zones; their responsiveness determines how well these levels hold during volatile conditions.
Trend Reversal Signals
Shorter MAs can indicate potential reversals earlier but at risk of false positives; longer MAs provide confirmation at expense of speed.
Combining Multiple Moving Averages
Many traders use multiple MAs with different periods—such as crossovers between short-term and long-term averages—to generate buy/sell signals based on their interactions:
- When short-term MA crosses above long-term MA: bullish signal.
- When it crosses below: bearish signal.
This approach leverages different sensitivities created by varying smoothing periods for more robust decision-making.
Recent Trends: Cryptocurrency Markets & Algorithmic Trading
In recent years, cryptocurrency markets have experienced heightened volatility due to factors like regulatory news, technological developments, and macroeconomic shifts. As such:
Traders increasingly prefer shorter-moving averages (like 20-day or even weekly) because they offer quicker insights into rapid price movements.
Algorithmic trading systems incorporate multiple smoothing periods simultaneously—sometimes blending several MAs—to adapt dynamically across different time frames while minimizing lag effects.
Furthermore, sentiment analysis techniques now compare short vs long-period MAs—for instance, using crossover strategies—to gauge overall market mood effectively amid unpredictable swings.
Risks Associated With Different Smoothing Periods
While selecting an appropriate window size is crucial, both extremes carry risks:
Overfitting With Very Short Periods
Using very short durations can lead your moving average too closely following random noise rather than meaningful trends—a phenomenon known as overfitting—which results in frequent false signals leading traders astray.
Missing Opportunities With Long Durations
On the other hand, overly long periods may delay recognition of genuine trend changes because these smooth out significant moves until they're well established—potentially causing missed profit windows especially during fast-paced markets like crypto assets.
| Key Consideration | Short-Term Focus | Long-Term Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Responsiveness | High | Low |
| Noise Sensitivity | High | Low |
| Signal Reliability | Lower | Higher |
Balancing these factors requires understanding your specific trading goals and risk tolerance.
Selecting The Right Smoothing Period For Your Strategy
To optimize your use of moving averages:
- Define your investment horizon – day trading versus position holding.
- Test different window sizes through backtesting historical data relevant to your asset class.
- Combine multiple SMAs/EMAs with varying lengths—for example: using both 50-day and 200-day MA—to confirm trend directions before acting.
- Be aware that no single setting fits all scenarios; adapt based on current market volatility levels.
Why Understanding Moving Average Responsiveness Matters
Grasping how smoothing periods influence responsiveness helps improve decision-making accuracy across diverse markets—from stocks and forex to cryptocurrencies—and enhances risk management practices by reducing reliance on noisy signals while capturing genuine trend shifts effectively.
By tailoring your technical analysis tools—including selecting appropriate moving average lengths—you gain better insight into ongoing market dynamics without falling prey either to premature entries triggered by fleeting fluctuations or delayed reactions missing profitable opportunities.
In summary, adjusting the smoothing period alters a moving average’s sensitivity: shorter ones respond faster but are noisier; longer ones are smoother yet slower at signaling changes. Recognizing this trade-off enables traders not only refine their strategies but also better interpret chart patterns within volatile environments such as crypto markets where timely reactions can make all difference.*


Lo
2025-05-09 08:14
What is the effect of smoothing periods on moving average responsiveness?
What Is the Effect of Smoothing Periods on Moving Average Responsiveness?
Understanding how moving averages respond to market changes is essential for traders and investors, especially in volatile markets like cryptocurrencies. One of the key factors influencing this responsiveness is the smoothing period — a parameter that determines how sensitive the moving average is to recent price fluctuations. In this article, we will explore what smoothing periods are, how they affect moving average responsiveness, and why choosing the right period matters for effective technical analysis.
What Are Moving Averages and How Do They Work?
Moving averages (MAs) are popular technical indicators used to smooth out price data over a specified time frame. They help traders identify trends by filtering out short-term volatility and highlighting longer-term movements. The most common types include Simple Moving Average (SMA) and Exponential Moving Average (EMA).
The calculation involves averaging closing prices over a set number of periods — for example, 20 days or 50 days — which results in a line that moves along with price action but with varying degrees of smoothness depending on the period selected.
The Role of Smoothing Periods in Moving Averages
The smoothing period refers to the number of data points used when calculating the moving average. It directly influences how quickly or slowly this indicator reacts to recent market changes:
Shorter Smoothing Periods (e.g., 5-day or 10-day MA): These produce more responsive lines that closely follow current prices. They react swiftly to sudden shifts but can also generate false signals due to noise.
Longer Smoothing Periods (e.g., 100-day or 200-day MA): These create smoother lines that lag behind rapid market movements but provide clearer signals about long-term trends.
Choosing an appropriate smoothing period depends on your trading style—whether you prefer quick signals suitable for short-term trading or more stable indicators aligned with long-term investing.
How Does Smoothing Period Affect Market Responsiveness?
Responsiveness refers to how quickly a moving average adjusts when prices change. Shorter periods make MAs highly sensitive; they will shift direction rapidly as new data comes in, making them useful for catching early trend reversals or entry points in fast-moving markets like cryptocurrencies.
Conversely, longer periods tend to filter out minor fluctuations—often considered noise—and focus on overarching trends. While this reduces false alarms caused by random price swings, it also means delayed responses which could cause missed opportunities during rapid market shifts.
For example:
- A 20-day EMA might signal an upward trend sooner than a 200-day SMA, but it may also be prone to whipsaws during volatile phases.
- Traders seeking quick entries might favor shorter SMAs/EMAs despite increased risk of false signals.
- Investors aiming for stability often rely on longer-period MAs as confirmation tools rather than primary triggers.
Impact on Trading Strategies
The choice of smoothing period influences various aspects of trading strategies:
Support and Resistance Levels
Moving averages often act as dynamic support/resistance zones; their responsiveness determines how well these levels hold during volatile conditions.
Trend Reversal Signals
Shorter MAs can indicate potential reversals earlier but at risk of false positives; longer MAs provide confirmation at expense of speed.
Combining Multiple Moving Averages
Many traders use multiple MAs with different periods—such as crossovers between short-term and long-term averages—to generate buy/sell signals based on their interactions:
- When short-term MA crosses above long-term MA: bullish signal.
- When it crosses below: bearish signal.
This approach leverages different sensitivities created by varying smoothing periods for more robust decision-making.
Recent Trends: Cryptocurrency Markets & Algorithmic Trading
In recent years, cryptocurrency markets have experienced heightened volatility due to factors like regulatory news, technological developments, and macroeconomic shifts. As such:
Traders increasingly prefer shorter-moving averages (like 20-day or even weekly) because they offer quicker insights into rapid price movements.
Algorithmic trading systems incorporate multiple smoothing periods simultaneously—sometimes blending several MAs—to adapt dynamically across different time frames while minimizing lag effects.
Furthermore, sentiment analysis techniques now compare short vs long-period MAs—for instance, using crossover strategies—to gauge overall market mood effectively amid unpredictable swings.
Risks Associated With Different Smoothing Periods
While selecting an appropriate window size is crucial, both extremes carry risks:
Overfitting With Very Short Periods
Using very short durations can lead your moving average too closely following random noise rather than meaningful trends—a phenomenon known as overfitting—which results in frequent false signals leading traders astray.
Missing Opportunities With Long Durations
On the other hand, overly long periods may delay recognition of genuine trend changes because these smooth out significant moves until they're well established—potentially causing missed profit windows especially during fast-paced markets like crypto assets.
| Key Consideration | Short-Term Focus | Long-Term Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Responsiveness | High | Low |
| Noise Sensitivity | High | Low |
| Signal Reliability | Lower | Higher |
Balancing these factors requires understanding your specific trading goals and risk tolerance.
Selecting The Right Smoothing Period For Your Strategy
To optimize your use of moving averages:
- Define your investment horizon – day trading versus position holding.
- Test different window sizes through backtesting historical data relevant to your asset class.
- Combine multiple SMAs/EMAs with varying lengths—for example: using both 50-day and 200-day MA—to confirm trend directions before acting.
- Be aware that no single setting fits all scenarios; adapt based on current market volatility levels.
Why Understanding Moving Average Responsiveness Matters
Grasping how smoothing periods influence responsiveness helps improve decision-making accuracy across diverse markets—from stocks and forex to cryptocurrencies—and enhances risk management practices by reducing reliance on noisy signals while capturing genuine trend shifts effectively.
By tailoring your technical analysis tools—including selecting appropriate moving average lengths—you gain better insight into ongoing market dynamics without falling prey either to premature entries triggered by fleeting fluctuations or delayed reactions missing profitable opportunities.
In summary, adjusting the smoothing period alters a moving average’s sensitivity: shorter ones respond faster but are noisier; longer ones are smoother yet slower at signaling changes. Recognizing this trade-off enables traders not only refine their strategies but also better interpret chart patterns within volatile environments such as crypto markets where timely reactions can make all difference.*
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
#Render glisse sous sa structure en triangle et approche la zone de demande $3.05–$3.25.
📊 Scénarios à surveiller : ✅ Si ça tient → possible rebond court terme vers $4.00+ 🚀 ❌ Si ça casse → chute probable vers la zone $2.50–$2.70 ⚠️
👉 Selon vous, $RNDR prépare un rebond solide ou une plongée plus profonde ?
#RNDR #AI #CryptoMarkets
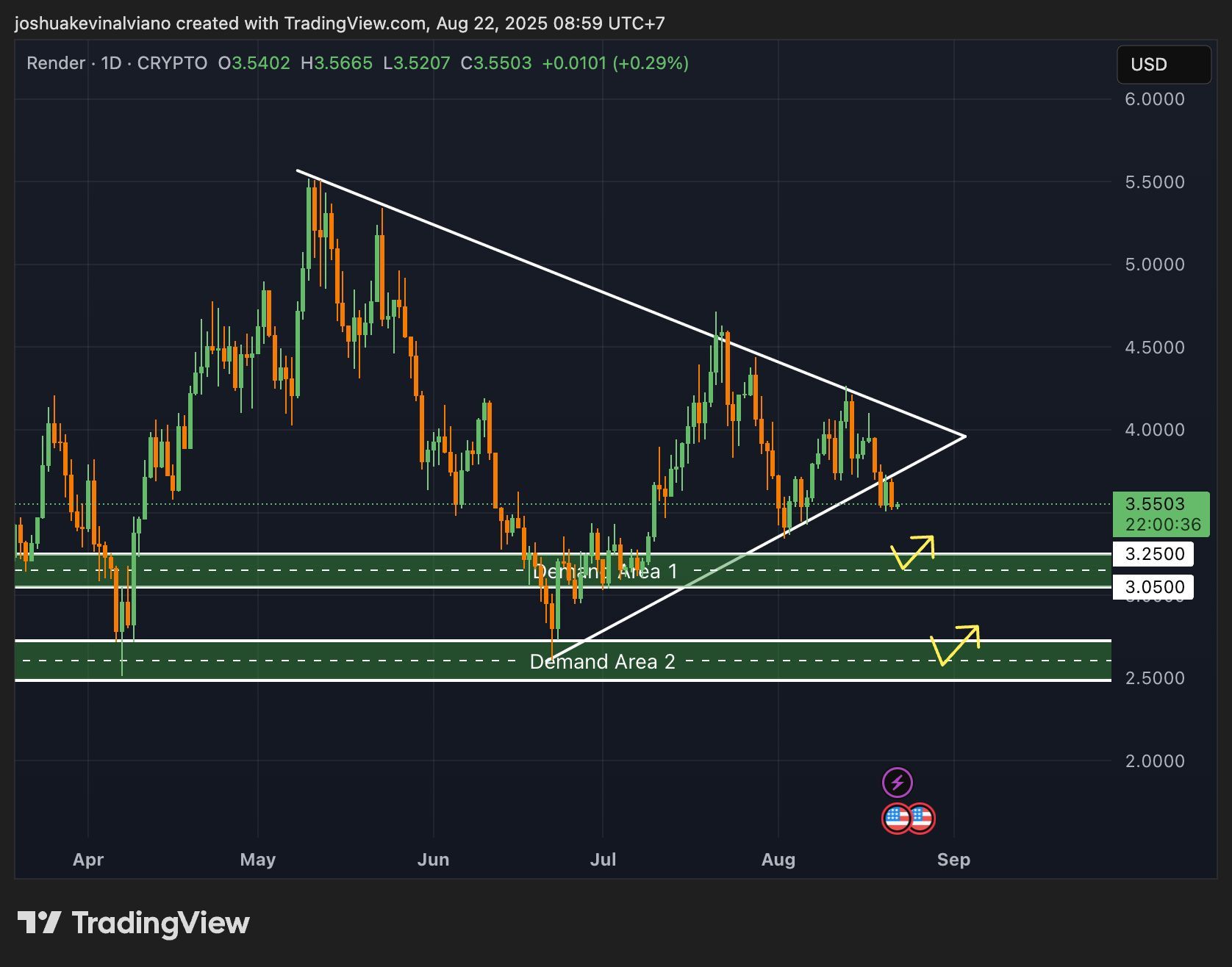


Carmelita
2025-08-22 11:50
$RNDR en zone critique : rebond ou cassure ?
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How is On-Chain Data Visualized?
Understanding how on-chain data is visualized is essential for anyone interested in blockchain technology, whether you're an investor, developer, or researcher. As blockchain networks generate vast amounts of data daily, transforming this raw information into understandable visuals helps users make informed decisions and gain insights into network health and activity. This article explores the main methods and tools used to visualize on-chain data effectively.
What Is On-Chain Data?
On-chain data encompasses all information stored directly on a blockchain. This includes transaction records, smart contract interactions, token movements, network metrics like block times and gas fees, as well as overall network activity. Because this data is decentralized and transparent by design—meaning anyone can verify transactions—it serves as a reliable source for analysis. However, its sheer volume can be overwhelming without proper visualization techniques.
Why Visualize On-Chain Data?
The exponential growth of blockchain networks has led to an increase in both the quantity and complexity of on-chain data. For users trying to interpret trends or detect anomalies—such as unusual transaction spikes or potential security breaches—visualization becomes indispensable. Well-designed visual representations help distill complex datasets into digestible formats that facilitate quick understanding and better decision-making.
Common Techniques for Visualizing On-Chain Data
There are several key methods used to represent on-chain information visually:
Transaction Volume & Frequency Charts
These graphs display the number of transactions over specific periods (daily or hourly). They reveal patterns such as peak activity times or seasonal fluctuations in network usage.Smart Contract Interaction Graphs
Visualizations showing how often certain smart contracts are called provide insights into dApp popularity and performance trends within decentralized applications (dApps).Network Metrics Dashboards
Metrics like average block time, transaction fees (gas prices), total active addresses, and hash rates are often displayed through line charts or heatmaps to assess network health.Tokenomics Visualization
Charts illustrating token supply distribution—such as pie charts showing holder concentration—or circulation metrics help investors understand market dynamics like scarcity or inflation rates.
Tools & Platforms for On-Chain Data Visualization
A variety of tools have emerged to aid users in visualizing blockchain data efficiently:
- Etherscan: Primarily focused on Ethereum-based networks; offers detailed transaction histories along with smart contract interaction logs.
- Chainalysis: Provides comprehensive analytics dashboards suitable for institutional clients seeking deep insights across multiple chains.
- CryptoSlate: Offers real-time price tracking combined with basic visualization features covering various cryptocurrencies.
- Google Data Studio: A versatile platform allowing analysts to create custom dashboards by importing raw blockchain datasets from APIs or CSV files.
Recent Innovations in Visualization Techniques
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) has revolutionized how we interpret on-chain data today:
- AI algorithms can automatically identify unusual patterns indicative of potential security threats such as hacks or fraud.
- Machine learning models enhance predictive analytics—for example predicting future transaction volumes based on historical trends.
These advancements enable more accurate anomaly detection while providing deeper insights that were previously difficult due to manual analysis limitations.
Adoption Trends Among Investors & Regulators
Institutional investors increasingly rely on sophisticated visualization tools when evaluating crypto assets because they demand transparency before committing capital. These tools help them assess risks by providing clear views into transactional flows and wallet activities—a critical factor amid growing regulatory scrutiny worldwide.
Regulators also benefit from improved visualization capabilities; transparent representations assist authorities in monitoring compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) standards while ensuring market integrity through clear audit trails embedded within these visualizations.
Potential Challenges & Ethical Considerations
Despite their benefits, there are challenges associated with relying heavily on visualization tools:
• Security Risks: Centralized platforms storing sensitive analytical data could become targets for cyberattacks if not properly secured.• Information Overload: The abundance of available datasets may overwhelm users unless filtering mechanisms are implemented effectively.• Ethical Concerns: AI-driven analyses might introduce biases if training datasets aren’t representative; maintaining transparency about methodologies is crucial for trustworthiness.
Key Facts About On-Chain Data Visualization
To appreciate its importance fully:
– Blockchain networks have expanded rapidly since 2017; this growth correlates directly with increased volume in stored transactional information.– Daily transaction volumes across major chains like Ethereum have surged over 500% since 2020.– Institutional interest continues rising—with many investing heavily in analytics firms specializing in blockchain intelligence—to leverage these visualizations strategically during investment processes.
Timeline Highlights
2017: The surge of initial coin offerings (ICOs) led to a spike in generated chain activity requiring better visualization solutions.*
2020: The COVID pandemic accelerated adoption due to increased digital asset trading.*
2023: AI-powered visualization tools became mainstream components within industry-standard platforms.
Final Thoughts
Visualizing on-chain data transforms complex raw information into actionable insights that support smarter decision-making across the crypto ecosystem—from individual traders analyzing market trends to institutions managing risk exposure—and enhances transparency vital for regulatory compliance. As technological innovations continue advancing—including AI integration—the capacity for more accurate real-time analysis will grow further while addressing current challenges related to security risks and ethical considerations remains essential for building trust within this rapidly evolving space.


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-26 17:52
How is on-chain data visualized?
How is On-Chain Data Visualized?
Understanding how on-chain data is visualized is essential for anyone interested in blockchain technology, whether you're an investor, developer, or researcher. As blockchain networks generate vast amounts of data daily, transforming this raw information into understandable visuals helps users make informed decisions and gain insights into network health and activity. This article explores the main methods and tools used to visualize on-chain data effectively.
What Is On-Chain Data?
On-chain data encompasses all information stored directly on a blockchain. This includes transaction records, smart contract interactions, token movements, network metrics like block times and gas fees, as well as overall network activity. Because this data is decentralized and transparent by design—meaning anyone can verify transactions—it serves as a reliable source for analysis. However, its sheer volume can be overwhelming without proper visualization techniques.
Why Visualize On-Chain Data?
The exponential growth of blockchain networks has led to an increase in both the quantity and complexity of on-chain data. For users trying to interpret trends or detect anomalies—such as unusual transaction spikes or potential security breaches—visualization becomes indispensable. Well-designed visual representations help distill complex datasets into digestible formats that facilitate quick understanding and better decision-making.
Common Techniques for Visualizing On-Chain Data
There are several key methods used to represent on-chain information visually:
Transaction Volume & Frequency Charts
These graphs display the number of transactions over specific periods (daily or hourly). They reveal patterns such as peak activity times or seasonal fluctuations in network usage.Smart Contract Interaction Graphs
Visualizations showing how often certain smart contracts are called provide insights into dApp popularity and performance trends within decentralized applications (dApps).Network Metrics Dashboards
Metrics like average block time, transaction fees (gas prices), total active addresses, and hash rates are often displayed through line charts or heatmaps to assess network health.Tokenomics Visualization
Charts illustrating token supply distribution—such as pie charts showing holder concentration—or circulation metrics help investors understand market dynamics like scarcity or inflation rates.
Tools & Platforms for On-Chain Data Visualization
A variety of tools have emerged to aid users in visualizing blockchain data efficiently:
- Etherscan: Primarily focused on Ethereum-based networks; offers detailed transaction histories along with smart contract interaction logs.
- Chainalysis: Provides comprehensive analytics dashboards suitable for institutional clients seeking deep insights across multiple chains.
- CryptoSlate: Offers real-time price tracking combined with basic visualization features covering various cryptocurrencies.
- Google Data Studio: A versatile platform allowing analysts to create custom dashboards by importing raw blockchain datasets from APIs or CSV files.
Recent Innovations in Visualization Techniques
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) has revolutionized how we interpret on-chain data today:
- AI algorithms can automatically identify unusual patterns indicative of potential security threats such as hacks or fraud.
- Machine learning models enhance predictive analytics—for example predicting future transaction volumes based on historical trends.
These advancements enable more accurate anomaly detection while providing deeper insights that were previously difficult due to manual analysis limitations.
Adoption Trends Among Investors & Regulators
Institutional investors increasingly rely on sophisticated visualization tools when evaluating crypto assets because they demand transparency before committing capital. These tools help them assess risks by providing clear views into transactional flows and wallet activities—a critical factor amid growing regulatory scrutiny worldwide.
Regulators also benefit from improved visualization capabilities; transparent representations assist authorities in monitoring compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) standards while ensuring market integrity through clear audit trails embedded within these visualizations.
Potential Challenges & Ethical Considerations
Despite their benefits, there are challenges associated with relying heavily on visualization tools:
• Security Risks: Centralized platforms storing sensitive analytical data could become targets for cyberattacks if not properly secured.• Information Overload: The abundance of available datasets may overwhelm users unless filtering mechanisms are implemented effectively.• Ethical Concerns: AI-driven analyses might introduce biases if training datasets aren’t representative; maintaining transparency about methodologies is crucial for trustworthiness.
Key Facts About On-Chain Data Visualization
To appreciate its importance fully:
– Blockchain networks have expanded rapidly since 2017; this growth correlates directly with increased volume in stored transactional information.– Daily transaction volumes across major chains like Ethereum have surged over 500% since 2020.– Institutional interest continues rising—with many investing heavily in analytics firms specializing in blockchain intelligence—to leverage these visualizations strategically during investment processes.
Timeline Highlights
2017: The surge of initial coin offerings (ICOs) led to a spike in generated chain activity requiring better visualization solutions.*
2020: The COVID pandemic accelerated adoption due to increased digital asset trading.*
2023: AI-powered visualization tools became mainstream components within industry-standard platforms.
Final Thoughts
Visualizing on-chain data transforms complex raw information into actionable insights that support smarter decision-making across the crypto ecosystem—from individual traders analyzing market trends to institutions managing risk exposure—and enhances transparency vital for regulatory compliance. As technological innovations continue advancing—including AI integration—the capacity for more accurate real-time analysis will grow further while addressing current challenges related to security risks and ethical considerations remains essential for building trust within this rapidly evolving space.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Strict Is Binance’s KYC Process?
Understanding the level of strictness in Binance’s Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures is essential for users, regulators, and industry observers alike. As one of the world’s largest cryptocurrency exchanges, Binance operates within a complex regulatory landscape that demands rigorous compliance measures. This article explores how stringent Binance’s KYC process is, what it entails, recent developments influencing its policies, and the implications for users and the platform itself.
What Does KYC Mean for Cryptocurrency Exchanges?
KYC stands for "Know Your Customer," a fundamental component of financial regulation designed to verify customer identities. For crypto exchanges like Binance, implementing effective KYC protocols helps prevent illegal activities such as money laundering, terrorist financing, and fraud. These procedures are mandated by international standards set by organizations like the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) and are enforced differently across jurisdictions.
In practice, KYC involves collecting personal identification documents—passports, driver’s licenses—and sometimes proof of address or source of funds. The goal is to establish user legitimacy before allowing significant trading or withdrawal activities. The depth and complexity of these processes can vary widely depending on regulatory requirements and internal risk assessments.
How Does Binance Implement Its KYC Procedures?
Binance's approach to KYC reflects both global compliance standards and its own operational policies. It employs a tiered verification system that allows users to access different levels of service based on their verification status:
- Level 1 (Basic Verification): Users provide minimal information such as email address or phone number.
- Level 2: Requires submission of government-issued ID documents like passports or driver’s licenses.
- Level 3: May involve additional steps such as facial recognition scans or proof of residence documents.
This layered approach aims to balance user convenience with security needs while adhering to AML/CFT regulations across various regions.
Documentation Requirements
For higher verification tiers—particularly Level 2—users must upload clear images or scans of official identification documents. Some regions may also require proof-of-address documentation like utility bills or bank statements. These measures help ensure that each account corresponds to a real individual with verifiable credentials.
Data Security Measures
Given concerns over privacy breaches in digital platforms today, Binance emphasizes strong data security practices during its KYC process. Personal data collected is stored securely following applicable data protection laws such as GDPR in Europe or similar frameworks elsewhere.
Recent Regulatory Developments Impacting Binance's KYC Policies
Binance has faced increased scrutiny from regulators worldwide in recent years—a trend that directly influences how strict its KYC processes are designed:
European Union Investigation (2023): The EU's Financial Intelligence Unit launched an inquiry into whether Binance complies with AML/CFT regulations within member states. This investigation underscores the importance placed on thorough customer verification.
US Senate Hearings (2024): Lawmakers questioned Binance's CEO about transparency around customer data handling and adherence to U.S.-specific regulations like FinCEN guidelines. Concerns raised during these hearings highlight potential vulnerabilities if compliance isn't maintained at high standards.
These developments suggest that regulatory bodies are pushing exchanges toward more rigorous identity checks while also demanding greater transparency regarding data privacy practices.
User Feedback: Balancing Security With Convenience
While many appreciate the enhanced security offered by strict KYC protocols—especially amid rising concerns over hacking incidents—others find these procedures burdensome:
- Some users report long wait times during document verification stages.
- Uploading high-quality images can be frustrating due to technical issues.
- Privacy-conscious individuals worry about how their personal information might be used or stored beyond regulatory requirements.
Such feedback indicates a tension between maintaining robust anti-fraud measures and providing seamless user experiences—a challenge faced by all major crypto platforms today.
Potential Impacts Of Stringent vs Lenient KYC Policies
The level of strictness in Binance's KYC process has tangible effects on both platform security and user engagement:
Positive Outcomes
- Improved prevention against illicit activities enhances overall platform integrity.
- Regulatory compliance reduces legal risks—including fines—and supports long-term operational stability.
- Transparent processes foster greater trust among compliant users who value safety assurances.
Challenges
- Overly complex procedures may deter new users from onboarding quickly.
- Excessive data collection raises privacy concerns; mishandling could lead to reputational damage if breaches occur.
- High operational costs associated with extensive identity checks might impact profitability margins over time.
Striking an optimal balance remains critical; too lenient approaches risk legal penalties while overly aggressive policies could hinder growth through user dissatisfaction.
How Does Binances’ Approach Compare With Industry Standards?
Compared globally, Binance’s tiered verification model aligns well with industry norms seen across leading exchanges such as Coinbase or Kraken—which also implement multi-level identity checks based on transaction volume thresholds or regional regulations. However,
some competitors have adopted even stricter measures post-regulatory pressure—for example,
requiring biometric authentication at every login stage—to further tighten security but potentially at the expense of convenience.
Binance continues evolving its policies amidst ongoing regulatory pressures; recent investigations suggest it may need further tightening depending on jurisdictional demands.
Final Thoughts: Is Binances’ KYC Process Too Strict?
Assessing whether Binance's current approach is excessively stringent depends largely on perspective:
From a regulator’s standpoint, rigorous identity verification aligns with global AML/CFT standards necessary for combating financial crimes effectively within decentralized finance environments where anonymity can be exploited maliciously.
From a user's perspective, some may find certain steps cumbersome but generally necessary given increasing cybersecurity threats today.
Overall,
Binance appears committed to maintaining high compliance levels through layered verification systems tailored per region—all while balancing usability challenges posed by evolving regulations.
By continuously refining its processes based on feedback from authorities and customers alike,
the exchange aims not only at meeting legal obligations but also fostering trustworthiness essential for sustainable growth in an increasingly regulated industry landscape.
This comprehensive overview highlights just how nuanced—and crucial—the question about “how strict” binance's kyc process truly is becomes when considering global regulation trends alongside user experience considerations.. Understanding this balance helps stakeholders navigate future developments confidently amid ongoing changes shaping cryptocurrency compliance standards worldwide


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-26 15:22
How strict is Binance’s KYC process?
How Strict Is Binance’s KYC Process?
Understanding the level of strictness in Binance’s Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures is essential for users, regulators, and industry observers alike. As one of the world’s largest cryptocurrency exchanges, Binance operates within a complex regulatory landscape that demands rigorous compliance measures. This article explores how stringent Binance’s KYC process is, what it entails, recent developments influencing its policies, and the implications for users and the platform itself.
What Does KYC Mean for Cryptocurrency Exchanges?
KYC stands for "Know Your Customer," a fundamental component of financial regulation designed to verify customer identities. For crypto exchanges like Binance, implementing effective KYC protocols helps prevent illegal activities such as money laundering, terrorist financing, and fraud. These procedures are mandated by international standards set by organizations like the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) and are enforced differently across jurisdictions.
In practice, KYC involves collecting personal identification documents—passports, driver’s licenses—and sometimes proof of address or source of funds. The goal is to establish user legitimacy before allowing significant trading or withdrawal activities. The depth and complexity of these processes can vary widely depending on regulatory requirements and internal risk assessments.
How Does Binance Implement Its KYC Procedures?
Binance's approach to KYC reflects both global compliance standards and its own operational policies. It employs a tiered verification system that allows users to access different levels of service based on their verification status:
- Level 1 (Basic Verification): Users provide minimal information such as email address or phone number.
- Level 2: Requires submission of government-issued ID documents like passports or driver’s licenses.
- Level 3: May involve additional steps such as facial recognition scans or proof of residence documents.
This layered approach aims to balance user convenience with security needs while adhering to AML/CFT regulations across various regions.
Documentation Requirements
For higher verification tiers—particularly Level 2—users must upload clear images or scans of official identification documents. Some regions may also require proof-of-address documentation like utility bills or bank statements. These measures help ensure that each account corresponds to a real individual with verifiable credentials.
Data Security Measures
Given concerns over privacy breaches in digital platforms today, Binance emphasizes strong data security practices during its KYC process. Personal data collected is stored securely following applicable data protection laws such as GDPR in Europe or similar frameworks elsewhere.
Recent Regulatory Developments Impacting Binance's KYC Policies
Binance has faced increased scrutiny from regulators worldwide in recent years—a trend that directly influences how strict its KYC processes are designed:
European Union Investigation (2023): The EU's Financial Intelligence Unit launched an inquiry into whether Binance complies with AML/CFT regulations within member states. This investigation underscores the importance placed on thorough customer verification.
US Senate Hearings (2024): Lawmakers questioned Binance's CEO about transparency around customer data handling and adherence to U.S.-specific regulations like FinCEN guidelines. Concerns raised during these hearings highlight potential vulnerabilities if compliance isn't maintained at high standards.
These developments suggest that regulatory bodies are pushing exchanges toward more rigorous identity checks while also demanding greater transparency regarding data privacy practices.
User Feedback: Balancing Security With Convenience
While many appreciate the enhanced security offered by strict KYC protocols—especially amid rising concerns over hacking incidents—others find these procedures burdensome:
- Some users report long wait times during document verification stages.
- Uploading high-quality images can be frustrating due to technical issues.
- Privacy-conscious individuals worry about how their personal information might be used or stored beyond regulatory requirements.
Such feedback indicates a tension between maintaining robust anti-fraud measures and providing seamless user experiences—a challenge faced by all major crypto platforms today.
Potential Impacts Of Stringent vs Lenient KYC Policies
The level of strictness in Binance's KYC process has tangible effects on both platform security and user engagement:
Positive Outcomes
- Improved prevention against illicit activities enhances overall platform integrity.
- Regulatory compliance reduces legal risks—including fines—and supports long-term operational stability.
- Transparent processes foster greater trust among compliant users who value safety assurances.
Challenges
- Overly complex procedures may deter new users from onboarding quickly.
- Excessive data collection raises privacy concerns; mishandling could lead to reputational damage if breaches occur.
- High operational costs associated with extensive identity checks might impact profitability margins over time.
Striking an optimal balance remains critical; too lenient approaches risk legal penalties while overly aggressive policies could hinder growth through user dissatisfaction.
How Does Binances’ Approach Compare With Industry Standards?
Compared globally, Binance’s tiered verification model aligns well with industry norms seen across leading exchanges such as Coinbase or Kraken—which also implement multi-level identity checks based on transaction volume thresholds or regional regulations. However,
some competitors have adopted even stricter measures post-regulatory pressure—for example,
requiring biometric authentication at every login stage—to further tighten security but potentially at the expense of convenience.
Binance continues evolving its policies amidst ongoing regulatory pressures; recent investigations suggest it may need further tightening depending on jurisdictional demands.
Final Thoughts: Is Binances’ KYC Process Too Strict?
Assessing whether Binance's current approach is excessively stringent depends largely on perspective:
From a regulator’s standpoint, rigorous identity verification aligns with global AML/CFT standards necessary for combating financial crimes effectively within decentralized finance environments where anonymity can be exploited maliciously.
From a user's perspective, some may find certain steps cumbersome but generally necessary given increasing cybersecurity threats today.
Overall,
Binance appears committed to maintaining high compliance levels through layered verification systems tailored per region—all while balancing usability challenges posed by evolving regulations.
By continuously refining its processes based on feedback from authorities and customers alike,
the exchange aims not only at meeting legal obligations but also fostering trustworthiness essential for sustainable growth in an increasingly regulated industry landscape.
This comprehensive overview highlights just how nuanced—and crucial—the question about “how strict” binance's kyc process truly is becomes when considering global regulation trends alongside user experience considerations.. Understanding this balance helps stakeholders navigate future developments confidently amid ongoing changes shaping cryptocurrency compliance standards worldwide
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What is the Chikou Span? A Complete Explanation
Understanding technical analysis tools is essential for traders and investors aiming to make informed decisions. Among these tools, the Ichimoku Cloud stands out for its comprehensive approach to market analysis, with the Chikou Span being a vital component. This article provides an in-depth look at what the Chikou Span is, how it functions within the Ichimoku system, and its relevance in both stock and cryptocurrency markets.
The Role of the Chikou Span in Technical Analysis
The Chikou Span, often called the Lagging Span, serves as a confirmation tool within the Ichimoku Cloud framework. Its primary purpose is to help traders identify trend direction and potential reversals by comparing current prices with past prices. Unlike leading indicators that predict future movements or oscillators that measure momentum, lagging indicators like the Chikou Span analyze historical data to validate current trends.
In practice, this means plotting a security’s closing price 26 periods behind its current position. If this lagging line remains above previous prices over time, it suggests sustained upward momentum; if below, it indicates downward pressure. When combined with other components of the Ichimoku system—such as Tenkan-sen (Conversion Line) or Kijun-sen (Base Line)—the Chikou Span enhances overall market insight.
How Is The Chikou Span Calculated?
The calculation of the Chikou Span is straightforward but crucial for accurate interpretation. It involves taking today's closing price and plotting it 26 periods back on your chart. For example:
- If today’s closing price is $100,
- You would plot $100 on your chart 26 days ago (or 26 candlesticks if using daily data).
This simple shift creates a visual representation that allows traders to compare past prices directly with current levels without complex formulas or additional calculations.
Interpreting The Chikou Span: What Do Different Positions Mean?
The position of the Chikou Span relative to past prices offers valuable insights into market sentiment:
- Above previous prices: Indicates bullish momentum; recent closes are higher than those from 26 periods ago.
- Below previous prices: Signals bearish sentiment; recent closes are lower than those from 26 periods ago.
- Crossing over: When this line crosses above or below historical price levels—especially when combined with other signals—it can suggest potential trend reversals.
For example:
- A rising Chikou span crossing above past prices may confirm an emerging uptrend.
- Conversely, crossing below could warn of a downtrend forming.
Traders often look for these crossovers as part of their decision-making process alongside other elements like cloud support/resistance levels.
Historical Background and Development
The Ichimoku Cloud was developed by Japanese journalist Goichi Hosoda during the late 1960s as an all-in-one trading system designed for quick decision-making without relying on multiple separate indicators. Its name translates roughly as "one glance" cloud because it provides a comprehensive view at a glance through five key components—including Tenkan-sen, Kijun-sen, Senkou Spans A & B (Leading Spans), and notably—the Chikou Span.
Since its inception decades ago, this method has gained worldwide popularity among professional traders due to its ability to depict trend strength and potential reversal points effectively across various markets—from stocks to forex and cryptocurrencies.
Practical Applications in Stock Trading
In stock markets today, many traders incorporate Ichimoku components—including the Chikoudo span—to enhance their technical analysis toolkit. It helps identify long-term trends by confirming whether recent price action aligns with historical movement patterns captured by lagging lines like Chiukō span.
For instance:
- When stock prices are above all cloud boundaries AND Chiukō spans remain above past lows—this typically signals strong bullish conditions.
- Conversely,if stock prices fall below key support levels while Chiukō spans stay beneath prior lows—it suggests bearish dominance or possible trend exhaustion.
Using these signals together improves confidence in trade entries/exits while reducing false positives common when relying solely on single indicators.
Application in Cryptocurrency Markets
Cryptocurrency trading has seen rapid growth over recent years—with high volatility making reliable analysis essential. Traders have adapted traditional tools like Ichimoku Cloud because they provide clear visual cues amidst turbulent price swings typical of digital assets such as Bitcoin or Ethereum.
In crypto markets:
- The Lagging span can help confirm whether recent surges are sustainable.
- Crossings between Chiukō spans and historical lows/highs serve as early warning signs for reversals amid volatile conditions.
However—as cryptocurrencies tend toward extreme volatility—the effectiveness of lagging indicators like Chiukō should be complemented with volume analysis or other momentum tools for better accuracy.
Limitations To Keep In Mind
While useful—like any indicator—theChikuo span isn’t perfect:
- Lag Effect: Since it's based on past data (26 periods behind), it may not react quickly enough during sudden market moves.
- False Signals: In highly volatile environments such as crypto markets or during news events—crossovers might generate misleading signals.
- Market Conditions: During sideways consolidation phases—or choppy ranges—the indicator's readings can become ambiguous.
Therefore—and especially when trading high-volatility assets—it’s advisable always to combine Lagging Spans with other technical tools such as volume profiles or oscillators like RSI/MACD.
How To Use The Chikou Spread Effectively
To maximize utility:
- Confirm trend direction via position relative to prior candles
- Watch for crossovers indicating possible reversals
- Use alongside cloud support/resistance zones
- Combine with volume confirmation where applicable
By integrating these strategies into your trading plan—and understanding both strengths & limitations—you’ll improve your chances of making more accurate predictions about future market movements.
Final Thoughts on The Importance Of The Lagging Indicator
TheChikuo span remains an integral part of modern technical analysis due primarily to its simplicity yet powerful confirmation capabilities within broader systems likeIchimoku Cloud . Whether you're analyzing stocks or cryptocurrencies , understanding how this indicator works will enhance your abilityto interpret long-term trends accurately .
While no single tool guarantees success — combiningLagging Spanswith other analytical methods will give you more robust insights into market dynamics . As always — continuous learningand practical experienceare key ingredientsfor successful trading.
Note: Always remember that no indicator should be used in isolation; effective risk management practices remain essential regardlessof which analytical techniques you employ.


kai
2025-05-20 03:02
What’s Chikou Span?
What is the Chikou Span? A Complete Explanation
Understanding technical analysis tools is essential for traders and investors aiming to make informed decisions. Among these tools, the Ichimoku Cloud stands out for its comprehensive approach to market analysis, with the Chikou Span being a vital component. This article provides an in-depth look at what the Chikou Span is, how it functions within the Ichimoku system, and its relevance in both stock and cryptocurrency markets.
The Role of the Chikou Span in Technical Analysis
The Chikou Span, often called the Lagging Span, serves as a confirmation tool within the Ichimoku Cloud framework. Its primary purpose is to help traders identify trend direction and potential reversals by comparing current prices with past prices. Unlike leading indicators that predict future movements or oscillators that measure momentum, lagging indicators like the Chikou Span analyze historical data to validate current trends.
In practice, this means plotting a security’s closing price 26 periods behind its current position. If this lagging line remains above previous prices over time, it suggests sustained upward momentum; if below, it indicates downward pressure. When combined with other components of the Ichimoku system—such as Tenkan-sen (Conversion Line) or Kijun-sen (Base Line)—the Chikou Span enhances overall market insight.
How Is The Chikou Span Calculated?
The calculation of the Chikou Span is straightforward but crucial for accurate interpretation. It involves taking today's closing price and plotting it 26 periods back on your chart. For example:
- If today’s closing price is $100,
- You would plot $100 on your chart 26 days ago (or 26 candlesticks if using daily data).
This simple shift creates a visual representation that allows traders to compare past prices directly with current levels without complex formulas or additional calculations.
Interpreting The Chikou Span: What Do Different Positions Mean?
The position of the Chikou Span relative to past prices offers valuable insights into market sentiment:
- Above previous prices: Indicates bullish momentum; recent closes are higher than those from 26 periods ago.
- Below previous prices: Signals bearish sentiment; recent closes are lower than those from 26 periods ago.
- Crossing over: When this line crosses above or below historical price levels—especially when combined with other signals—it can suggest potential trend reversals.
For example:
- A rising Chikou span crossing above past prices may confirm an emerging uptrend.
- Conversely, crossing below could warn of a downtrend forming.
Traders often look for these crossovers as part of their decision-making process alongside other elements like cloud support/resistance levels.
Historical Background and Development
The Ichimoku Cloud was developed by Japanese journalist Goichi Hosoda during the late 1960s as an all-in-one trading system designed for quick decision-making without relying on multiple separate indicators. Its name translates roughly as "one glance" cloud because it provides a comprehensive view at a glance through five key components—including Tenkan-sen, Kijun-sen, Senkou Spans A & B (Leading Spans), and notably—the Chikou Span.
Since its inception decades ago, this method has gained worldwide popularity among professional traders due to its ability to depict trend strength and potential reversal points effectively across various markets—from stocks to forex and cryptocurrencies.
Practical Applications in Stock Trading
In stock markets today, many traders incorporate Ichimoku components—including the Chikoudo span—to enhance their technical analysis toolkit. It helps identify long-term trends by confirming whether recent price action aligns with historical movement patterns captured by lagging lines like Chiukō span.
For instance:
- When stock prices are above all cloud boundaries AND Chiukō spans remain above past lows—this typically signals strong bullish conditions.
- Conversely,if stock prices fall below key support levels while Chiukō spans stay beneath prior lows—it suggests bearish dominance or possible trend exhaustion.
Using these signals together improves confidence in trade entries/exits while reducing false positives common when relying solely on single indicators.
Application in Cryptocurrency Markets
Cryptocurrency trading has seen rapid growth over recent years—with high volatility making reliable analysis essential. Traders have adapted traditional tools like Ichimoku Cloud because they provide clear visual cues amidst turbulent price swings typical of digital assets such as Bitcoin or Ethereum.
In crypto markets:
- The Lagging span can help confirm whether recent surges are sustainable.
- Crossings between Chiukō spans and historical lows/highs serve as early warning signs for reversals amid volatile conditions.
However—as cryptocurrencies tend toward extreme volatility—the effectiveness of lagging indicators like Chiukō should be complemented with volume analysis or other momentum tools for better accuracy.
Limitations To Keep In Mind
While useful—like any indicator—theChikuo span isn’t perfect:
- Lag Effect: Since it's based on past data (26 periods behind), it may not react quickly enough during sudden market moves.
- False Signals: In highly volatile environments such as crypto markets or during news events—crossovers might generate misleading signals.
- Market Conditions: During sideways consolidation phases—or choppy ranges—the indicator's readings can become ambiguous.
Therefore—and especially when trading high-volatility assets—it’s advisable always to combine Lagging Spans with other technical tools such as volume profiles or oscillators like RSI/MACD.
How To Use The Chikou Spread Effectively
To maximize utility:
- Confirm trend direction via position relative to prior candles
- Watch for crossovers indicating possible reversals
- Use alongside cloud support/resistance zones
- Combine with volume confirmation where applicable
By integrating these strategies into your trading plan—and understanding both strengths & limitations—you’ll improve your chances of making more accurate predictions about future market movements.
Final Thoughts on The Importance Of The Lagging Indicator
TheChikuo span remains an integral part of modern technical analysis due primarily to its simplicity yet powerful confirmation capabilities within broader systems likeIchimoku Cloud . Whether you're analyzing stocks or cryptocurrencies , understanding how this indicator works will enhance your abilityto interpret long-term trends accurately .
While no single tool guarantees success — combiningLagging Spanswith other analytical methods will give you more robust insights into market dynamics . As always — continuous learningand practical experienceare key ingredientsfor successful trading.
Note: Always remember that no indicator should be used in isolation; effective risk management practices remain essential regardlessof which analytical techniques you employ.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Are Related-Party Disclosures?
Related-party disclosures refer to the mandatory financial reporting requirements that compel companies to reveal transactions and relationships with related parties. These related parties include entities or individuals who have significant influence over the company, such as subsidiaries, affiliates, key management personnel, or owners with substantial control. The primary purpose of these disclosures is to provide transparency about dealings that could potentially influence a company's financial position or decision-making processes.
In practice, related-party disclosures encompass a wide range of transactions—such as loans, sales and purchases of goods or services, leases, guarantees, and other financial arrangements—that occur between the company and its related parties. These disclosures are typically included in the notes section of financial statements under standards like IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards) and US GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles). They serve as an essential tool for stakeholders to assess whether such transactions are conducted at arm's length or if they might be influenced by personal interests.
Why Are Related-Party Disclosures Important?
The significance of related-party disclosures extends across multiple facets of corporate governance and investor protection. First and foremost, they enhance financial transparency by shedding light on dealings that could otherwise remain hidden from public view. When companies disclose their related-party transactions comprehensively, investors gain a clearer understanding of potential conflicts of interest that may impact the company's operations or profitability.
From a corporate governance perspective, these disclosures act as safeguards against unethical practices such as insider trading or favoritism. They enable boards of directors and regulators to monitor whether transactions are fair and justified rather than manipulated for personal gains by insiders or controlling shareholders.
Furthermore, adherence to standardized disclosure requirements promotes comparability across different companies within an industry or jurisdiction. This consistency allows investors to make more informed decisions based on reliable data rather than opaque arrangements hidden within complex corporate structures.
Regulatory bodies like the SEC in the United States enforce strict compliance with these disclosure standards because they play a vital role in maintaining market integrity. Failure to properly disclose related-party dealings can lead not only to legal penalties but also damage a company's reputation among investors.
How Do Related-Party Disclosures Support Investor Confidence?
Investors rely heavily on transparent financial reporting when making investment choices. When companies openly disclose their relationships with related parties—including details about transaction terms—they reduce information asymmetry that often exists between insiders and external stakeholders.
By providing detailed insights into how much money flows between affiliated entities—and whether those deals are conducted at fair market value—related-party disclosures help investors evaluate potential risks associated with conflicts of interest. For example:
- Are certain subsidiaries receiving favorable treatment?
- Do key executives benefit personally from specific deals?
- Is there any indication that some transactions might be used for earnings management?
Addressing these questions through transparent reporting builds trust in the company's integrity while enabling better risk assessment strategies for investors seeking long-term stability.
Additionally, comprehensive disclosures can prevent fraudulent activities by exposing irregularities early on before they escalate into scandals—like those seen historically in cases such as Enron—which ultimately benefits both shareholders and broader capital markets.
Recent Developments Enhancing Related-Party Disclosure Practices
The landscape surrounding related-party disclosures has evolved significantly over recent years due to legislative reforms, regulatory enforcement intensification, technological advancements—and high-profile scandals emphasizing their importance.
Legislative Changes
In 2025, U.S.-based lawmakers introduced new legislation aimed at strengthening ethical standards around related-party transactions. Notably modeled after previous efforts like the PELOSI Act (which focused on congressional ethics), this bill seeks stricter regulation enforcement concerning insider trading prevention linked directly with affiliated party dealings[1]. Such legislative initiatives reflect growing recognition among policymakers about safeguarding market fairness through enhanced transparency obligations.
Regulatory Actions
Regulators worldwide have increased scrutiny over compliance issues involving related-party disclosure requirements. The SEC has stepped up enforcement efforts during recent years—imposing fines on firms failing timely disclosure—or misrepresenting—their associated party dealings[1]. This trend underscores regulators' commitment toward ensuring consistent application across industries while deterring misconduct through tangible consequences for non-compliance.
Impactful Corporate Scandals
Historical cases like Enron’s collapse highlighted how lackluster disclosure practices regarding affiliated entity transactions can facilitate frauds leading to catastrophic outcomes[1]. More recently though high-profile scandals continue emphasizing this point; improved regulations aim at preventing similar incidents by mandating more rigorous reporting standards which foster accountability within organizations’ internal controls systems[1].
Technological Innovations
Advances in digital technology have transformed how companies manage their data—including complex webs of inter-company relationships—and facilitate real-time monitoring capabilities[2]. Automated systems now enable more accurate tracking & recording; however increased reliance also introduces cybersecurity risks—as exemplified recently during Coinbase’s 2025 data breach—that necessitate robust security measures alongside transparent reporting protocols[2].
Key Milestones & Dates Shaping Current Practices
Understanding historical milestones helps contextualize current trends:
2001: Enron scandal exposed severe deficiencies in disclosing affiliate-related party deals; prompted widespread reforms.
2010: Dodd–Frank Wall Street Reform Act mandated additional transparency around executive compensation & affiliated transaction reporting.
2020s: SEC intensified enforcement actions targeting non-compliance; fines became commonplace.
May 2025: Introduction of House Republicans’ bill aiming at tightening regulations further—reflecting ongoing legislative focus on ethical conduct concerning connected entities [1].
These developments underscore an ongoing global effort towards improving transparency standards—a critical component underpinning investor confidence today.[3]
References:
- [Research Article] Related Party Disclosures: Significance, Recent Developments
- Industry Reports & Regulatory Updates (e.g., SEC Enforcement Trends)
- Historical Case Studies: Enron & Dodd–Frank Impact Analysis


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-19 15:32
What is the significance of related-party disclosures?
What Are Related-Party Disclosures?
Related-party disclosures refer to the mandatory financial reporting requirements that compel companies to reveal transactions and relationships with related parties. These related parties include entities or individuals who have significant influence over the company, such as subsidiaries, affiliates, key management personnel, or owners with substantial control. The primary purpose of these disclosures is to provide transparency about dealings that could potentially influence a company's financial position or decision-making processes.
In practice, related-party disclosures encompass a wide range of transactions—such as loans, sales and purchases of goods or services, leases, guarantees, and other financial arrangements—that occur between the company and its related parties. These disclosures are typically included in the notes section of financial statements under standards like IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards) and US GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles). They serve as an essential tool for stakeholders to assess whether such transactions are conducted at arm's length or if they might be influenced by personal interests.
Why Are Related-Party Disclosures Important?
The significance of related-party disclosures extends across multiple facets of corporate governance and investor protection. First and foremost, they enhance financial transparency by shedding light on dealings that could otherwise remain hidden from public view. When companies disclose their related-party transactions comprehensively, investors gain a clearer understanding of potential conflicts of interest that may impact the company's operations or profitability.
From a corporate governance perspective, these disclosures act as safeguards against unethical practices such as insider trading or favoritism. They enable boards of directors and regulators to monitor whether transactions are fair and justified rather than manipulated for personal gains by insiders or controlling shareholders.
Furthermore, adherence to standardized disclosure requirements promotes comparability across different companies within an industry or jurisdiction. This consistency allows investors to make more informed decisions based on reliable data rather than opaque arrangements hidden within complex corporate structures.
Regulatory bodies like the SEC in the United States enforce strict compliance with these disclosure standards because they play a vital role in maintaining market integrity. Failure to properly disclose related-party dealings can lead not only to legal penalties but also damage a company's reputation among investors.
How Do Related-Party Disclosures Support Investor Confidence?
Investors rely heavily on transparent financial reporting when making investment choices. When companies openly disclose their relationships with related parties—including details about transaction terms—they reduce information asymmetry that often exists between insiders and external stakeholders.
By providing detailed insights into how much money flows between affiliated entities—and whether those deals are conducted at fair market value—related-party disclosures help investors evaluate potential risks associated with conflicts of interest. For example:
- Are certain subsidiaries receiving favorable treatment?
- Do key executives benefit personally from specific deals?
- Is there any indication that some transactions might be used for earnings management?
Addressing these questions through transparent reporting builds trust in the company's integrity while enabling better risk assessment strategies for investors seeking long-term stability.
Additionally, comprehensive disclosures can prevent fraudulent activities by exposing irregularities early on before they escalate into scandals—like those seen historically in cases such as Enron—which ultimately benefits both shareholders and broader capital markets.
Recent Developments Enhancing Related-Party Disclosure Practices
The landscape surrounding related-party disclosures has evolved significantly over recent years due to legislative reforms, regulatory enforcement intensification, technological advancements—and high-profile scandals emphasizing their importance.
Legislative Changes
In 2025, U.S.-based lawmakers introduced new legislation aimed at strengthening ethical standards around related-party transactions. Notably modeled after previous efforts like the PELOSI Act (which focused on congressional ethics), this bill seeks stricter regulation enforcement concerning insider trading prevention linked directly with affiliated party dealings[1]. Such legislative initiatives reflect growing recognition among policymakers about safeguarding market fairness through enhanced transparency obligations.
Regulatory Actions
Regulators worldwide have increased scrutiny over compliance issues involving related-party disclosure requirements. The SEC has stepped up enforcement efforts during recent years—imposing fines on firms failing timely disclosure—or misrepresenting—their associated party dealings[1]. This trend underscores regulators' commitment toward ensuring consistent application across industries while deterring misconduct through tangible consequences for non-compliance.
Impactful Corporate Scandals
Historical cases like Enron’s collapse highlighted how lackluster disclosure practices regarding affiliated entity transactions can facilitate frauds leading to catastrophic outcomes[1]. More recently though high-profile scandals continue emphasizing this point; improved regulations aim at preventing similar incidents by mandating more rigorous reporting standards which foster accountability within organizations’ internal controls systems[1].
Technological Innovations
Advances in digital technology have transformed how companies manage their data—including complex webs of inter-company relationships—and facilitate real-time monitoring capabilities[2]. Automated systems now enable more accurate tracking & recording; however increased reliance also introduces cybersecurity risks—as exemplified recently during Coinbase’s 2025 data breach—that necessitate robust security measures alongside transparent reporting protocols[2].
Key Milestones & Dates Shaping Current Practices
Understanding historical milestones helps contextualize current trends:
2001: Enron scandal exposed severe deficiencies in disclosing affiliate-related party deals; prompted widespread reforms.
2010: Dodd–Frank Wall Street Reform Act mandated additional transparency around executive compensation & affiliated transaction reporting.
2020s: SEC intensified enforcement actions targeting non-compliance; fines became commonplace.
May 2025: Introduction of House Republicans’ bill aiming at tightening regulations further—reflecting ongoing legislative focus on ethical conduct concerning connected entities [1].
These developments underscore an ongoing global effort towards improving transparency standards—a critical component underpinning investor confidence today.[3]
References:
- [Research Article] Related Party Disclosures: Significance, Recent Developments
- Industry Reports & Regulatory Updates (e.g., SEC Enforcement Trends)
- Historical Case Studies: Enron & Dodd–Frank Impact Analysis
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Role Do Cash Flow Projections Play in Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Models?
Understanding the core of financial valuation methods is essential for investors, analysts, and business owners alike. Among these methods, Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) models stand out as a fundamental approach to estimating a company's intrinsic value. At the heart of DCF analysis are cash flow projections—forecasts of future cash inflows and outflows—that serve as the foundation for valuation. This article explores the critical role that cash flow projections play within DCF models, recent developments influencing their use, and best practices to ensure accurate and realistic valuations.
The Significance of Cash Flow Projections in Valuation
Cash flow projections are essentially educated estimates about how much money a company will generate or spend over a specific period. These forecasts typically include operating cash flows—such as earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT), depreciation expenses, and changes in working capital—as well as non-operating cash flows like dividends or interest payments.
In DCF models, these projected cash flows serve multiple purposes:
- Estimating Future Company Value: By projecting future cash flows over several years, analysts can gauge what the company might be worth at different points in time.
- Calculating Present Value: Since money today is worth more than money tomorrow due to inflation and risk factors, future cash flows are discounted back to their present value using an appropriate discount rate.
- Determining Terminal Value: Beyond explicit forecast periods—usually 5 to 10 years—a terminal value estimates ongoing cash flows into perpetuity using assumptions about long-term growth rates.
Accurate forecasting is vital because even small errors can significantly impact valuation outcomes. Overly optimistic projections may lead investors to overpay for assets; conversely, overly conservative forecasts could undervalue promising investments.
Recent Trends: Emphasizing Conservative Assumptions
Recent financial research underscores the importance of adopting conservative assumptions when developing cash flow projections within DCF models. Experts recommend cautious approaches particularly concerning terminal growth rates—the assumed rate at which a company's free cash flows will grow indefinitely beyond forecast horizons—and discount rates that reflect investment risk.
Why does this matter? Because overly aggressive assumptions tend to inflate valuations artificially. For example:
- Using high terminal growth rates without sufficient justification can lead to exaggerated long-term company values.
- Underestimating discount rates may make future prospects seem more attractive than they realistically are.
Recent analyses from 2025 highlight that employing modest or conservative terminal growth assumptions helps prevent overvaluation pitfalls while providing more reliable estimates aligned with market realities[1][2].
Key Factors Influencing Cash Flow Projection Accuracy
Several elements influence how precise your projected figures will be:
- Assumption Quality: The credibility of your forecasts hinges on realistic expectations about revenue growth, profit margins, capital expenditures, and working capital needs.
- Market Conditions: Economic trends such as inflation rates or industry-specific shifts should inform your outlooks.
- Company-Specific Data: Historical performance data provides valuable insights but must be adjusted for anticipated changes.
- Risk Considerations: Incorporate appropriate discount rates reflecting operational risks; higher uncertainty warrants higher discounting.
Adopting conservative assumptions across these factors ensures that valuations remain grounded in reality rather than inflated by overly optimistic predictions.
Potential Risks from Misapplied Cash Flow Projections
Failing to incorporate prudent assumptions can have serious consequences:
Overestimating future earnings leads investors astray by valuing companies above their true worth—a common cause of market bubbles or corrections when expectations aren't met.
Conversely, excessively cautious forecasts might cause undervaluation opportunities where potential exists but isn't recognized due to overly conservative estimates.
Striking a balance between optimism and realism is crucial for credible valuation results that guide sound investment decisions.
Best Practices for Developing Reliable Cash Flow Forecasts
To enhance accuracy in your DCF analysis through better projection techniques:
Use historical data as a baseline but adjust based on current market conditions and strategic plans.
Apply sensitivity analysis by testing various scenarios with different growth rates or discount factors; this helps understand potential valuation ranges under varying circumstances.
Keep terminal growth rates modest—generally aligning with long-term economic growth—to avoid unrealistic perpetuity assumptions[1].
Regularly update forecasts with new information such as quarterly earnings reports or macroeconomic indicators ensuring relevance over time[2].
By adhering to these practices rooted in recent research findings—and emphasizing conservatism—you improve both the reliability and credibility of your valuations.
Implications for Investors and Analysts
For those relying on DCF models for investment decisions—or conducting corporate valuations—the quality of underlying cash flow projections directly impacts outcomes. Conservative yet realistic forecasts help mitigate risks associated with overvaluation while capturing genuine opportunities missed by overly cautious approaches alone.
Furthermore,
- Transparent assumption-setting enhances trustworthiness among stakeholders,
- Regular model updates reflect changing conditions,
- Clear communication regarding projection methodologies fosters better decision-making processes,
ultimately leading toward more informed investment choices aligned with actual market dynamics.
References
1. Recent analysis emphasizes adopting modest terminal growth rates within DCF models (2025).
2. Experts highlight the importance of conservative assumptions especially regarding discount rate selection (2025).


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-19 14:44
What role do cash flow projections play in DCF models?
What Role Do Cash Flow Projections Play in Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Models?
Understanding the core of financial valuation methods is essential for investors, analysts, and business owners alike. Among these methods, Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) models stand out as a fundamental approach to estimating a company's intrinsic value. At the heart of DCF analysis are cash flow projections—forecasts of future cash inflows and outflows—that serve as the foundation for valuation. This article explores the critical role that cash flow projections play within DCF models, recent developments influencing their use, and best practices to ensure accurate and realistic valuations.
The Significance of Cash Flow Projections in Valuation
Cash flow projections are essentially educated estimates about how much money a company will generate or spend over a specific period. These forecasts typically include operating cash flows—such as earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT), depreciation expenses, and changes in working capital—as well as non-operating cash flows like dividends or interest payments.
In DCF models, these projected cash flows serve multiple purposes:
- Estimating Future Company Value: By projecting future cash flows over several years, analysts can gauge what the company might be worth at different points in time.
- Calculating Present Value: Since money today is worth more than money tomorrow due to inflation and risk factors, future cash flows are discounted back to their present value using an appropriate discount rate.
- Determining Terminal Value: Beyond explicit forecast periods—usually 5 to 10 years—a terminal value estimates ongoing cash flows into perpetuity using assumptions about long-term growth rates.
Accurate forecasting is vital because even small errors can significantly impact valuation outcomes. Overly optimistic projections may lead investors to overpay for assets; conversely, overly conservative forecasts could undervalue promising investments.
Recent Trends: Emphasizing Conservative Assumptions
Recent financial research underscores the importance of adopting conservative assumptions when developing cash flow projections within DCF models. Experts recommend cautious approaches particularly concerning terminal growth rates—the assumed rate at which a company's free cash flows will grow indefinitely beyond forecast horizons—and discount rates that reflect investment risk.
Why does this matter? Because overly aggressive assumptions tend to inflate valuations artificially. For example:
- Using high terminal growth rates without sufficient justification can lead to exaggerated long-term company values.
- Underestimating discount rates may make future prospects seem more attractive than they realistically are.
Recent analyses from 2025 highlight that employing modest or conservative terminal growth assumptions helps prevent overvaluation pitfalls while providing more reliable estimates aligned with market realities[1][2].
Key Factors Influencing Cash Flow Projection Accuracy
Several elements influence how precise your projected figures will be:
- Assumption Quality: The credibility of your forecasts hinges on realistic expectations about revenue growth, profit margins, capital expenditures, and working capital needs.
- Market Conditions: Economic trends such as inflation rates or industry-specific shifts should inform your outlooks.
- Company-Specific Data: Historical performance data provides valuable insights but must be adjusted for anticipated changes.
- Risk Considerations: Incorporate appropriate discount rates reflecting operational risks; higher uncertainty warrants higher discounting.
Adopting conservative assumptions across these factors ensures that valuations remain grounded in reality rather than inflated by overly optimistic predictions.
Potential Risks from Misapplied Cash Flow Projections
Failing to incorporate prudent assumptions can have serious consequences:
Overestimating future earnings leads investors astray by valuing companies above their true worth—a common cause of market bubbles or corrections when expectations aren't met.
Conversely, excessively cautious forecasts might cause undervaluation opportunities where potential exists but isn't recognized due to overly conservative estimates.
Striking a balance between optimism and realism is crucial for credible valuation results that guide sound investment decisions.
Best Practices for Developing Reliable Cash Flow Forecasts
To enhance accuracy in your DCF analysis through better projection techniques:
Use historical data as a baseline but adjust based on current market conditions and strategic plans.
Apply sensitivity analysis by testing various scenarios with different growth rates or discount factors; this helps understand potential valuation ranges under varying circumstances.
Keep terminal growth rates modest—generally aligning with long-term economic growth—to avoid unrealistic perpetuity assumptions[1].
Regularly update forecasts with new information such as quarterly earnings reports or macroeconomic indicators ensuring relevance over time[2].
By adhering to these practices rooted in recent research findings—and emphasizing conservatism—you improve both the reliability and credibility of your valuations.
Implications for Investors and Analysts
For those relying on DCF models for investment decisions—or conducting corporate valuations—the quality of underlying cash flow projections directly impacts outcomes. Conservative yet realistic forecasts help mitigate risks associated with overvaluation while capturing genuine opportunities missed by overly cautious approaches alone.
Furthermore,
- Transparent assumption-setting enhances trustworthiness among stakeholders,
- Regular model updates reflect changing conditions,
- Clear communication regarding projection methodologies fosters better decision-making processes,
ultimately leading toward more informed investment choices aligned with actual market dynamics.
References
1. Recent analysis emphasizes adopting modest terminal growth rates within DCF models (2025).
2. Experts highlight the importance of conservative assumptions especially regarding discount rate selection (2025).
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Options Greeks Chart: A Complete Guide for Traders and Investors
What Is an Options Greeks Chart?
An options Greeks chart is a vital analytical tool used by traders and investors to understand how various factors influence the price of options. It visually represents key metrics—Delta, Gamma, Theta, and Vega—that measure an option’s sensitivity to underlying asset movements, time decay, and volatility changes. These metrics help traders assess risk exposure, optimize trading strategies, and make informed decisions in both traditional markets like stocks or commodities and emerging sectors such as cryptocurrencies.
The chart consolidates complex mathematical data into an accessible format that allows users to quickly gauge how different market conditions might impact their options positions. By analyzing these sensitivities collectively on a single chart, traders can better anticipate potential profit or loss scenarios under varying circumstances.
The Four Main Components of Options Greeks
Understanding each component of the options Greeks is essential for effective trading:
Delta: This measures how much the price of an option will change with a $1 move in the underlying asset. For example, a Delta of 0.5 indicates that if the stock increases by $1, the option's price will increase by approximately $0.50. Delta also provides insight into whether an option behaves more like a stock (high Delta) or less (low Delta).
Gamma: Gamma indicates how much Delta will change when the underlying asset's price moves by one dollar. It reflects the curvature in the relationship between option prices and underlying prices—higher Gamma means greater sensitivity to small movements in asset prices.
Theta: Often called time decay, Theta quantifies how much value an option loses each day as expiration approaches if all other factors remain constant. For instance, a Theta of -0.05 suggests that daily time decay reduces the option’s value by five cents per day.
Vega: This measures sensitivity to volatility changes; specifically, it shows how much an option's premium will fluctuate with a 1% change in implied volatility of the underlying asset.
These components work together within an options Greeks chart to provide comprehensive insights into potential risks and rewards associated with specific trades.
Why Are Options Greeks Important for Traders?
Options trading involves managing multiple variables simultaneously; therefore understanding these sensitivities is crucial for risk management and strategic planning:
- They enable traders to predict how market movements affect their positions.
- Help determine optimal entry and exit points based on expected changes in volatility or time.
- Facilitate hedging strategies—adjusting portfolios against adverse market shifts.
For example, if you hold long calls with high Delta but low Gamma exposure during volatile periods (like earnings reports), you might want to adjust your position because sudden large moves could significantly impact your profits or losses.
Moreover, institutional investors rely heavily on these metrics for portfolio risk assessment while individual traders use them for tactical decision-making—especially when employing advanced strategies such as spreads or straddles.
Historical Development of Options Greeks
The concept originated during decades when financial mathematicians sought more precise models for pricing derivatives beyond simple formulas like Black-Scholes (1973). In particular:
During 1970s–1980s: Researchers developed sophisticated models incorporating multiple variables influencing options prices.
In 1990s: Emanuel Derman and Nassim Nicholas Taleb popularized terminology—the "Greeks"—to describe these sensitivities systematically.
This evolution allowed both institutional players and retail investors access to tools previously limited due to complexity but now integral across markets worldwide—including equities—and increasingly applied within cryptocurrency derivatives markets where high volatility amplifies importance.
Modern Applications & Recent Trends
In recent years:
Expansion into Cryptocurrency Markets
Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin have introduced new opportunities—and challenges—for applying traditional options analysis due to their extreme volatility levels. Traders now utilize Greek-based models tailored specifically toward digital assets’ unique behavior patterns—a development driven partly by increasing institutional interest seeking hedging solutions against crypto exposure.
Advanced Trading Platforms
Modern software offers real-time analytics on Greek values enabling dynamic adjustments during trading sessions rather than static assessments at trade initiation—a significant advantage amid fast-moving markets like crypto exchanges or volatile equity sectors.
Regulatory Environment
Regulatory bodies worldwide are scrutinizing derivatives activities more closely; transparency requirements are increasing which benefits informed trading based on solid Greek analysis while discouraging overly risky leverage practices that could lead to systemic issues if misused.
Risks Associated With Using Options Greeks
While powerful tools:
- Over-reliance can lead traders astray—particularly if they ignore broader market signals.
- High leverage combined with misjudged Greek values may amplify losses rapidly.
- Rapid shifts typical in cryptocurrency markets can cause sudden swings in Greek metrics making real-time monitoring essential but challenging.
Therefore understanding limitations alongside benefits ensures prudent application aligned with sound risk management principles.
Key Dates Shaping Understanding of Options Sensitivities
Tracking historical milestones helps contextualize current practices:
- 1970s–1980s: Development of foundational models like Black-Scholes laid groundwork for calculating initial "Greeks."
- 1990s: Formal naming ("Greeks") brought clarity; expanded understanding among practitioners globally.
- 2010s: Adoption within cryptocurrency derivatives increased awareness about adapting classical models beyond traditional assets.
- 2020s: Integration into advanced platforms enables seamless real-time analysis supporting complex multi-leg strategies across diverse markets.
This timeline underscores ongoing innovation driven by technological advances coupled with evolving financial landscapes.
How To Use An Options Greeks Chart Effectively
To maximize its utility:
- Regularly monitor all four components rather than focusing solely on one metric.
- Adjust positions dynamically based on changing Greek values during market fluctuations.
- Combine Greek analysis with fundamental research about underlying assets' prospects—for example, assessing macroeconomic trends affecting implied volatility (Vega).
By doing so — especially when managing large portfolios — traders can better control downside risks while capitalizing on favorable moves.
Final Thoughts
An options Greeks chart remains indispensable within modern financial analysis frameworks due its ability to distill complex derivative sensitivities into actionable insights. Whether applied traditionally across stocks or innovatively within cryptocurrencies' high-volatility environment—the core principles remain relevant today as they did decades ago—with continuous advancements enhancing accessibility through technology-driven solutions.
Understanding these metrics thoroughly empowers traders not only through improved decision-making but also fosters deeper trustworthiness grounded in quantitative rigor—a cornerstone principle aligning well with expert-level investment standards aimed at sustainable success over time.


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-19 07:19
What is Options Greeks Chart?
Options Greeks Chart: A Complete Guide for Traders and Investors
What Is an Options Greeks Chart?
An options Greeks chart is a vital analytical tool used by traders and investors to understand how various factors influence the price of options. It visually represents key metrics—Delta, Gamma, Theta, and Vega—that measure an option’s sensitivity to underlying asset movements, time decay, and volatility changes. These metrics help traders assess risk exposure, optimize trading strategies, and make informed decisions in both traditional markets like stocks or commodities and emerging sectors such as cryptocurrencies.
The chart consolidates complex mathematical data into an accessible format that allows users to quickly gauge how different market conditions might impact their options positions. By analyzing these sensitivities collectively on a single chart, traders can better anticipate potential profit or loss scenarios under varying circumstances.
The Four Main Components of Options Greeks
Understanding each component of the options Greeks is essential for effective trading:
Delta: This measures how much the price of an option will change with a $1 move in the underlying asset. For example, a Delta of 0.5 indicates that if the stock increases by $1, the option's price will increase by approximately $0.50. Delta also provides insight into whether an option behaves more like a stock (high Delta) or less (low Delta).
Gamma: Gamma indicates how much Delta will change when the underlying asset's price moves by one dollar. It reflects the curvature in the relationship between option prices and underlying prices—higher Gamma means greater sensitivity to small movements in asset prices.
Theta: Often called time decay, Theta quantifies how much value an option loses each day as expiration approaches if all other factors remain constant. For instance, a Theta of -0.05 suggests that daily time decay reduces the option’s value by five cents per day.
Vega: This measures sensitivity to volatility changes; specifically, it shows how much an option's premium will fluctuate with a 1% change in implied volatility of the underlying asset.
These components work together within an options Greeks chart to provide comprehensive insights into potential risks and rewards associated with specific trades.
Why Are Options Greeks Important for Traders?
Options trading involves managing multiple variables simultaneously; therefore understanding these sensitivities is crucial for risk management and strategic planning:
- They enable traders to predict how market movements affect their positions.
- Help determine optimal entry and exit points based on expected changes in volatility or time.
- Facilitate hedging strategies—adjusting portfolios against adverse market shifts.
For example, if you hold long calls with high Delta but low Gamma exposure during volatile periods (like earnings reports), you might want to adjust your position because sudden large moves could significantly impact your profits or losses.
Moreover, institutional investors rely heavily on these metrics for portfolio risk assessment while individual traders use them for tactical decision-making—especially when employing advanced strategies such as spreads or straddles.
Historical Development of Options Greeks
The concept originated during decades when financial mathematicians sought more precise models for pricing derivatives beyond simple formulas like Black-Scholes (1973). In particular:
During 1970s–1980s: Researchers developed sophisticated models incorporating multiple variables influencing options prices.
In 1990s: Emanuel Derman and Nassim Nicholas Taleb popularized terminology—the "Greeks"—to describe these sensitivities systematically.
This evolution allowed both institutional players and retail investors access to tools previously limited due to complexity but now integral across markets worldwide—including equities—and increasingly applied within cryptocurrency derivatives markets where high volatility amplifies importance.
Modern Applications & Recent Trends
In recent years:
Expansion into Cryptocurrency Markets
Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin have introduced new opportunities—and challenges—for applying traditional options analysis due to their extreme volatility levels. Traders now utilize Greek-based models tailored specifically toward digital assets’ unique behavior patterns—a development driven partly by increasing institutional interest seeking hedging solutions against crypto exposure.
Advanced Trading Platforms
Modern software offers real-time analytics on Greek values enabling dynamic adjustments during trading sessions rather than static assessments at trade initiation—a significant advantage amid fast-moving markets like crypto exchanges or volatile equity sectors.
Regulatory Environment
Regulatory bodies worldwide are scrutinizing derivatives activities more closely; transparency requirements are increasing which benefits informed trading based on solid Greek analysis while discouraging overly risky leverage practices that could lead to systemic issues if misused.
Risks Associated With Using Options Greeks
While powerful tools:
- Over-reliance can lead traders astray—particularly if they ignore broader market signals.
- High leverage combined with misjudged Greek values may amplify losses rapidly.
- Rapid shifts typical in cryptocurrency markets can cause sudden swings in Greek metrics making real-time monitoring essential but challenging.
Therefore understanding limitations alongside benefits ensures prudent application aligned with sound risk management principles.
Key Dates Shaping Understanding of Options Sensitivities
Tracking historical milestones helps contextualize current practices:
- 1970s–1980s: Development of foundational models like Black-Scholes laid groundwork for calculating initial "Greeks."
- 1990s: Formal naming ("Greeks") brought clarity; expanded understanding among practitioners globally.
- 2010s: Adoption within cryptocurrency derivatives increased awareness about adapting classical models beyond traditional assets.
- 2020s: Integration into advanced platforms enables seamless real-time analysis supporting complex multi-leg strategies across diverse markets.
This timeline underscores ongoing innovation driven by technological advances coupled with evolving financial landscapes.
How To Use An Options Greeks Chart Effectively
To maximize its utility:
- Regularly monitor all four components rather than focusing solely on one metric.
- Adjust positions dynamically based on changing Greek values during market fluctuations.
- Combine Greek analysis with fundamental research about underlying assets' prospects—for example, assessing macroeconomic trends affecting implied volatility (Vega).
By doing so — especially when managing large portfolios — traders can better control downside risks while capitalizing on favorable moves.
Final Thoughts
An options Greeks chart remains indispensable within modern financial analysis frameworks due its ability to distill complex derivative sensitivities into actionable insights. Whether applied traditionally across stocks or innovatively within cryptocurrencies' high-volatility environment—the core principles remain relevant today as they did decades ago—with continuous advancements enhancing accessibility through technology-driven solutions.
Understanding these metrics thoroughly empowers traders not only through improved decision-making but also fosters deeper trustworthiness grounded in quantitative rigor—a cornerstone principle aligning well with expert-level investment standards aimed at sustainable success over time.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
